LONDON: In wartime, the destruction of a school is more than collateral damage — it represents the theft of a child’s future. The past year has been especially bad in this regard, with one in three children in conflict zones or fragile states deprived of schooling.
With wars taking place in Gaza, Lebanon, Sudan, Ukraine, and elsewhere around the globe, the UN children’s fund, UNICEF, described 2024 as “one of the worst years” in its history for children in conflict.

“By almost every measure, 2024 has been one of the worst years on record for children in conflict in UNICEF’s history — both in terms of the number of children affected and the level of impact on their lives,” said Catherine Russell, the agency’s executive director.
“A child growing up in a conflict zone is far more likely to be out of school, malnourished, or forced from their home — too often repeatedly — compared to a child living in places of peace.
“This must not be the new normal. We cannot allow a generation of children to become collateral damage to the world’s unchecked wars.”
Nearly one in six children worldwide live in conflict zones, with more than 473 million enduring the highest levels of violence since the Second World War, according to the Peace Research Institute Oslo.

Infographic courtesy of Save the Children
In contexts like Gaza and Sudan, where many educational facilities have been damaged or destroyed by fighting and where teachers have been forced to flee, learning and play have been replaced by trauma and loss.
In Gaza, at least 658,000 school-aged children remain out of classrooms for the second consecutive academic year, with around 96 percent of school buildings damaged or destroyed since October 2023, despite their protected status under international humanitarian law.
The Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, which saw 1,200 killed and 250 taken hostage, triggered the devastating war in Gaza, which killed at least 47,000 Palestinians and displaced 90 percent of the population, according to Gazan officials.
Despite the fragile Israel-Hamas ceasefire deal reached earlier this month, a return to classrooms in Gaza remains a distant hope. UNICEF said in November that at least 87 percent of the enclave’s schools will require extensive reconstruction before they can reopen.
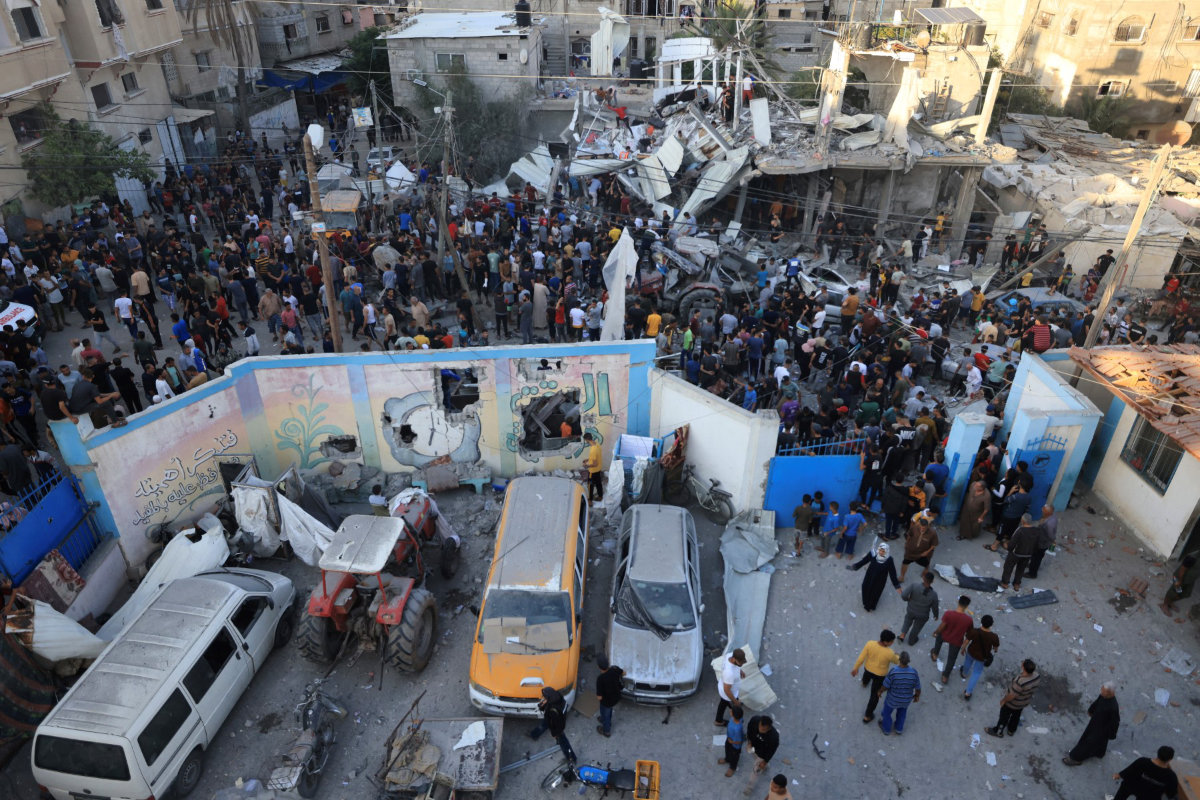
Palestinians inspect the debris after an Israeli strike near a UN-run school in Khan Yunis, in the southern Gaza Strip on October 21, 2023. (AFP)
Although Israel says it does not deliberately target civilian infrastructure, few educational institutions have been spared damage, including UN-run schools sheltering displaced civilians.
