LONDON: More than 1 million children in the Gaza Strip are at risk of contracting type 2 poliovirus, a highly infectious disease that can lead to paralysis and even death, as displacement and the destruction of sanitation infrastructure leaves the population vulnerable to disease.
The World Health Organization has announced plans to send 1.2 million polio vaccines to Gaza after the virus was detected in wastewater samples taken last month from displacement camps in the northern governorates of Khan Younis and Deir Al-Balah.
Although no clinical cases of polio have been diagnosed so far, Hanan Balkhy, the WHO’s regional director, warned that the virus could “spread further, including across borders” unless agencies acted quickly to vaccinate the population.
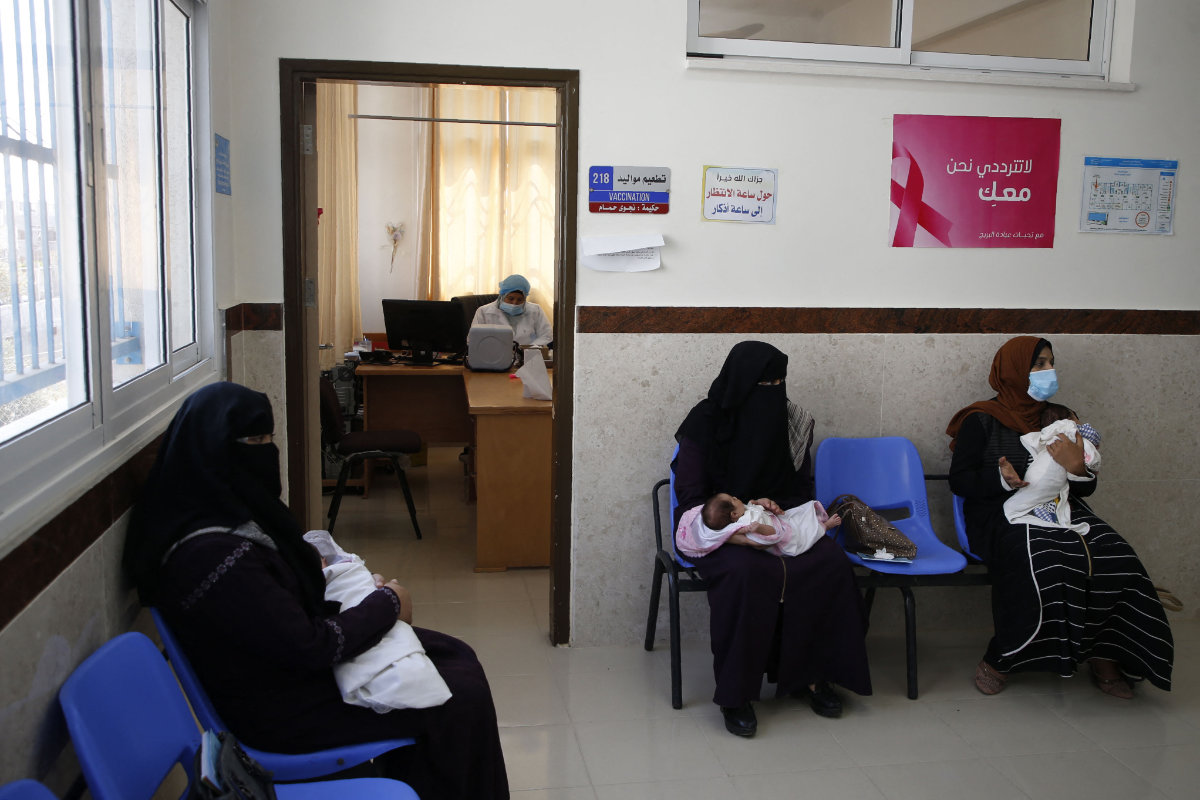

In this photo taken on September 9, 2020, a UNRWA employee provides poliomyeletis vaccine for children at a clinic in Bureij refugee camp in the Gaza Strip. Health officials have detected poliovirus in Gaza again amid a raging war that has destroyed most of the health centers in the area. (AFP/File)
However, any mass polio immunization campaign in Gaza, targeting 600,000 children under the age of 8, would face a host of challenges, chief among them the absence of a ceasefire which would allow medics to safely access displaced communities.
