DUBAI: Wars devastate lives, economies, and infrastructure, but what is often overlooked is the lasting damage they cause to the environment in the form of emissions, pollutants, and the destruction of habitats. The war in Gaza has been no exception.
Since the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, the Gaza Strip has come under intense Israeli bombardment, pulverizing buildings, demolishing sanitation services, lacing the earth with explosive remnants, and leaving the air thick with smoke and powdered concrete.
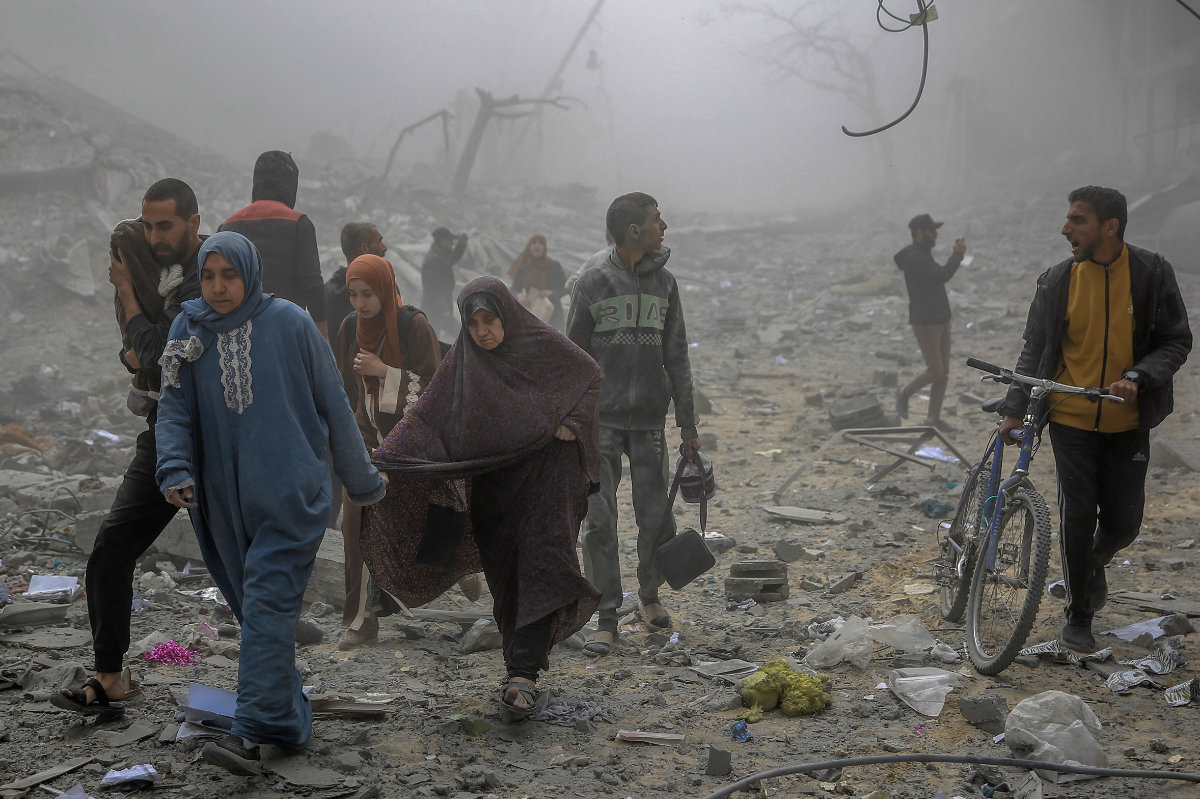

Palestinians flee their homes amid Israeli bombardment in central Gaza City on March 18, 2024. (AFP/File)
Although almost 33,000 Palestinians have been killed and more than 75,000 injured, according to the Gaza health ministry, by the bombardment, many doubt a ceasefire agreement will be reached soon, as Israel appears determined to press on into Rafah.
