BEIRUT/DUBAI: Just when it seemed the phrase “a perfect storm of crises” had become the ultimate cliche in describing the many daunting challenges confronting Lebanon, yet another threat appeared on the horizon — the likelihood of a deadly earthquake.
On Aug. 16, the National Center for Geophysical Research in Lebanon recorded an earthquake measuring 4.2 on the Richter scale, originating from Hama in neighboring Syria, where its magnitude reached 5.2.
The tremor came less than 72 hours after another earthquake on Aug. 12, again originating in Hama, with a magnitude of 4.8. Although several people in Syria were injured in both quakes, there were no fatalities.

General view of Lebanon's second city of Tripoli, on the Mediterranean coast. (AFP/File photo)
Residents of Lebanon’s northern cities of Tripoli and Akkar felt the tremors particularly strongly, with many rushing into the streets, fearing the buildings around them may collapse, such was the strength of the quakes.
“The two earthquakes occurred within a well-known geological context in our region, specifically in western Syria, where the fault of the Dead Sea known as the Masyaf fault passes, and then you have the Al-Ghab fault,” Tony Nemer, professor of geology at the American University of Beirut, told Arab News.
“The first tremor occurred to the east of the Masyaf fault, about 25 km from the city of Hama, where there are ruptures branching off from the main faults. It was followed by aftershocks and three days later by another tremor.”

Tony Nemer, professor of geology at the American University of Beirut. (Supplied)
Nemer said that significant aftershocks could be expected. “When the area is seismically active, small tremors are generated, and it is possible that they may also generate a large tremor,” he said.
“It is not easy to determine whether this will constitute future danger as the matter requires a comprehensive and time-consuming on-the-ground evaluation and study.