“We need a ceasefire, even a temporary ceasefire, to successfully undertake these campaigns,” Balkhy said at a press briefing on Wednesday.
Children under the age of 5, and especially infants, are most at risk from polio, as many missed out on the regular vaccination campaigns that had taken place in Gaza before the conflict began on Oct. 7.
The virus, which spreads through contact with the feces, saliva or nasal mucus of an infected individual, attacks nerves in the spinal cord and the brain stem, leading to partial or total paralysis within hours.
It can also immobilize chest muscles, causing trouble breathing, even leading to death.

PAHO/WHO infographic
Polio was eradicated in Europe in 2003 thanks to an effective vaccination campaign. There have been no confirmed cases of paralysis due to polio caught in the UK since 1984.
Wild poliovirus cases have fallen by more than 99 percent since 1988, from an estimated 350,000 cases in more than 125 endemic countries to six reported cases in 2021.
Of the three strains of wild poliovirus, type 2 was eradicated in 1999 and type 3 was eradicated in 2020. As of 2022, endemic type 1 remained in just two countries — Pakistan and Afghanistan.
In Gaza, overcrowding, a lack of clean water and hygiene materials, a deteriorating health system, and the destruction of sanitation plants have all contributed to the reemergence of type 2, according to Hamid Jafari, the WHO’s director of polio eradication, speaking at Wednesday’s press briefing.
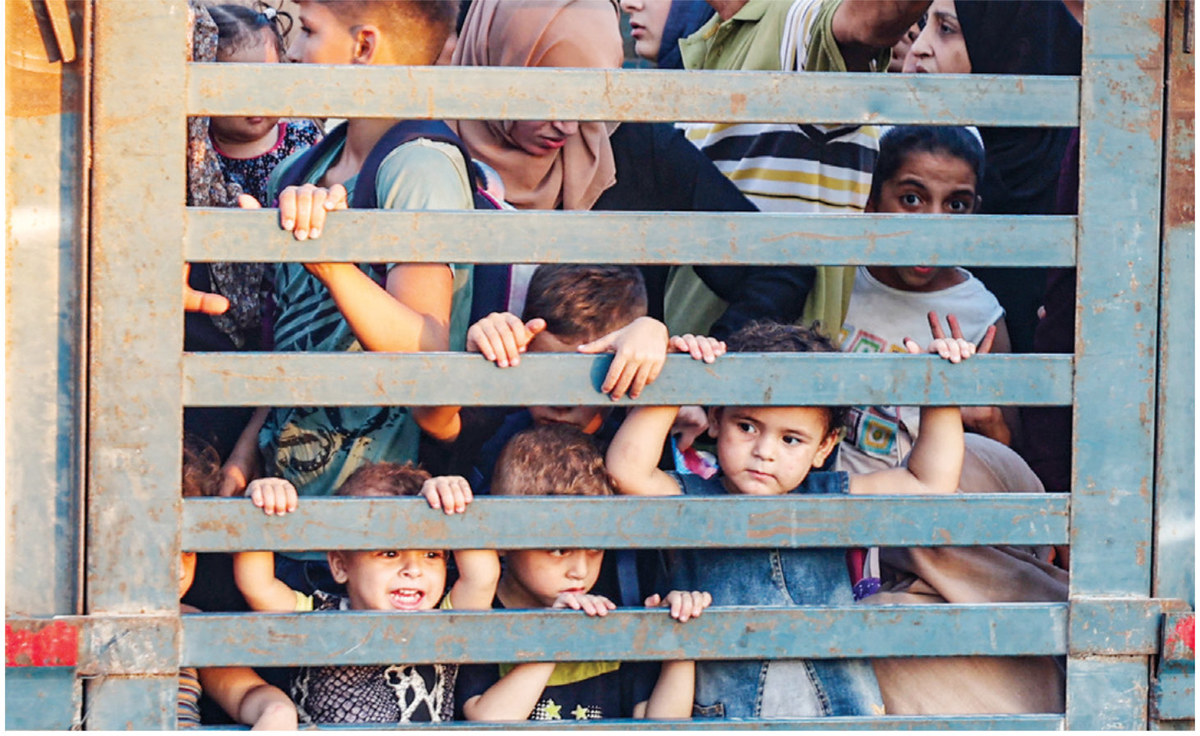

WHO says overcrowding, a lack of clean water and hygiene materials, a deteriorating health system, and the destruction of sanitation plants have all contributed to the reemergence of polio in Gaza. (AFP)
The UN estimates at least 70 percent of Gaza’s water and sanitation plants, including wastewater treatment facilities and sewage pumping stations, have been damaged or destroyed since the start of the conflict.