What is more certain is that whenever and however the conflict ends, any postwar government in Gaza will have its work cut out restoring the local environment and dealing with the long-term damage.
“Climate action is inextricably linked to lasting peace progress,” Rana Hajirasouli, founder and CEO of The Surpluss, a Dubai-based global climate tech platform, told Arab News.
“Understanding the critical link between environmental harm and the current structures of governance, power, and sovereignty should take precedence in climate policy to ensure peace and stability.”
The destruction wrought on Gaza by Israel’s military campaign has intensified existing environmental challenges in the region, from increased air and water pollution to the degradation of ecosystems

According to a study conducted by Queen Mary University of London, Lancaster University, and the Climate and Community Project, the carbon footprint created in the first 60 days of the war alone surpassed the annual emissions of 20 small countries.
Published by the Social Science Research Network on Jan. 9, the paper, titled “A multitemporal snapshot of greenhouse gas emissions from the Israel-Gaza conflict,” found the impact of the war was comparable to burning at least 150,000 tonnes of coal.
Much of this was generated by Israeli fighter jets during bombing raids and by armored vehicles used in the ground invasion. Other contributors were the US military, flying supplies to Israel. Less than 1 percent of the emissions were caused by Hamas rockets.
Responding to the study’s findings, Hajirasouli said: “This does not include indirect emissions such as energy-intensive production of military equipment, infrastructure construction, and post-conflict reconstruction efforts.”
Moreover, there is evidence that the destruction of densely populated urban areas has profound consequences for both human health and the environment.
Fires caused by airstrikes, particularly those that pulverize building materials, release a range of harmful emissions and air pollutants, including asbestos, said Hajirasouli.
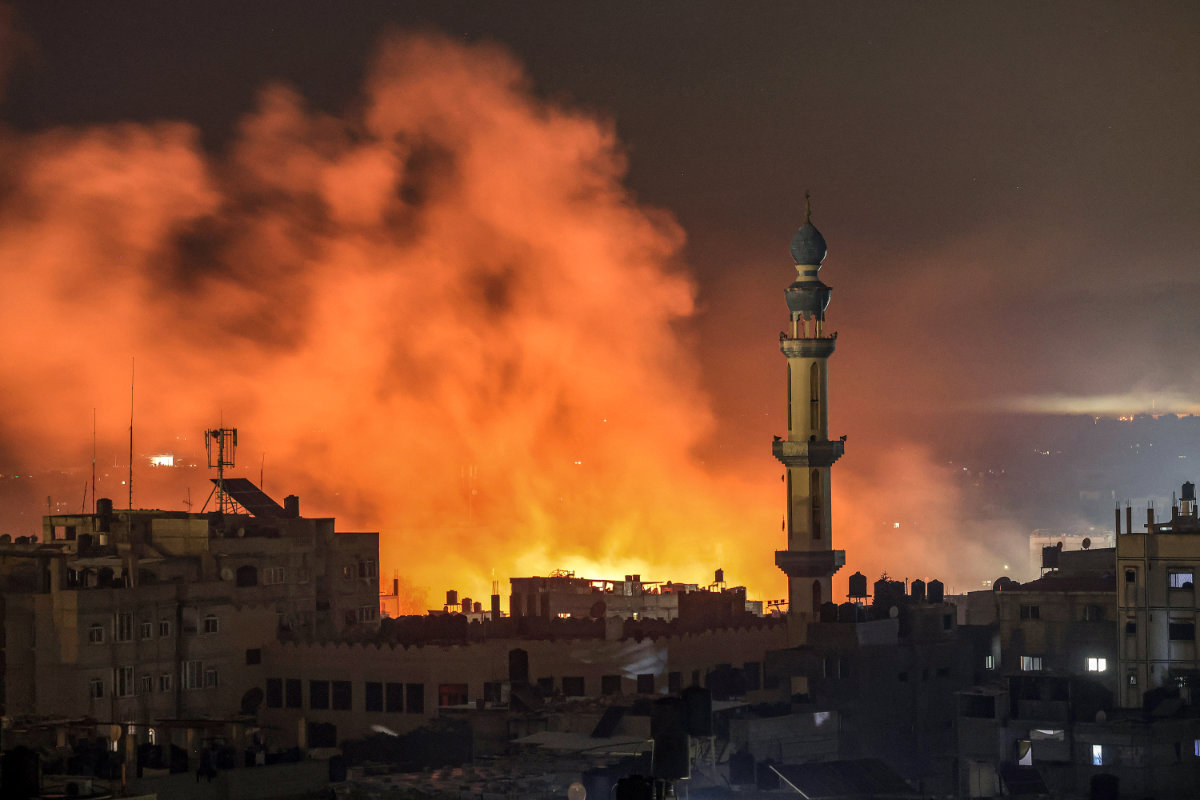

Fire and smoke erupt after Israeli bombardment in Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip on December 14, 2023. (AFP/File)
These emissions have lasting effects on the environment and exacerbate respiratory illnesses, posing a significant threat to public health.