“In light of the second earthquake, it has become necessary for Syrian colleagues to be present in the field to study surface phenomena and install temporary seismic monitoring devices to shed light on the causes of the current seismic movement.”
The tremors brought back memories of the massive twin earthquakes that struck southeast Turkiye and northwest Syria on Feb. 6, 2023, with magnitudes of 7.8 and 7.5 felt throughout the region.
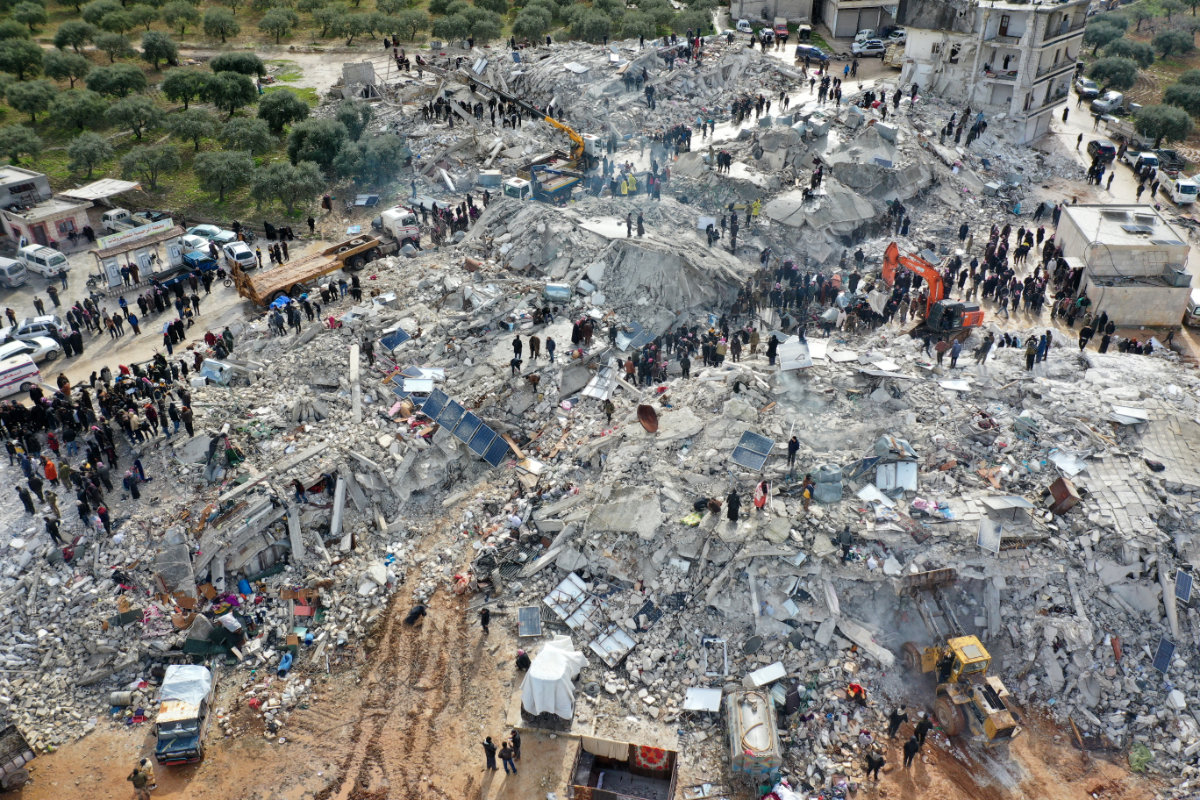

Residents search for victims and survivors amid the rubble of collapsed buildings following an earthquake in the village of Besnia near the town of Harim, in Syria's northwestern Idlib province on the border with Turkey, on February 6, 2023. (AFP/File)
The twin earthquakes were among the deadliest of the past decade, killing more than 55,000 people and flattening tens of thousands of buildings across both countries. Although Turkiye was harder hit, a decade of civil war left Syria uniquely vulnerable to the disaster.
Lebanon is also in a poor condition to withstand such a disaster — five years into a severe economic crisis, paralyzed politically, and now a proxy battlefield between the Israeli military and the Iran-backed Hezbollah militia, which threatens to drag the country into a regional war.
If a larger earthquake were to strike the region, or the epicenter to fall closer to Lebanon, the country, with its ramshackle infrastructure and gutted emergency services, may be ill-equipped to withstand the tremors or launch effective search and rescue operations.
How likely is such a disaster? Lebanon is located at the meeting point of three tectonic plates — the Arab plate, the Turkish plate and the African plate — which makes the region especially prone to seismic activity.

According to the government’s own disaster and crisis response plan, Lebanon is located on a geological fault line that passes through the middle of Lebanon and extends for 1,000 km from the Red Sea in the south to the Anatolian mountains in southern Turkiye.
