RIYADH: In a display of economic ambition, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have unveiled new currency symbols for the riyal and dirham, marking a pivotal moment in their quest for global recognition.
Within just a few weeks of each other, the two Gulf powerhouses introduced these symbols — a strategic move designed to elevate their currencies on the world stage, signaling modernization, stability, and a vision for the future of trade and digital finance.
Saudi Arabia took the lead as King Salman approved the launch of a new riyal symbol in late February. The design, rooted in Arabic calligraphy, merges cultural heritage with modernity — a reflection of the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 ambitions.
In an interview with Arab News, economist and policy adviser Mahmoud Khairy said: “Currency symbols play a vital role in shaping how people view a nation’s money, and introducing new symbols for the riyal and dirham could help position them as modern and independent currencies.”
He added that a well-crafted symbol fosters national pride and distinguishes these currencies from others, crucial for gaining international recognition.

The Saudi riyal symbol. Supplied
When it was revealed, Saudi Central Bank Gov. Ayman Al-Sayari described the symbol as a reinforcement of the riyal’s identity both domestically and internationally.
The design comes as Saudi Arabia embraces digital transformation, having joined Project mBridge, a multinational CBDC initiative that includes China, Hong Kong, Thailand, and the UAE. This move underscores the Kingdom’s commitment to reshaping global trade through blockchain technology.
The UAE followed closely, revealing the new dirham symbol, a sleek and meaningful design that blends the English letter “D” with two horizontal lines symbolizing financial strength.
The inclusion of elements from the UAE flag underscores national pride while reinforcing the currency’s role in international markets.
The Central Bank of the UAE emphasized that the symbol will soon be integrated into global typographical fonts, ensuring the dirham stands alongside the US dollar, British pound, and euro as a recognizable financial emblem.
This rebrand is not merely cosmetic. It coincides with the UAE’s adoption of the FX Global Code, making the CBUAE the first central bank in the Arab world to join this framework, which promotes transparency and best practices in foreign exchange markets.
Additionally, the UAE is pushing forward with its digital dirham, a blockchain-based central bank digital currency set to revolutionize financial transactions.
CBUAE Gov. Khaled Mohamed Balama has hailed the initiative as a leap forward for financial inclusion, security, and efficiency.
The digital dirham will feature smart contracts, tokenization for fractional asset ownership, and seamless cross-border payments — positioning the UAE as a leader in the digital economy.
The bigger picture: a strategic assertion of financial independence
The introduction of these symbols is far more than a typographical update — it is a calculated assertion of financial independence.
Historically, dominant currencies such as the dollar and euro have enjoyed instant recognition through their symbols, reinforcing their influence in global markets.
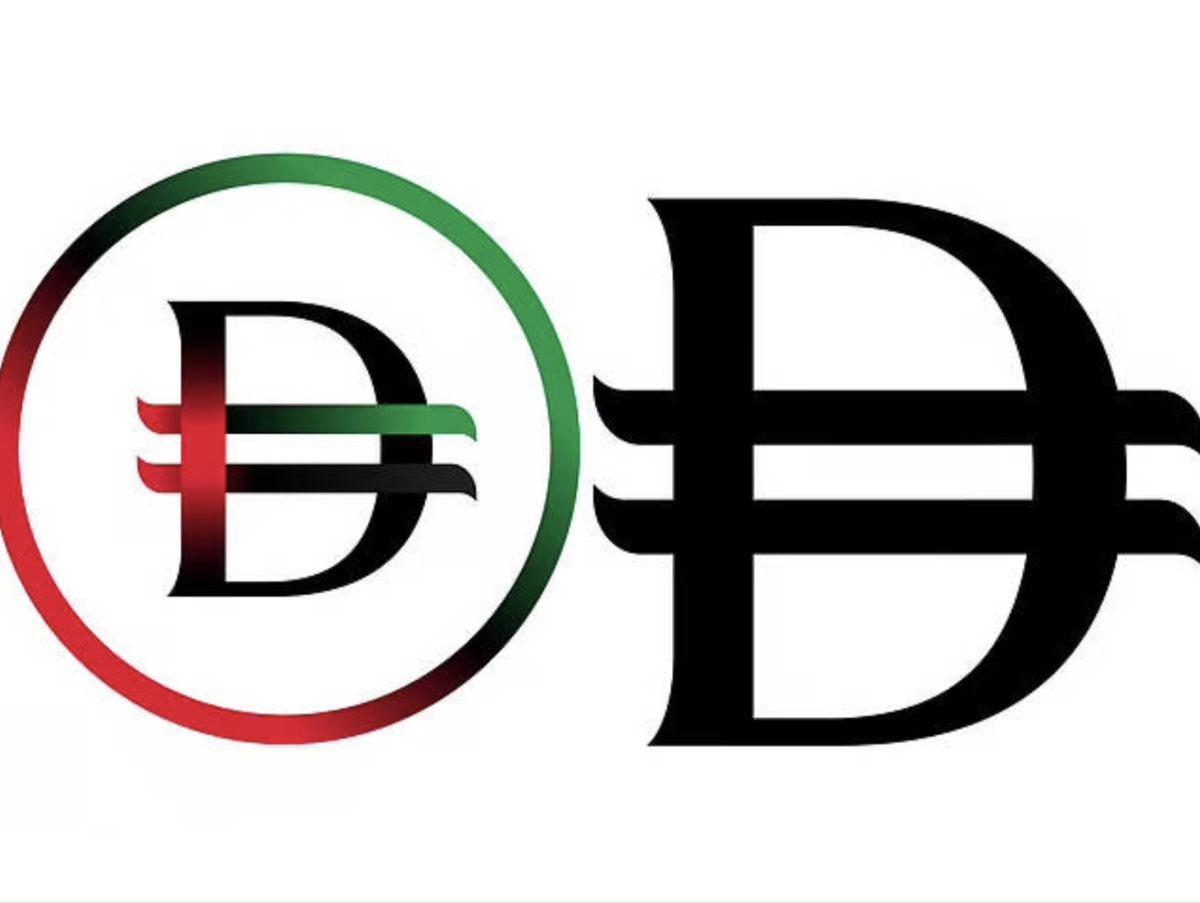
The new UAE dirham symbol. File
By establishing their own, Saudi Arabia and the UAE are declaring their currencies as serious contenders in international trade and finance.
“The new currency symbols for the Saudi riyal and UAE dirham are more than design updates. They’re strategic instruments of soft power and economic diplomacy,” said Andreas Hassellof, CEO of tech firm Ombori. “By embedding cultural identity into global financial language, both nations are signaling a readiness to elevate the riyal and dirham on the world stage.”
Hassellof believes that familiar symbols create a perception of legitimacy, influencing how currencies are referenced, traded, and held.
Arun Leslie John, chief market analyst at investment planning firm Century Financial, told Arab News that the rebranding reflects economic confidence and institutional maturity, which are key to attracting foreign direct investment.
“The new logos will bring more visibility in cross-border transactions, making the UAE dirham and Saudi riyal practical as invoicing currencies for trade, thereby reducing reliance on traditional denominations like the dollar and euro,” he said.
The UAE dirham has already been ranked among the top 10 most traded currencies by a leading UK forex provider, signaling its growing prominence. Saudi Arabia, with its vast oil wealth and economic diversification efforts, is similarly positioning the riyal as a currency of stability and innovation.