Often the weapons themselves pollute the air and soil. “Highly incendiary white phosphorus leaves behind a trail of chemicals in its wake,” said Hajirasouli. The accumulation of phosphoric acid released by this weapon depletes soil fertility, exacerbates erosion, and harms agriculture, she added.
Around 339 hectares of greenhouses, crucial for growing various crops, have been destroyed, many of them in Gaza City, North Gaza, and Khan Younis.
The war has also severely disrupted the harvesting of olives and citrus fruits, which serve as vital sources of income for many in Gaza.
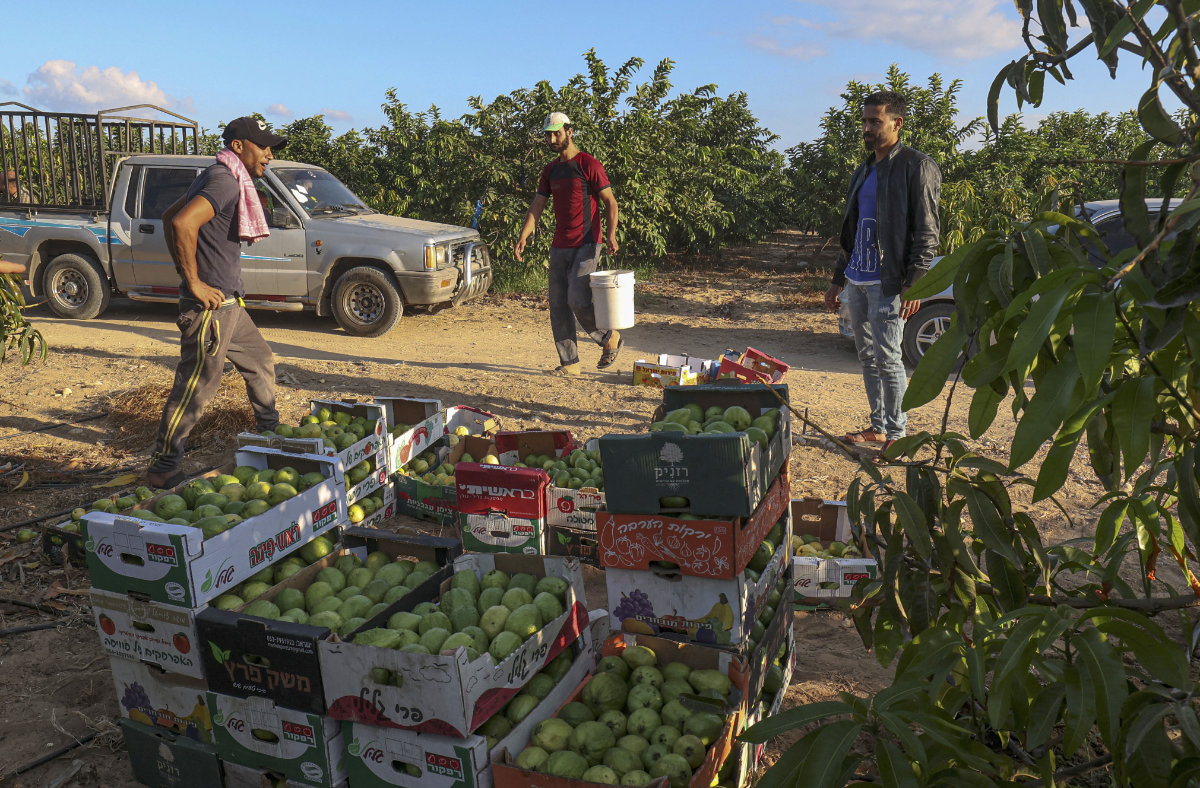

Palestinian farmers gather guavas at the start of the annual harvest season in Khan Yunis, in the southern Gaza Strip, on September 15, 2022. (AFP/File)
Maurizio Martina, deputy director-general of the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, highlighted the impact of the war on Gaza’s agriculture during a UN Security Council meeting in February on the protection of civilians amid armed conflicts.