This is called the Dead Sea Transform fault, which is responsible for the largest seismic events in the Middle East.
The fault system branches off when it enters Lebanese territory, forming several faults known as the Yamoune fault, the Rum fault, the Hasbaya fault, the Rashaya fault and the Sarghaya fault.
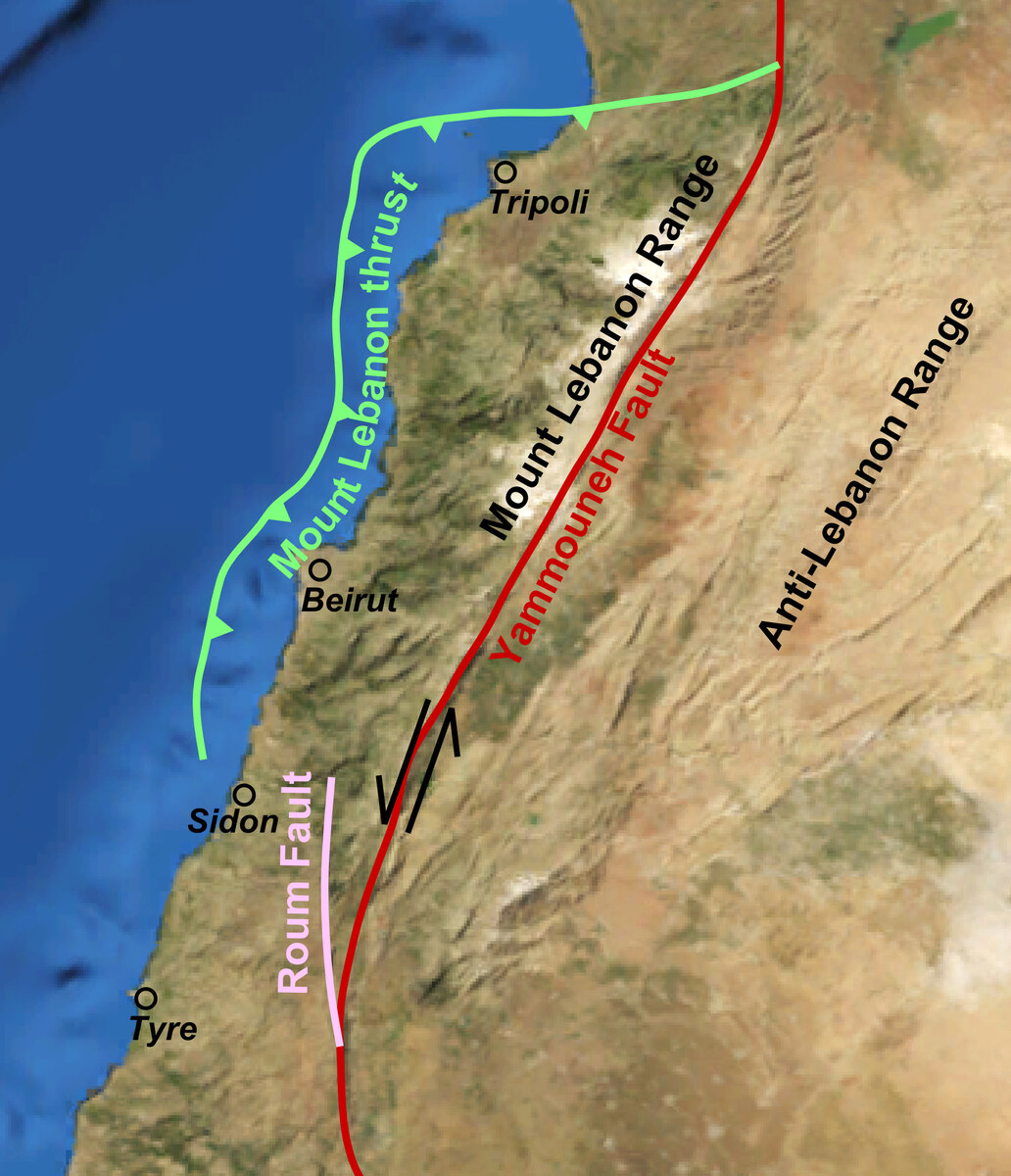
(Infographic credit: Wikimedia Commons/ Mikenorton)
Although it does not constitute a meeting point of tectonic plates, the Yamoune fault is considered one of the most dangerous for Lebanon, as it runs up the middle of the country from the south to the north.
“In studying seismic events in Lebanon and the Middle East, it becomes clear that this part of the world has been exposed since 2000 B.C. to strong earthquakes that caused a lot of devastation, destruction and loss of life,” said Nemer.
The last major seismic event in Lebanon took place in 1956 in the town of Chehim in the Kharoub region between Mount Lebanon and the south. An earthquake of magnitude 5.8 caused significant destruction and loss of life.
FASTFACTS
• Lebanon lies on active fault lines, including the Dead Sea Transform, making it highly earthquake prone.
• Aged, substandard buildings are highly vulnerable due to weak construction regulations and materials.
• The nation’s disaster management focuses on post-quake responses, neglecting crucial preventive measures.
In 1997, the same town witnessed a moderate earthquake on the Rum fault. The Srifa area in southern Lebanon also witnessed a series of mild earthquakes in 2008, causing some damage.
There are also marine faults in Lebanese waters, which extend along the beaches between Damour and Batroun, at a distance ranging from 10 to 30 km off the coastline, which could pose a significant tsunami threat.
If waves were to come from Cyprus, it could take around 10 minutes for them to reach Lebanese shores. But if the waves were to form in Lebanese waters, they could reach the coast within three minutes, leaving precious little time to raise the alarm and evacuate.