UN experts voiced concern last year over what they considered the systematic destruction of education in Gaza, not only through the crippling of schools and colleges but also the arrest and killing of teachers.
“It may be reasonable to ask if there is an intentional effort to comprehensively destroy the Palestinian education system, an action known as scholasticide,” the UN experts said in a joint statement.
“These attacks are not isolated incidents. They present a systematic pattern of violence aimed at dismantling the very foundation of Palestinian society,” the statement added, lamenting that “when schools are destroyed, so too are hopes and dreams.”
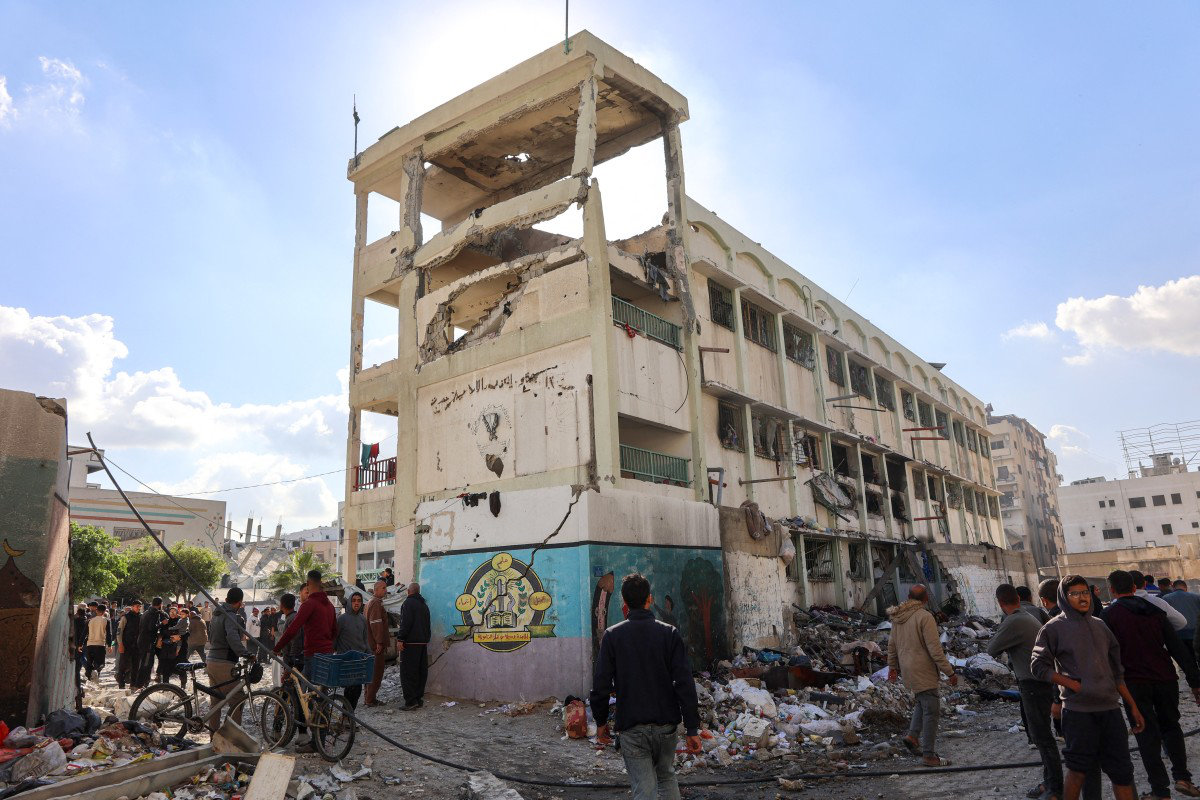

People inspect the damage following an Israeli strike on the UNWRA-run Al-Majda Wasila school housing displaced Palestinians in Gaza City on December 14, 2024. (AFP)
By September last year, at least 10,490 school and university students and more than 500 schoolteachers and university lecturers had been killed, according to Gaza’s Ministry of Education.
In October alone, the UN documented at least 64 Israeli attacks on schools in Gaza, averaging almost two attacks per day.