Agriculture, he said, is a “critical source of sustenance and income” for Gazans, as is the fishing industry, which provides an income to some 100,000 individuals.
Martina also highlighted the death of livestock under airstrikes and as a result of shortages of water and fodder. As of Feb. 15, almost half of Gaza’s arable land had sustained damage, with sheep and dairy farms among the hardest hit.
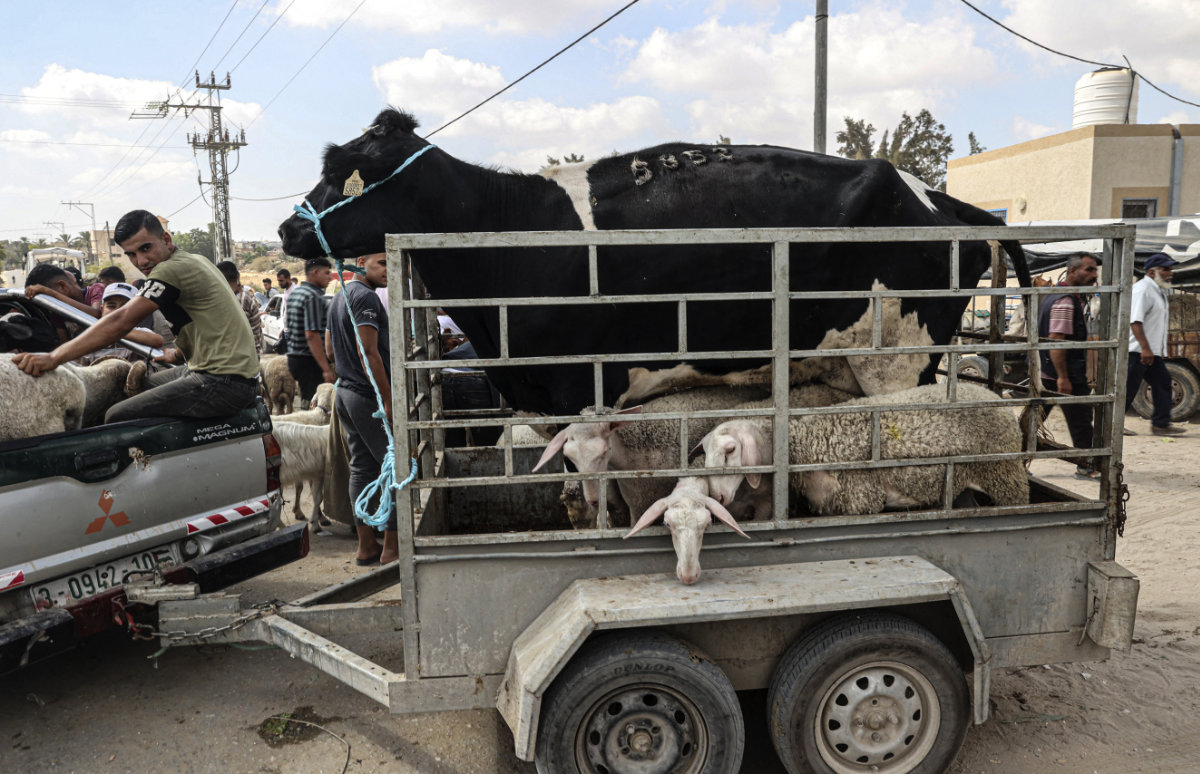

The destruction of Gaza's arable lands and wells, aggravated by environmental pollution from Israeli bombs and the subsequent fires caused, also threaten animal production in the Palestinian enclave. (AFP/File)
He also said more than 25 percent of wells have been destroyed, significantly impacting the availability of water in North Gaza and Gaza City.