In late July, Gaza’s health authority declared the enclave a “polio epidemic zone,” blaming the resurgence of the virus on Israel’s bombing campaign and the ensuing damage this had caused to the healthcare system.
The Israeli military began its bombardment of the Gaza Strip in retaliation for the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel. Although the Israeli military insists it does not target civilian infrastructure, schools, hospitals, and utilities have suffered major damage.
The more than 490 attacks on medical facilities and personnel, documented by the UN during the first six months of the conflict alone, have left Gaza’s healthcare system in tatters. Just 16 of Gaza’s 36 health facilities remain partially functioning.
INNUMBERS
1.2 million Polio vaccines the WHO plans to send to Gaza to prevent outbreak.
600,000 Children under the age of 8 to be targeted in vaccination drive.
70% Proportion of Gaza’s sanitation facilities damaged or destroyed.
1.9 million Palestinians in Gaza displaced multiple times since the conflict began.
Three of these facilities are in the north, seven in Gaza City, three in Deir Al-Balah, three in Khan Younis, and none in the southern city of Rafah, according to the US-based nongovernmental organization Physicians for Human Rights.
Javid Abdelmoneim, a medical team leader for Medecins Sans Frontieres, who was working at the Nasser Hospital in southern Gaza last month, told the organization “every day in July has been one shock after another.”
Recounting one particularly traumatic incident, he said: “I walked in behind a curtain, and there was a little girl alone, dying by herself. And that’s the outcome of a collapsed health system. A little 8-year-old girl, dying alone on a trolley in the emergency room.
“In a functioning health system, she would have been saved.”
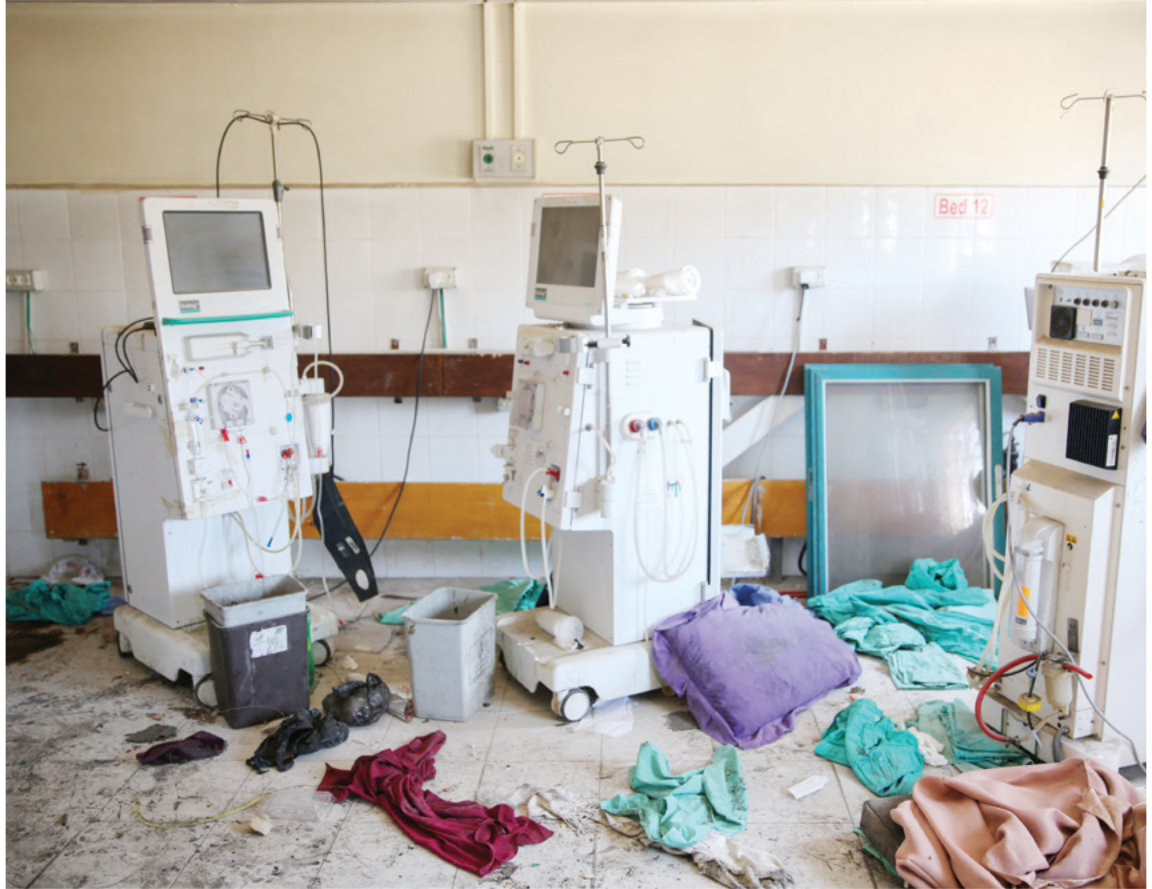

Medical equipment are laid to waste at a hospital in Gaza that had been destroyed by Israeli bombardment. (AFP)
Despite calls from the WHO and other aid bodies for the warring parties in Gaza to allow “absolute freedom of movement” so that medics can roll out a vaccination campaign, the possibility of a ceasefire appears no closer.
On Wednesday, the Israeli military issued new evacuation orders for several parts of northern Gaza, including Beit Hanoun, Manshiyya and Sheikh Zayed.
Avichay Adraee, the Israeli army’s spokesperson, posted the evacuation orders on the social media platform X. He instructed the residents of Beit Hanoun to “relocate immediately” to Deir Al-Balah and Zawayda.
“Beit Hanoun area is still considered a dangerous combat zone,” he added.
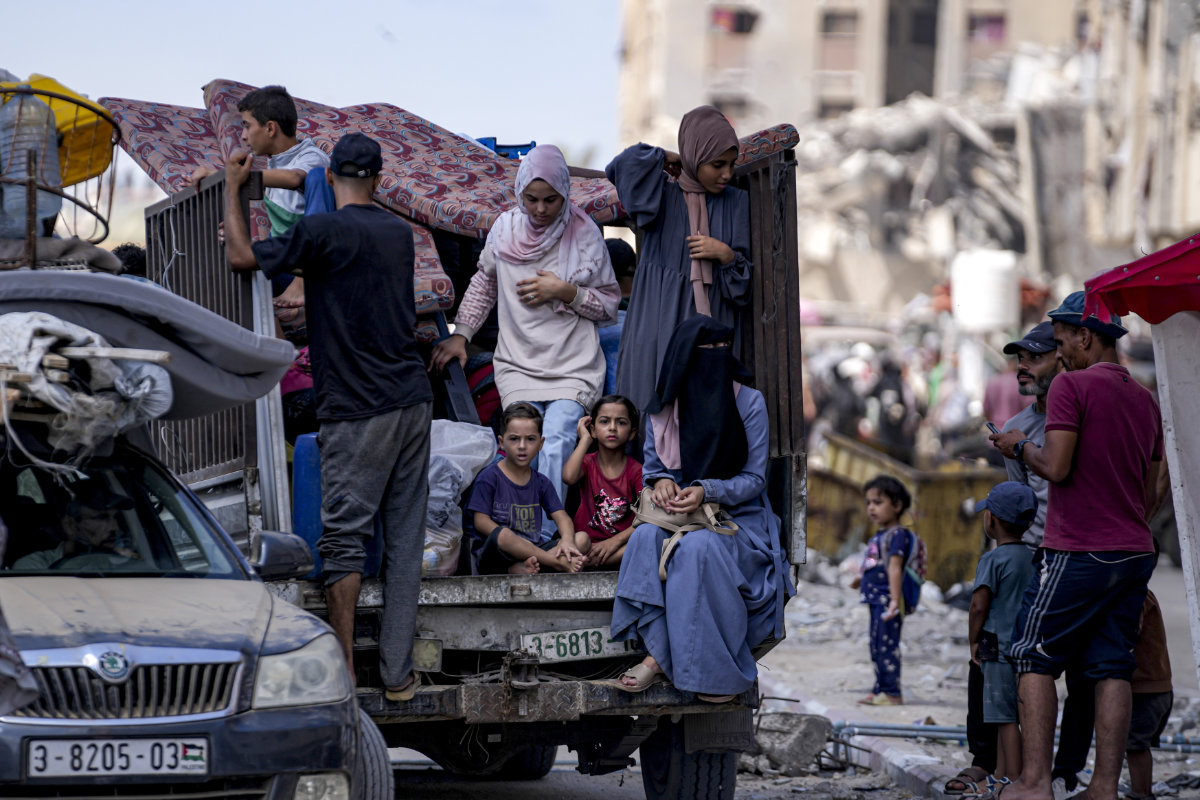

