RIYADH: The Center for Space Futures, hosted by the Saudi Space Agency, will bring together space industries to send a mission to the moon and build a $2 trillion global space economy by 2035, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson has said.
During a visit to Riyadh this week, the US space agency chief said in a special interview with the Asharq TV channel: “The future of the space center is to bring together space industries, commercial companies, together with the government programs.”
On April 29, the Saudi Space Agency and the World Economic Forum signed an agreement to establish a Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution focused on space.

The World Economic Forum and the Saudi Space Agency signed an agreement to establish the Center for Space Futures. (AN photo by Abdulrahman Bin Shalhoubh)
Set to open in the fall of 2024, the Center for Space Futures will be the first center in the C4IR network. It aims to facilitate public-private discussions on space collaboration and contribute to accelerating space technologies.
Nelson told business anchor Maya Hojeij that, after a hiatus of half a century, NASA plans to “go back to the moon.” However, he added: “This time with not only commercial partners, but also with international partners.”
He highlighted that the Center for Space Futures will “bring together those commercial and government programs in order to build a significant space economy.”
Earlier this year, NASA announced that its Artemis II lunar mission will aim to land the first astronauts near the moon’s South Pole in September 2025.
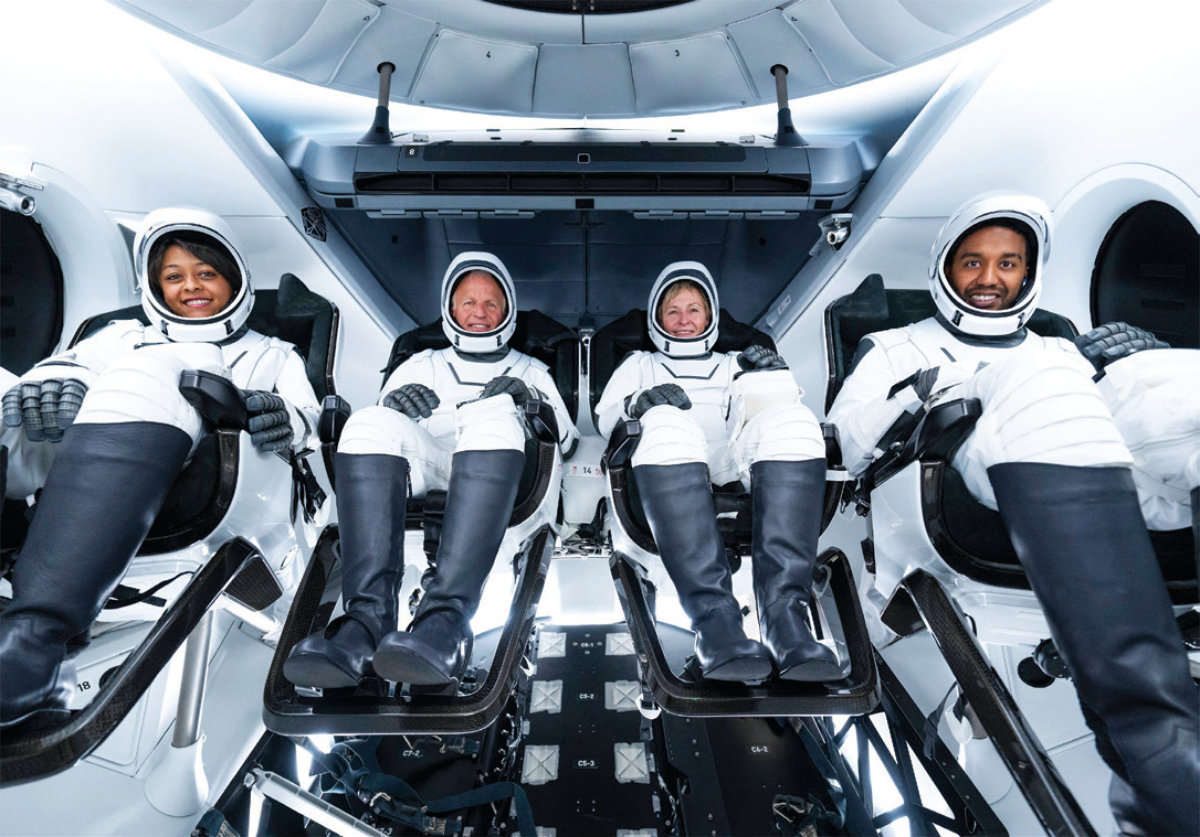