According to Hajirasouli, Gaza’s groundwater, of which 95 percent has been deemed undrinkable due to contamination with wastewater and seawater, is almost completely depleted.
“A lack of access to clean water heightens the risk of waterborne diseases, such as cholera, in addition to creating fertile ground for the rapid spread of diseases,” she said.
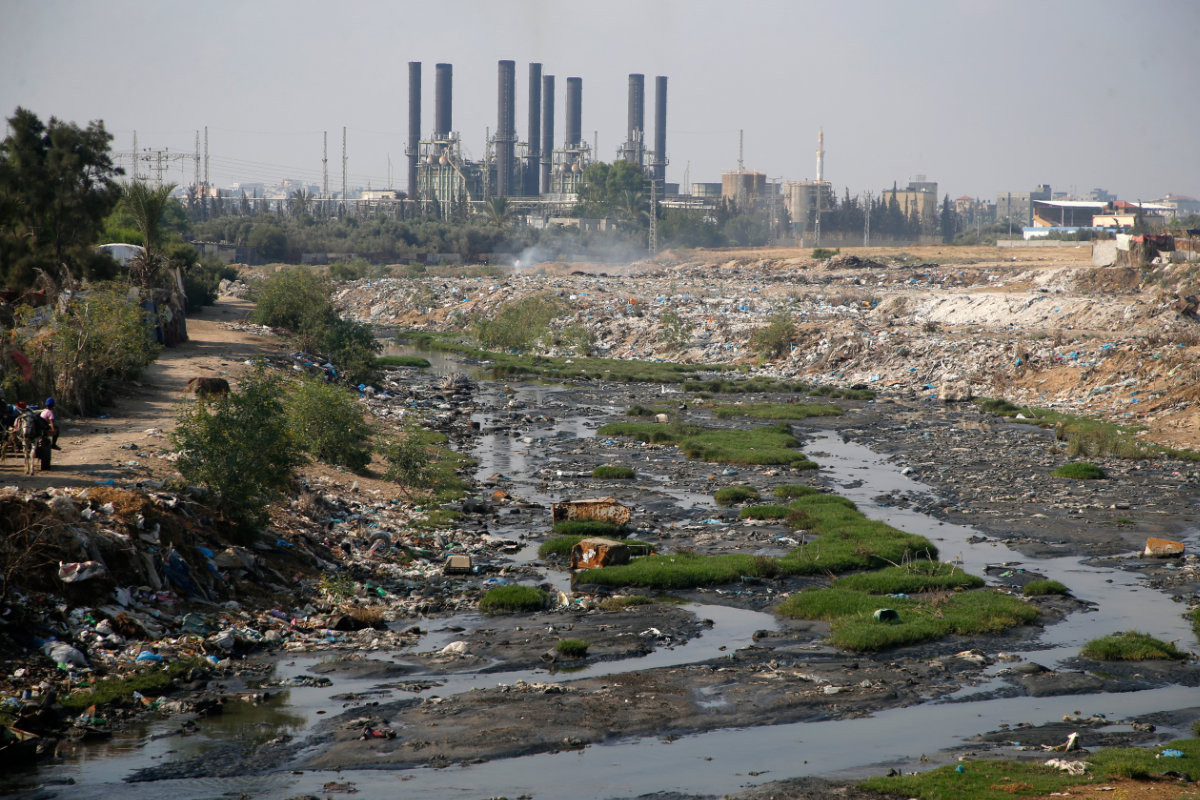

Sewage left untreated as a result of the war in Gaza is not only causing environmental damage but also creating conditions for a health crisis. (AFP/File)
The Norwegian Refugee Council estimates more than 130,000 cubic meters of untreated sewage was released into the Mediterranean Sea from Gaza each day in October, not only causing environmental damage but also creating conditions for a health crisis.