Arun Leslie John, chief market analyst, Century Financial. Supplied
The digital frontier: reshaping finance and inclusion
Both nations are leveraging these rebrands to accelerate their digital finance agendas.
The UAE’s digital dirham, part of its Financial Infrastructure Transformation Programme, will be legally recognized as a universal payment method, available through banks, fintech firms, and exchange houses. Its features — such as instant settlement and automated smart contracts — promise to redefine financial transactions.
“The rollout of digital currencies, particularly the UAE’s blockchain-based digital dirham, represents a bold leap toward a more efficient and inclusive financial ecosystem,” said Hassellof.
“Traditional cross-border transactions are slow and feel-heavy, especially for smaller enterprises and remittance flows. Digital currencies remove these frictions, enabling near-instant settlement at a fraction of the cost.”

Andreas Hassellof, CEO, Ombori. Supplied
Century Financial’s Leslie John highlighted the operational benefits, stating: “The UAE’s mBridge will facilitate intra-regional payments at a faster pace, with fast settlement terms and smart contracts of the digital dirham enabling trade finance flows, minimizing operating costs, and improving efficiency.”
He also emphasized how tokenization allows fractional ownership of assets, opening investment opportunities for SMEs and retail investors.
Khairy pointed to the broader economic implications, saying: “Digital currencies like the UAE’s digital dirham or Saudi Arabia’s CBDC pilot aren’t just tech experiments — they could reshape how trade is settled, how foreign investors view regional stability, and how citizens connect with their economies.”
He stressed that faster, cheaper cross-border payments could make Gulf economies more attractive to global partners.
Saudi Arabia, meanwhile, is integrating its new riyal symbol into digital and physical transactions, with plans for gradual implementation across financial platforms. Its participation in Project mBridge highlights a shared Gulf vision for blockchain-powered trade efficiency.
A unified Gulf financial future?
The parallel moves by Saudi Arabia and the UAE suggest deeper monetary cooperation could be on the horizon. “Today’s digital dirham and symbolic riyal may well be the foundation stones of tomorrow’s unified Gulf financial future,” said Hassellof.
Leslie John expanded on this, saying: “The simultaneous digital money and rebranding moves by Saudi Arabia and the UAE present the potential for further deepening monetary integration of the Gulf Cooperation Council, paving the way for interoperable payment mechanisms or even a future digital GCC currency union.”



