“Schools should never be on the front lines of war, and children should never be indiscriminately attacked while seeking shelter,” UNICEF’s Russell said in early November.
“The horrors we are seeing in Gaza are setting a dark precedent for humanity, one where children are hit with bombs at record numbers while looking for safety inside classrooms. Trauma and loss have become their daily norm.”

A man inspects the damage at the site of an Israeli strike that targeted the Musa bin Nusayr School in the Al-Daraj neighborhood in Gaza City on December 22, 2024. (AFP)
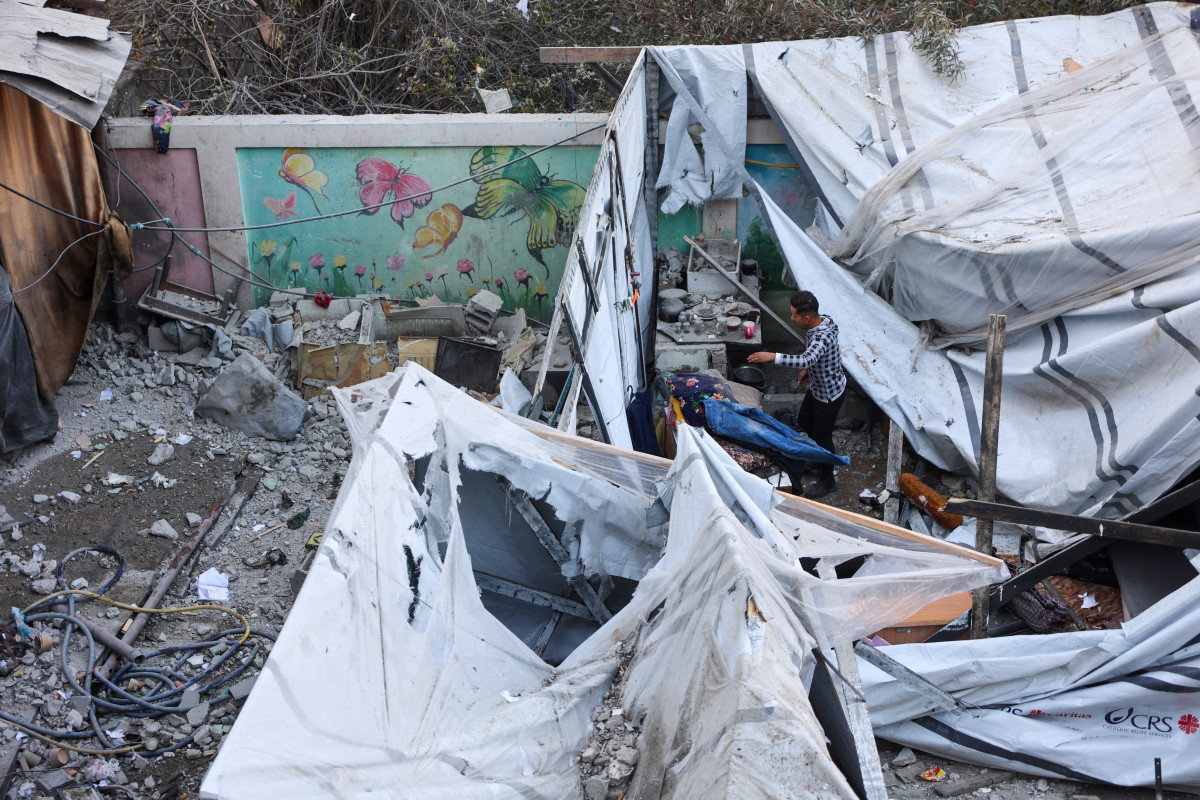
The situation is equally dire in Sudan, where a brutal civil war has wrought havoc on civilians and critical infrastructure since April 2023, killing tens of thousands and displacing more than 11.4 million, according to UN figures.
Attacks on schools, which Save the Children reports have increased fourfold since the conflict began, have forced most institutions to close, leaving more than 18 million of the country’s 22 million children without a formal education for more than a year.
Such attacks, Save the Children says, include airstrikes on schools, the abduction, torture, and killing of teachers, and sexual violence against students inside education facilities.
Other violations include armed groups occupying schools, using them to store weapons, and fighting battles on school grounds.