Even if the population is able to evacuate in time, Lebanon’s Mediterranean coast is home to several major cities and significant infrastructure, including the nation’s main international airport, power plants, ports and tourist facilities
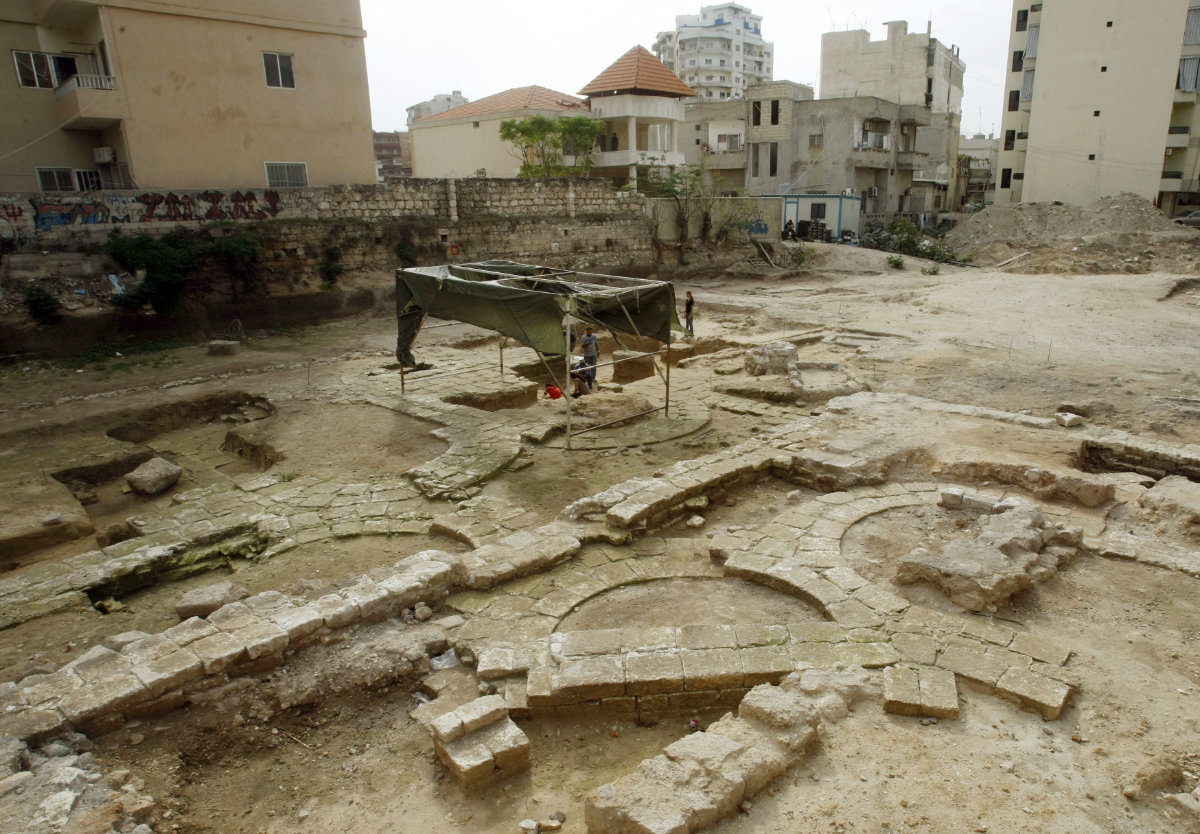

A general view photographed on October 21, 2010 shows an excavation site in southern Lebanon's port of Tyre. The ancient city was among those devastated by a masssive tsunami in 365 A.D. that was triggered by an earthquake that centered on the Mediterranean island of Crete. (AFp/File photo)
The historical archive contains several terrifying accounts of earthquakes and tsunamis that have battered the region.
The most prominent was a tsunami in 365 A.D., when the site of present-day Beirut witnessed waves more than 10 meters in height, after an earthquake likely exceeding a magnitude of 8 struck the Greek island of Crete.
Another famous disaster befell the region in 551 A.D. when an earthquake measuring 7.5 on the Richter scale resulted in a tsunami that devastated present-day Beirut, Tire and Tripoli in what was then Phoenicia.
In 1202, a 7.5 magnitude earthquake struck Syria, with aftershocks traveling up Lebanon’s Yamoune fault. Lebanon witnessed 50 earthquakes in 60 days, causing major subsidence along the coastline, sinking many small islands and destroying Tripoli and Baalbek.
In 1956, Lebanon was hit by a catastrophic 5.6 earthquake, which mainly affected the regions of Chouf, Jezzine, Saida and parts of Beqaa.