Meanwhile, the loss of vegetation amid the fighting has limited the land’s capacity to sequester carbon, further contributing to climate change, said Hajirasouli.
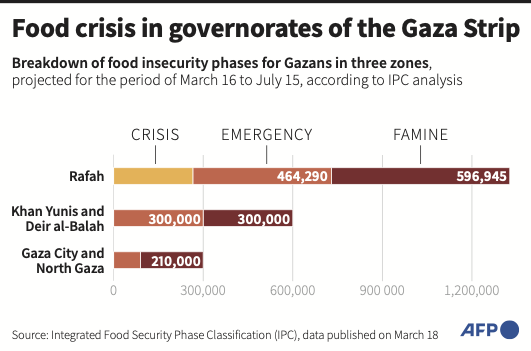
“A growing population coupled with shrinking farmlands contribute to catastrophic hunger,” she said, emphasizing the UN’s recent announcement that 80 percent of those experiencing famine or catastrophic hunger worldwide are Gazan.
DID YOUKNOW?
• Since October last year, waste management facilities have been damaged or destroyed, and power has been cut or interrupted in Gaza.
• At least 100,000 cubic meters of sewage and wastewater are being dumped daily onto land in Gaza or into the Mediterranean Sea (UNEP).
• Solid waste is being dumped in informal sites, where hazardous substances can leach into the porous soil, and potentially into the aquifer, Gaza’s main source of water.
• Total quantity of debris generated by wartime destruction in Gaza amounted to 22.9 million tons as of Jan. 7 (UNEP).
• Burning of solid waste in open fires in Gaza releases hazardous gases and particulate pollutants into the air.
According to aid agencies, approximately half a million people in Gaza are on the brink of starvation, while 2.3 million are dealing with acute food shortages.
Carl Skau, the deputy head of UN aid coordination, has warned that famine is “almost inevitable” unless there is an immediate and substantial increase in aid efforts. And yet, the FAO has highlighted continued constraints on the flow of aid deliveries into Gaza, hampering effective humanitarian efforts.
“A critical priority is to restore safe and sustained humanitarian access throughout the Gaza Strip and to all those in need of lifesaving assistance,” Martina told the UN Security Council last month.
He called for the restoration of basic services such as cross-border water pipelines, telecommunications, electricity distribution, and health facilities.
Even when the fighting eventually stops, postwar reconstruction is likely to be another significant contributor to emissions.
According to estimates reported in the Social Science Research Network study, the carbon cost of reconstructing Gaza’s 100,000 damaged buildings using modern construction methods will result in the emission of at least 30 million metric tonnes of warming gases.