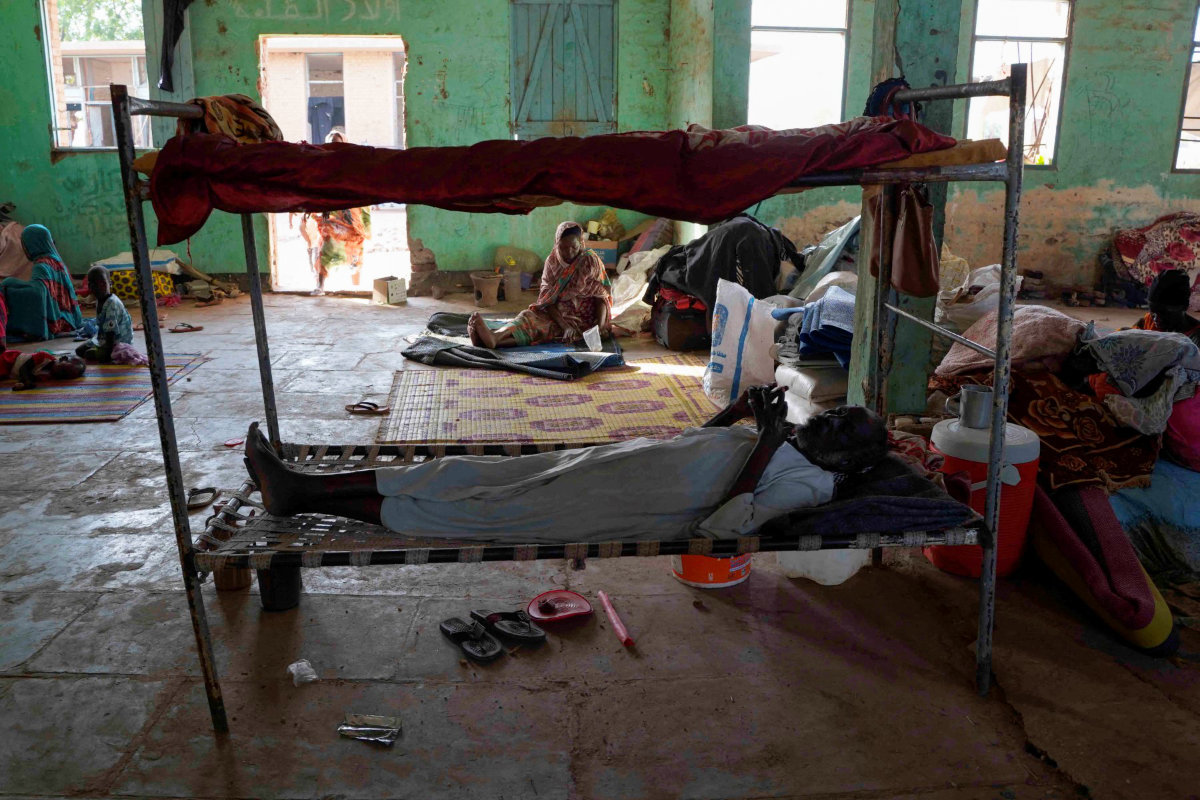

People fleeing violence in Sudan reside at the Hasahisa secondary school in Jazira state (AFP photo)
Adil Al-Mahi, MedGlobal’s Sudan country director, believes that even if the violence ends, a full return to normal education is unlikely in the near future.
“Cities controlled by the Rapid Support Forces are badly damaged, including education facilities in those areas,” Al-Mahi told Arab News.
By early 2024, the paramilitary RSF had seized most of the capital, Khartoum, and much of Al-Jazirah state, Sudan’s agricultural heartland.
INNUMBERS
• 25 million Children in 22 conflict-affected countries who are out of
• 103 million Children in 34 conflict-affected countries denied schooling in 2024.
(Source: Save the Children)
However, in January, the Sudanese Armed Forces announced they had advanced into Omdurman, Sudan’s second-largest city, located in Khartoum state, reclaiming some areas previously held by the RSF.
Schools in these areas have been “used by the RSF as warehouses for military equipment,” and therefore many have been targeted by the air force, Al-Mahi said. “Around 70 percent of the facilities might not be safe for children’s education.”