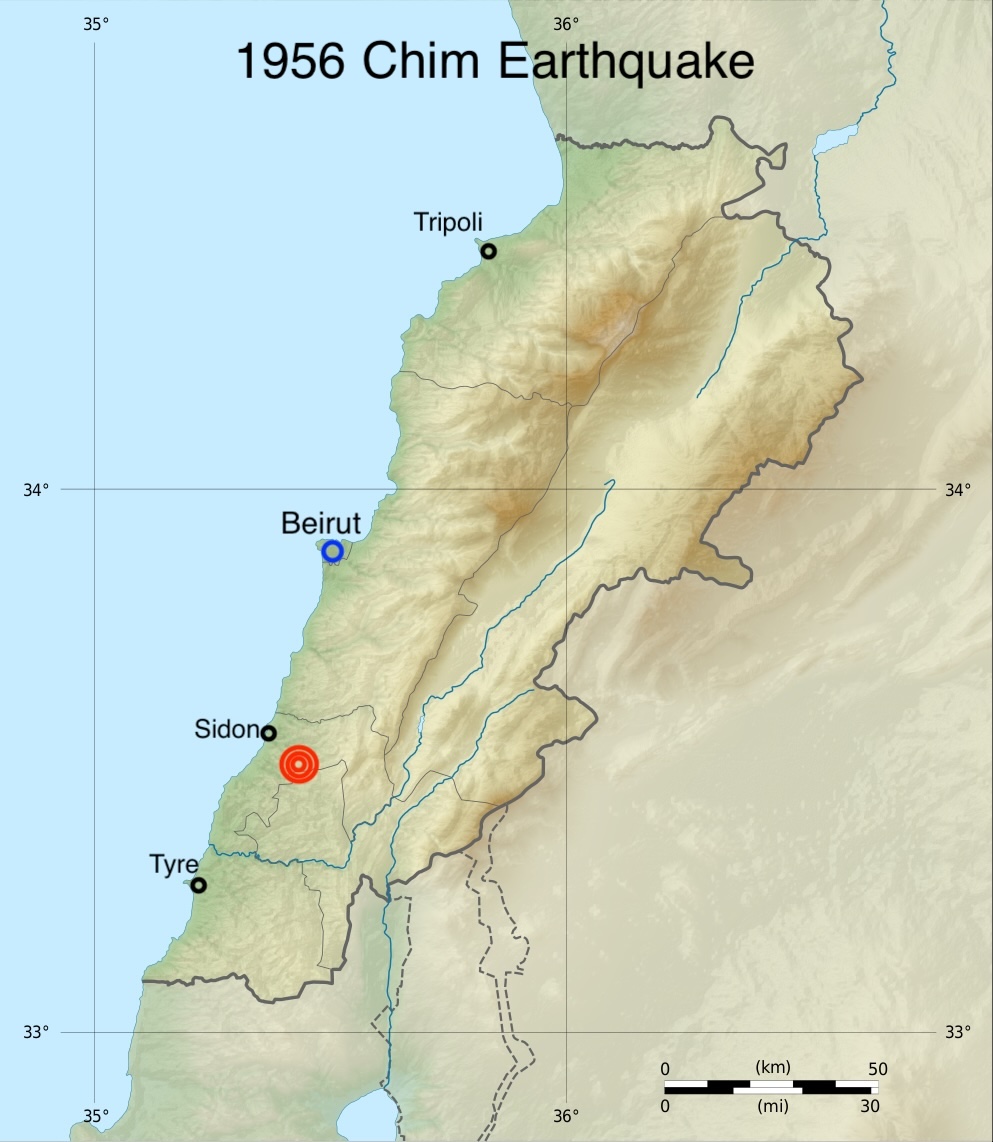
(Infographic credit: Wikimedia Commons/Sting & NordNordWest)
While Turkish authorities have been preparing over many years for the possibility of a major earthquake striking Istanbul, studying ways to fortify its buildings, officials in Lebanon, by contrast, appear resigned to their fate.
Indeed, the national response plan for natural disasters primarily focuses on what can be done after an earthquake has taken place — not on what can be done to limit the damage.
The infrastructure of Lebanese cities has not been retrofitted to guard against tremors. Some 20 percent of the nation’s buildings are more than 50 years old, while hundreds of thousands of residents, including Syrian and Palestinian refugees, live in informal and substandard structures.
Officials in Lebanon, according to the UN Program for Disaster Risk Reduction, have not taken the risk of earthquakes seriously, and buildings that contain vital institutions such as ministries, health centers and army barracks have not been sufficiently retrofitted.