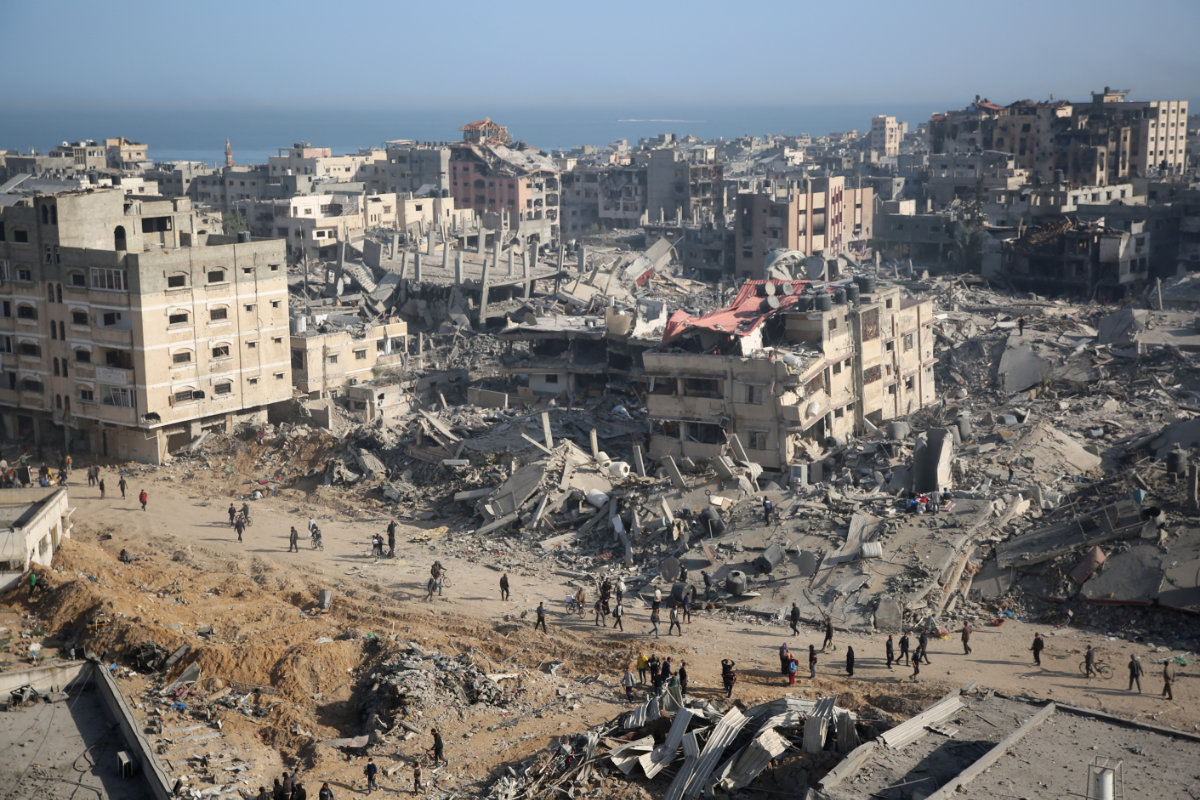

A general view shows the destruction in the area surrounding Gaza's Al-Shifa hospital after intense Israeli bombardment. (AFP)
This is comparable to the annual CO2 emissions of New Zealand and surpasses the emissions of 135 other countries and territories, including Sri Lanka, Lebanon, and Uruguay.
Hajirasouli added: “Whilst the long-term impacts on the climate will undoubtedly remain due to potent greenhouse gas emissions, many around the world will also feel the impact of its consequences.”
What is perhaps most striking is that Israelis and Palestinians — despite their decades-old animosity — face the same common threats from climate change and environmental degradation.
The World Bank’s Country Climate and Development Report for the West Bank and Gaza, published in December, highlighted the borderless nature of climate change and showed that the environment shared by Palestinians and Israelis is intertwined.
“Left unaddressed or tackled only by one side, the negative impacts of climate change will spill across borders and impacts on both Palestinian and Israeli lives and livelihood,” the report added.



