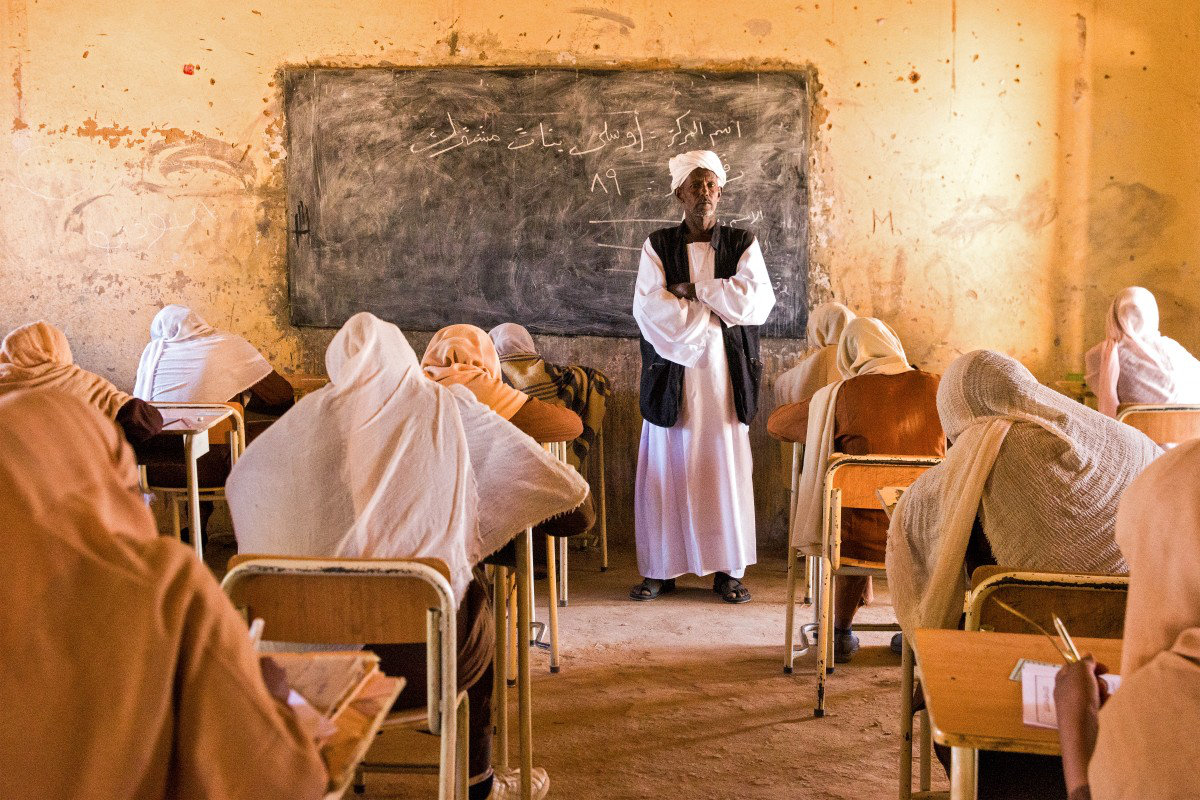

A teacher invigilates middle school students during their end-of-year exams in the northern Sudanese village of Usli on November 24, 2024. (AFP)
Aid agencies warned in May that Sudan is on the brink of the world’s worst education crisis. Displacement has compounded the already dire situation, even in areas where schooling remains relatively accessible.
With no formal camps for internally displaced persons, many families have sought refuge on school grounds, disrupting the education of local children, said Al-Mahi.
In the eastern coastal city of Port Sudan, for example, “some schools have reopened,” but they face significant challenges as “the schools themselves were used as shelters for IDPs arriving from the conflict area.”
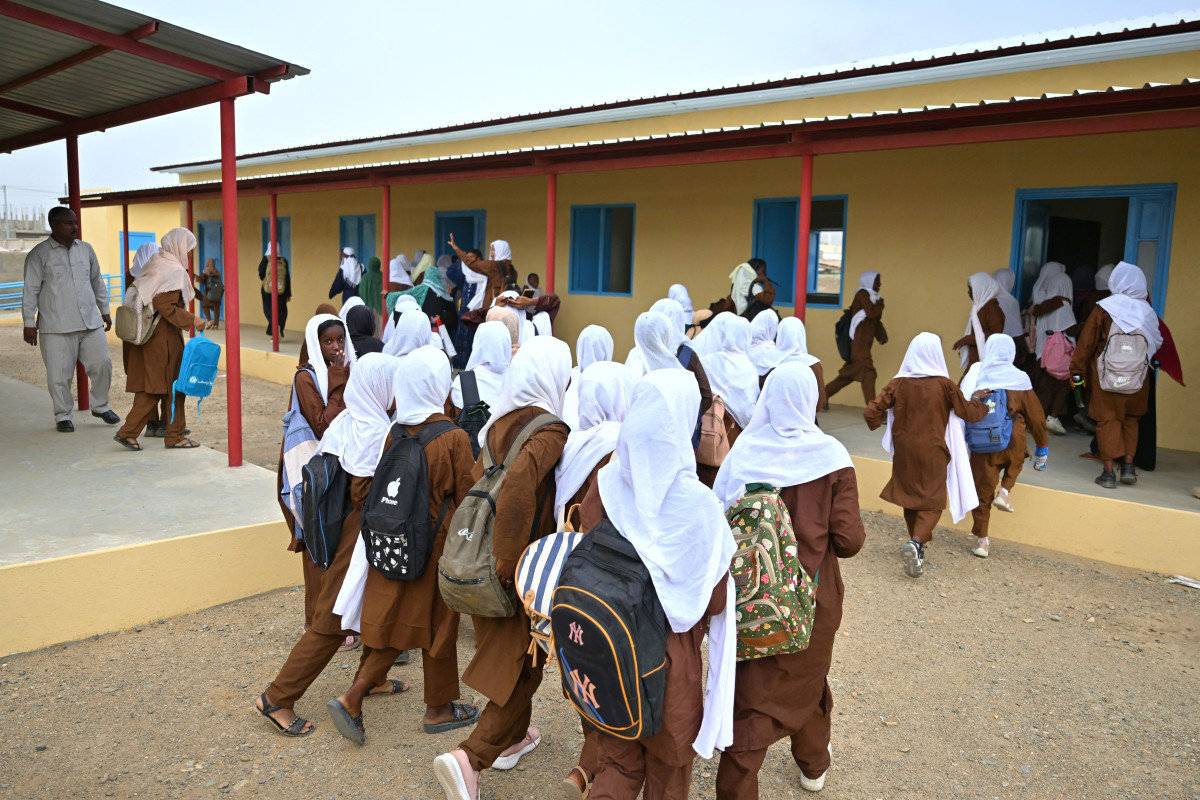

Students walk at the beginning of the new the academic year in Sudan's Red Sea State, at Wahda School west of Port Sudan, on September 16, 2024. (AFP)
Al-Mahi said the situation has created tensions with local communities, who wanted to reclaim the spaces and reopen the schools.