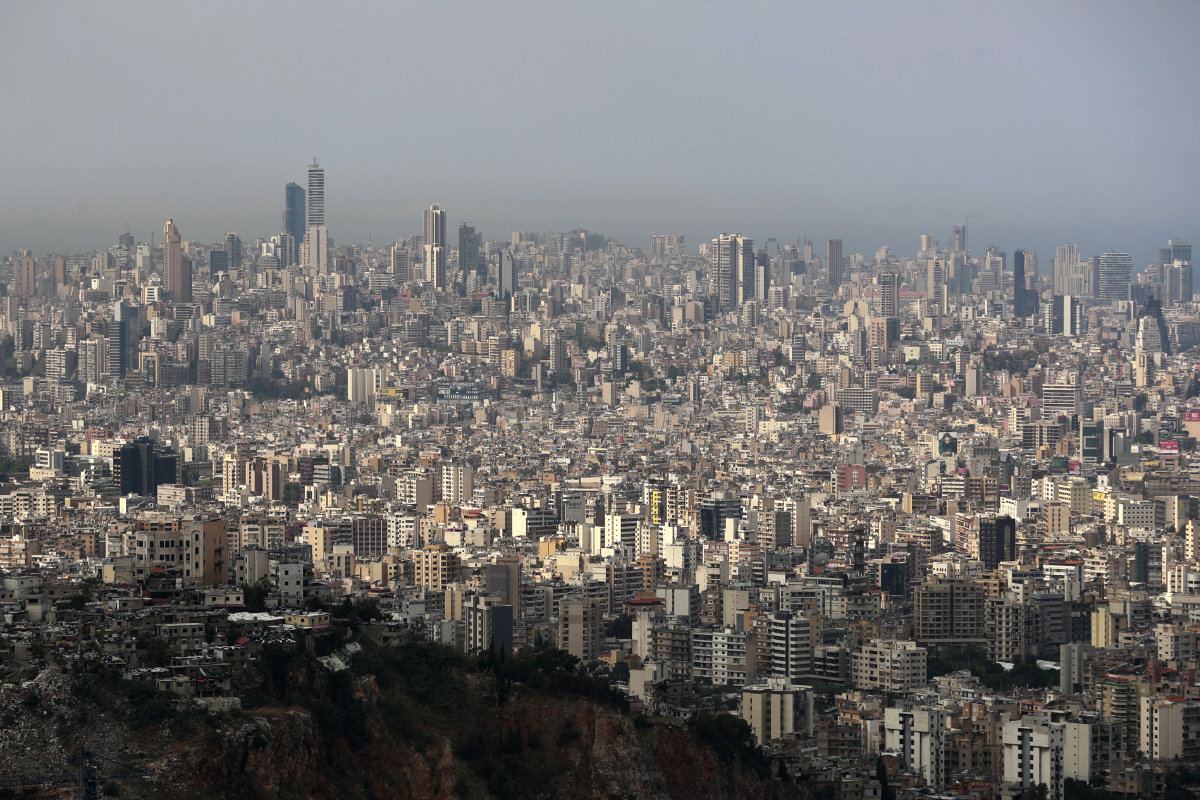

A general view of the Lebanese capital, Beirut. A recent report of the he Lebanese Real Estate Authority has warned that at least 16,000 buildings in Lebanon are vulnerable to collapse. (AFP/File)
In the wake of August’s earthquakes, the Lebanese Real Estate Authority has warned that at least 16,000 buildings are vulnerable to collapse, “without counting the buildings that were damaged as a result of the Beirut port explosion” of 2020.
“The economic hardship, the port explosion, the migration of capital, the absence of official support and the absence of control over the quality of building materials played a negative role in the increase in the number of cracked buildings that are on the verge of collapse or total or partial collapse,” Imad Al-Hussami, head of the authority’s engineering committee, told Arab News.
In the absence of official preparations, the Lebanese Real Estate Authority has urged citizens to “monitor the condition of cracks and fissures in their buildings, avoid being under worn out and protruding roofs, open windows to relieve pressure, and seek the assistance of experienced engineers and experts to protect themselves.”
































