RIYADH: Rising concern over disinformation’s role in manipulating public opinion has motivated Preslav Nakov, a professor at the UAE’s Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, to develop an AI-powered tool for detecting propaganda.
FRAPPE, short for Framing, Persuasion and Propaganda Explorer, is designed to assess news framing techniques and identify potential instances of information manipulation.
Nakov, chair of the natural language processing department and professor of natural language processing at the Abu Dhabi-based MBZUAI, said that AI plays a central role in FRAPPE by analyzing, categorizing and detecting complex patterns that influence readers’ opinions and emotions.
The tool offers real-time, on-the-fly analysis of individual articles while enabling a comprehensive comparison of framing and persuasion strategies across a wide range of media outlets, he told Arab News.

The UN defines disinformation as inaccurate information deliberately created and disseminated with the intent to deceive the public and cause serious harm. It can be spread by both state and non-state actors and can affect human rights, fuel armed conflict and undermine public policy responses.
The Global Risks Report 2024 by the World Economic Forum identifies misinformation and disinformation as a top short-term global risk. These forms of deceptive communication not only mislead the public but also erode trust, deepen societal divisions and threaten fundamental human rights.
Nevertheless, the WEF highlighted in an article in June that while AI technologies are being used in the production of both misinformation and disinformation, they can be harnessed to combat this risk by analyzing patterns, language and context.

Prof. Preslav Nakov, developer of an AI-powered tool for detecting propaganda. (Supplied)
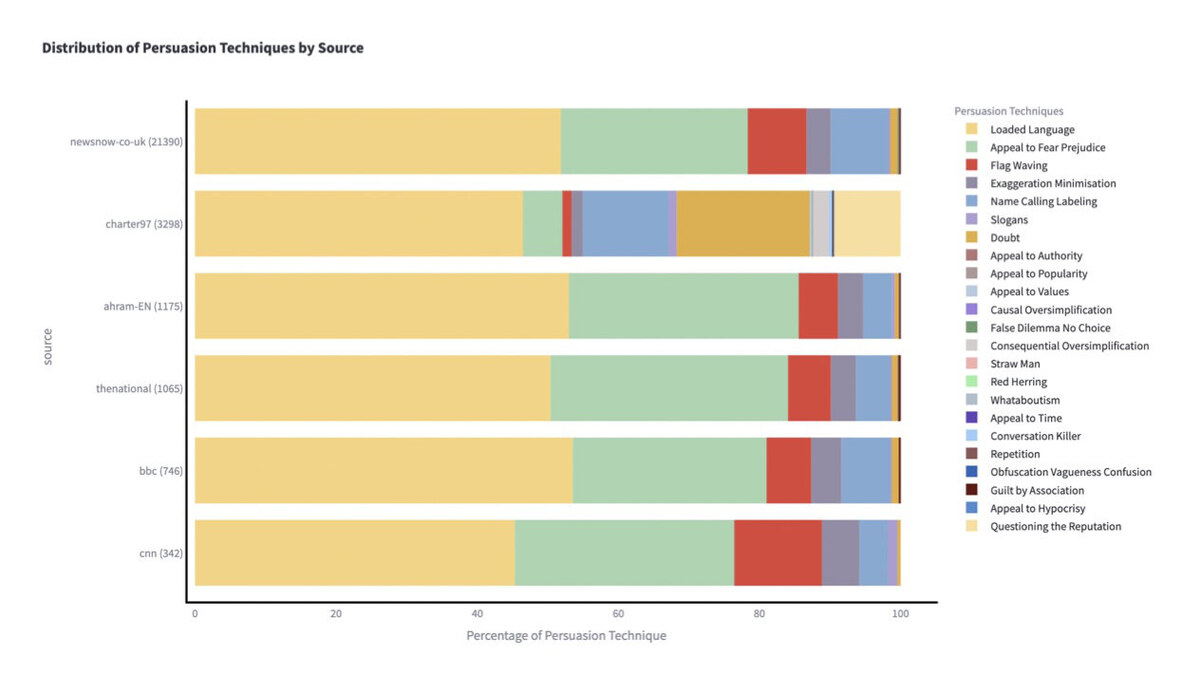
Nakov said that FRAPPE, trained with 23 different linguistic techniques, “uses AI to identify specific persuasion and propaganda techniques, such as name-calling, loaded language, appeals to fear, exaggeration and repetition.”
“FRAPPE further uses AI to perform framing analysis,” he said, adding that the tool distinguishes “the main perspectives from which an issue is being discussed: Morality, fairness, equality, political, and cultural identity.”
With a database of in excess of 2.5 million articles from more than 8,000 sources, the multilingual system enables users to explore and compare how different countries and outlets frame and present information.
DID YOUKNOW?
• Disinformation is the intentional spread of false information to sway public opinion.
• Propaganda often employs loaded language to elicit emotional reactions.
• A WEF report identifies disinformation and misinformation as a top short-term risk.
Moreover, to build the training data for the system, more than 40 journalists from several European countries contributed to the manual analysis of news content in 13 languages.
This manual analysis, according to Nakov, allows FRAPPE to discern the underlying frames that shape how stories are told and perceived. By identifying the dominant frames within an article, FRAPPE compares these across media sources, countries and languages, providing valuable insights into how framing varies globally.
FRAPPE is designed for a broad audience, including the general public, journalists, researchers, and even policymakers.