The constant evacuation of Palestinian families in the Gaza Strip has hampered the rollout of a vaccination campaign. (AP)
Despite assurances that these areas would be treated as safe zones in which civilians could shelter, both Deir Al-Balah and Zawayda have come under regular Israeli attack in recent months.
The UN reported that while nowhere in Gaza is safe, 86 percent of the besieged Palestinian enclave is under Israeli evacuation orders. About 1.9 million of Gaza’s 2.1 million population have been displaced multiple times since Oct. 7.
“Nowhere is safe. Everywhere is a potential killing zone,” UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said at the opening of the UNRWA Pledging Conference on July 12.
The continuous movement of families in Gaza has made it difficult for aid agencies, which are already short of funds and struggling to reach affected populations, to locate and identify unvaccinated children.
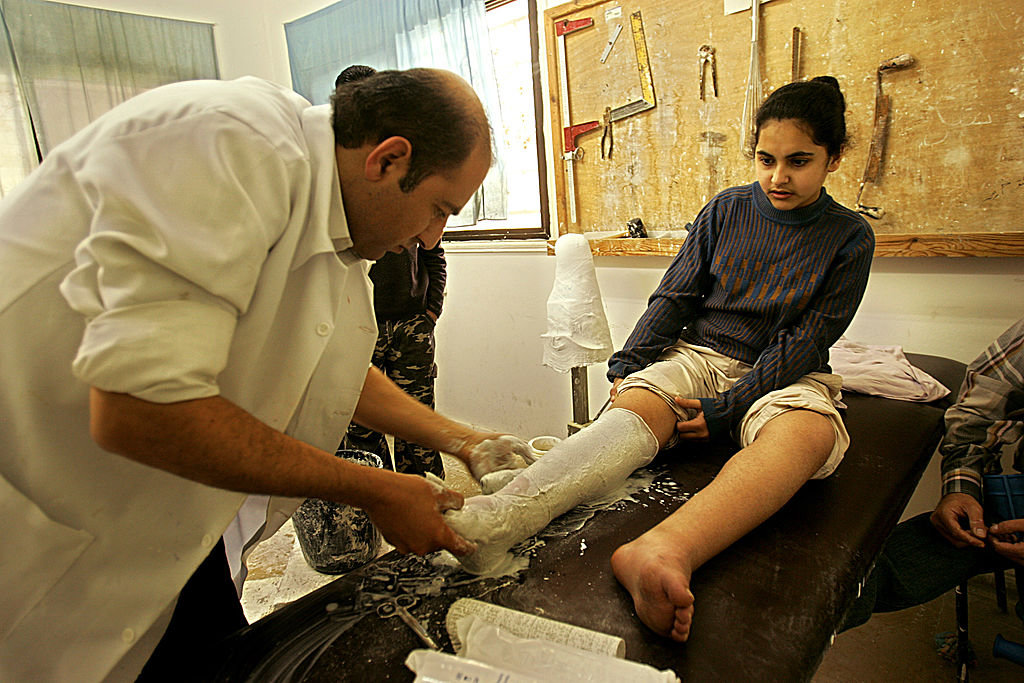
In this file photo, a polio patient is fitted for an artificial limb at a rehabilitation center for prosthetics and treating polio in Gaza City. The war in Gaza has hampered the operation of the rehab center. (Getty Images)
The WHO’s polio specialist Jafari warned that the virus could have been circulating in Gaza since September, as the enclave offered “ideal conditions” for its transmission.