A similar issue emerged in the River Nile state. However, according to Al-Mahi, “the problem was resolved to get the families out of the classrooms and have them in proper tents in the open areas within the school — the playgrounds — and then have the schools also operate.”
Nevertheless, facilities in these areas continue to struggle with overcrowding. “Most of the cities that received IDPs have seen their populations increase three or fourfold, making it very difficult to accommodate children, even if the school is no longer housing IDPs,” Al-Mahi said.
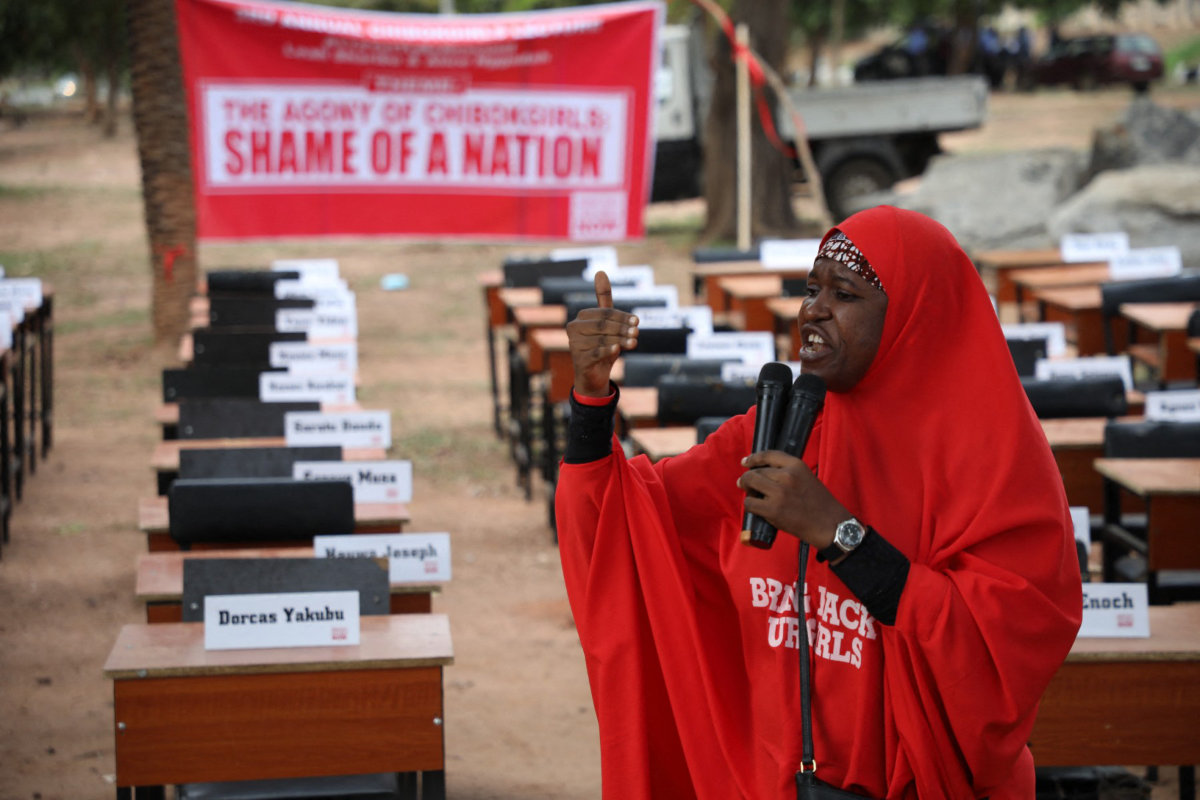

Aisha Yesufu, a leader of Nigeria's Bring Back Our Girls movement, delivers a speech on April 14, 2019, during the 5th Year Commemoration of the abduction of the 276 Chibok Schoolgirls by Boko Haram terrorists on April 14, 2014 in Chibok, Borno state. (AFP)
The disruption of formal learning in conflict zones has cast a shadow over children’s futures, leaving many with mental health issues and at an increased risk of child labor and child marriage.