With an extensive database, FRAPPE's multilingual system enables users to explore and compare how different countries and outlets frame and present information. (Supplied)
“For the general user, FRAPPE serves as an educational tool to explore how news content is framed, enabling them to identify propaganda techniques like name-calling, flag-waving, loaded language and appeals to fear,” Nakov said.
“For journalists and policymakers, FRAPPE offers a powerful tool to examine and compare framing and persuasion strategies across different countries, languages and outlets,” he added.
The system relies on annotations from journalists who manually identified persuasion and propaganda techniques across a wide range of articles. This minimizes the risk of overly subjective or one-sided interpretations.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Transparency and unbiased analysis were fundamental in the development of FRAPPE. Nakov said: “Users should be aware that our models use neural networks and, as such, they lack explainability.”
He also warned that “despite our intent, due to potential unintended article selection biases, FRAPPE might be favoring some political or social standpoints.”
On the positive side, however, “FRAPPE has the potential to influence the way news articles are perceived and consumed, and journalists may become more aware of the language they use and its potential impact on readers.”
FRAPPE has the ability to spot persuasive or manipulative techniques in news content. (Supplied)
To spot persuasive or manipulative techniques in news content, Nakov advises readers and viewers to “watch out for emotional language designed to provoke strong reactions like fear or anger, and be mindful of loaded words, such as ‘radical’ and ‘heroic, which carry emotional weight.”
He urged readers to critically assess articles that rely too heavily on a single expert or selective quotes, stressing the importance of considering how different outlets might report the same event in contrasting ways.
To gain a clearer perspective, Nakov advises cross-checking sources and comparing how different media outlets cover the same story. This approach helps reveal varying angles, biases or framing techniques.
He also stressed that oversimplified “us versus them” narratives “often indicate manipulation, as do articles that frame an issue with a particular angle, leaving out important details.
FRAPPE has been featured in numerous EU workshops focused on combating fake news. (Supplied)
“False dilemmas, where only extreme choices are presented and repetitive phrases meant to reinforce a point are also red flags,” he said.
“FRAPPE envisions empowering individuals and institutions to make more informed decisions by revealing the framing and persuasion techniques embedded in media content. Its aim is to enhance transparency in journalism, promote trust in media and contribute to a more informed, media-literate public.”
Developed in collaboration with the European Commission’s Joint Research Center and several academic institutions across Europe, FRAPPE was launched ahead of the 2024 European Parliament election, held in the EU between June 6-9 this year.
The tool, integrated into the Europe Media Monitor, has been featured in numerous EU workshops focused on combating fake news.
