Before Oct. 7, polio vaccine coverage in the Occupied Palestinian Territories was estimated at 89 percent, according to the WHO.
Even if the planned 1.2 million vaccines are successfully brought into Gaza, it will be a “huge logistical challenge” to ensure their successful deployment, WHO official Andrea King told the BBC.
The vaccines must be stored within a limited temperature range from the moment they are manufactured until they are administered. Bringing these chilled vaccines into Gaza and keeping them at the required temperature would be a difficult undertaking at the best of times.
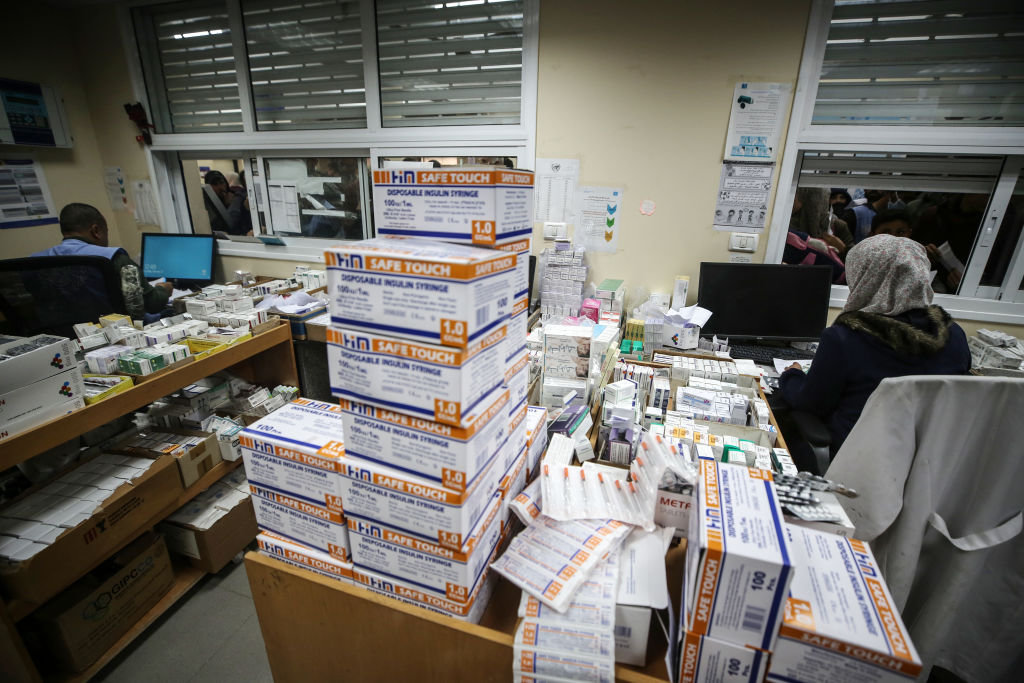

With a war going on, bringing chilled vaccines into Gaza and keeping them at the required temperature would be a difficult undertaking at the best of times, say WHO officials. (Getty Images)
The WHO’s Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said on Wednesday that a ceasefire or at least a few days of calm was essential to protect Gaza’s children.
As of July 7, the WHO has recorded a surge in infectious diseases, including 1 million cases of acute respiratory infections, 577,000 of acute watery diarrhea, 107,000 of acute jaundice syndrome, and 12,000 of bloody diarrhea.
It says this is primarily due to a lack of clean drinking water and the destruction of a critical water facility in Rafah, southern Gaza.






