“Education is lifesaving,” James Cox, Save the Children’s global education policy and advocacy lead, told Arab News.
“School protects children from things like child labor, early marriage and pregnancy, recruitment into armed forces, and helps build critical thinking, healthy social relationships, and mental wellbeing.
“Children being denied their right to education on any scale has significant implications for society as well as the individual children. Studies have shown that in low- and middle-income countries, the probability of conflict has almost tripled when the level of educational inequality doubled.”
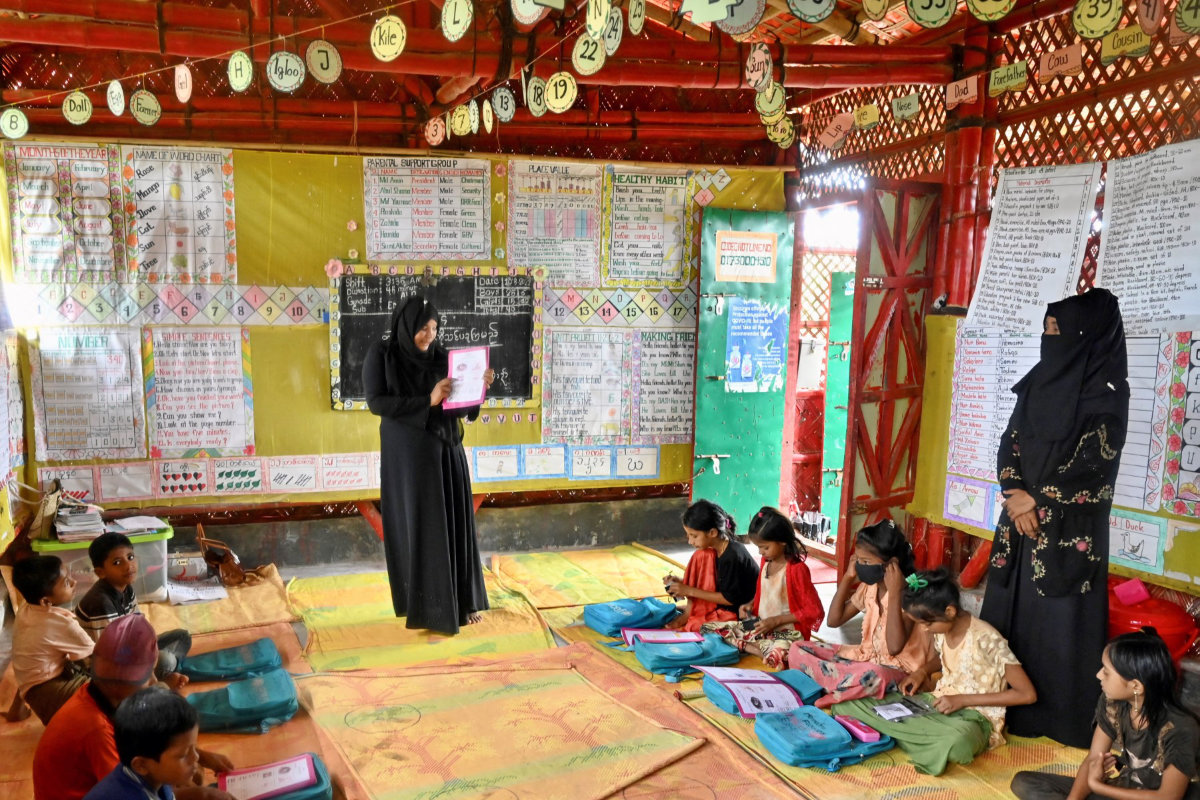

A Rohingya refugee woman teaches language at a school in Kutupalong refugee camp in Ukhia, Bangladeshon August 10, 2022. (AFP)
It also impacts economic prosperity. UNESCO estimates that by 2030, the annual global social costs of children who leave school early will reach $6.3 trillion — or 11 percent of global gross domestic product.
Cox also warned that “when children are prevented from attending school for a long period, learning is significantly impacted — and can often regress.”
He said: “The longer children are out of school, the greater the risk that they never return — and, without the right support, of dropping out for those who try to return.”
For school-age children in conflict zones, the mental health impact can be immense. Jeeda Al-Hakim, a specialist counseling psychologist at City University of London, described being out of school as “an emotional wound that goes beyond missed lessons.
“School offers much-needed stability, a sense of normalcy, and a safe space to form friendships and express themselves,” she told Arab News. “Without it, children are left isolated and burdened by uncertainty, often grappling with feelings of fear, loss, and despair.”
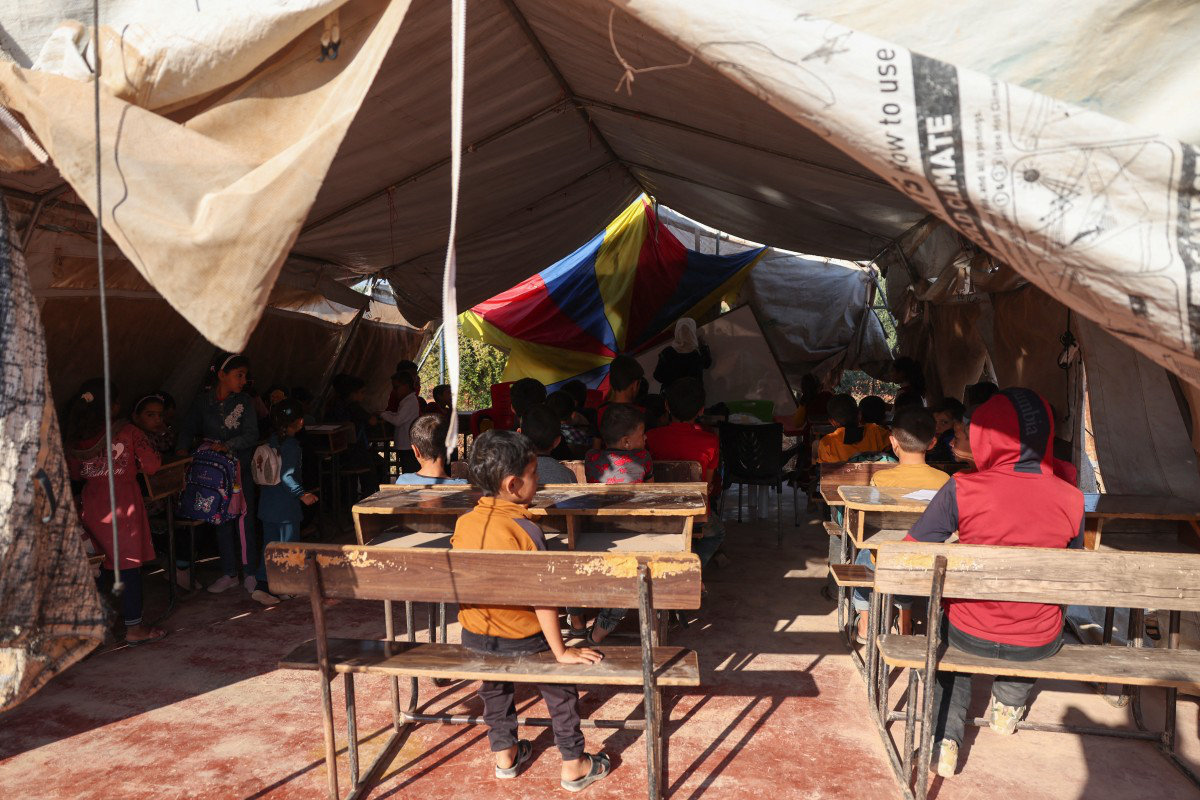

Children attend class at a makeshift school set up in a camp for internally displaced Syrians, in the village of Haranabush, Idlib province, on September 29, 2024. (AFP)
Many of those children “are thrust into adult responsibilities — caring for siblings or finding ways to survive — while their own emotional needs are sidelined,” she said.
“Premature adultification can lead to profound feelings of loneliness and anxiety, as children miss out on the freedom to simply be children.”
Stressing that “the emotional cost of these experiences cannot be understated,” Al-Hakim said: “While informal learning or community support can provide glimmers of hope, nothing replaces the emotional security and opportunities that come from a stable environment.
“To truly support these children, we must prioritize ending the conflicts that strip them of both their childhoods and their futures.”






