On May 21, 2023, Saudi astronauts Rayyanah Barnawi (L) and Ali Al-Qarni (R) launched toward the International Space Station together with American astronauts Peggy Whitson (2R) and pilot John Shoffner (2L). (Axiom Space photo/file)
NASA’s administrator added: “We’re talking about a space economy that will be almost $2 trillion dollars by the year 2035 — only a little over a decade away — a significant part of the economic sector of a country.”
Elaborating, he said that the “$2 trillion is worldwide. And that is a lot of startup companies, such as I have seen here in Riyadh today, that are partnering with other companies from around the world that are including incentives by the Saudi government.
“So, we do that in America, and that’s where I mentioned that we’re going back to the moon, this time after a half century, because we were on the moon a half-century ago.
“This time, we’re going back to the moon for a different reason, we’re going to learn, to invent, to create in order to be able to go to Mars and beyond. And this time we go back with commercial enterprises.”
NASA’s Apollo 17, which celebrated its 50th anniversary in December 2022, was the space agency’s sixth and final mission to land people on the moon.
The mission landed on the Taurus-Littrow site, which offered a mix of mountainous highlands and valley lowlands, allowing the crew to collect 741 lunar samples.
Nelson told Asharq’s Hojeij that NASA has partnered with Saudi Arabia on multiple scientific instruments to send Artemis II to the moon for economic benefits and to better understand climate change.
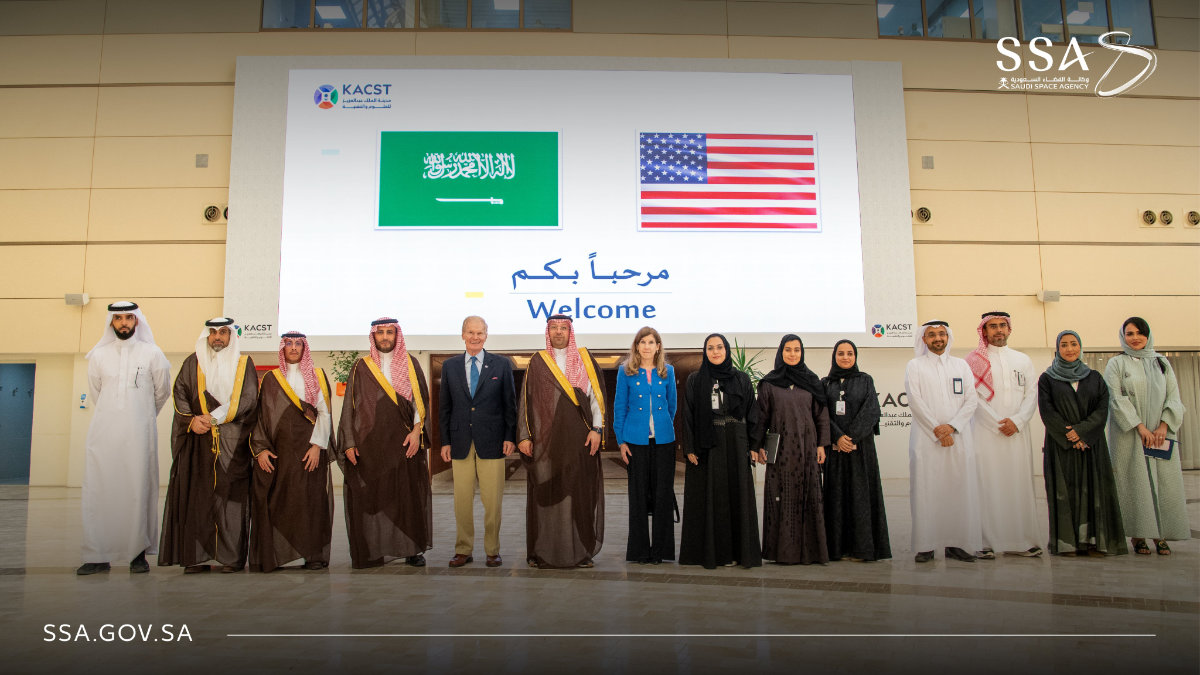

During a meeting organized by the Saudi Space Agency and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology in Riyadh, Saudi space officials met with NASA chief Bill Nelson and discussed ways to deepen the cooperation in the fields of space. (Courtesy: SSA)
“We have a partnership with Saudi Arabia,” he said. “We’ve already partnered on a number of scientific instruments, but we’ve got a whole way to go.
“We’re going back to the moon and then we’re going to Mars. We are constantly looking down on Earth to help our climate, to better understand what is happening to the Earth, to give very precise measurements of exactly what’s happening there.
“We’re going to coordinate and partner with Saudi Arabia on all of these things.”
Asked about space challenges and how the partnership between Riyadh and Washington sought to address them, Nelson said that debris in space was among the biggest threats to satellites and spacecraft.
“Debris in space is a major problem,” he said. “We are too often having to move our International Space Station to get it out of the way of a piece of space junk that otherwise could hit it.
“Same thing with a lot of our satellites. And so that applies to everybody’s satellites, not just US satellites, Saudi satellites.”
Nelson added that NASA was working with partners “to come up with systems and mechanisms by which we can require the manufacturers of satellites to be able, after their useful life, have a precise landing back through the Earth’s atmosphere to burn up and if any pieces are left over, that they would fall harmlessly in the southern Pacific Ocean.”
Underscoring the importance of these efforts, he said that “whenever something is left in space, it becomes a dangerous projectile that could always ram into something, like our space station.”
The UNU Institute for Environment and Human Security, in its Interconnected Disaster Risks 2023 report, included space debris among its six risk tipping points.
The report, released in February, found that there were 35,150 tracked objects in orbit in 2023. Just 25 percent of these were working satellites while the rest were considered junk, including broken satellites and rocket parts.
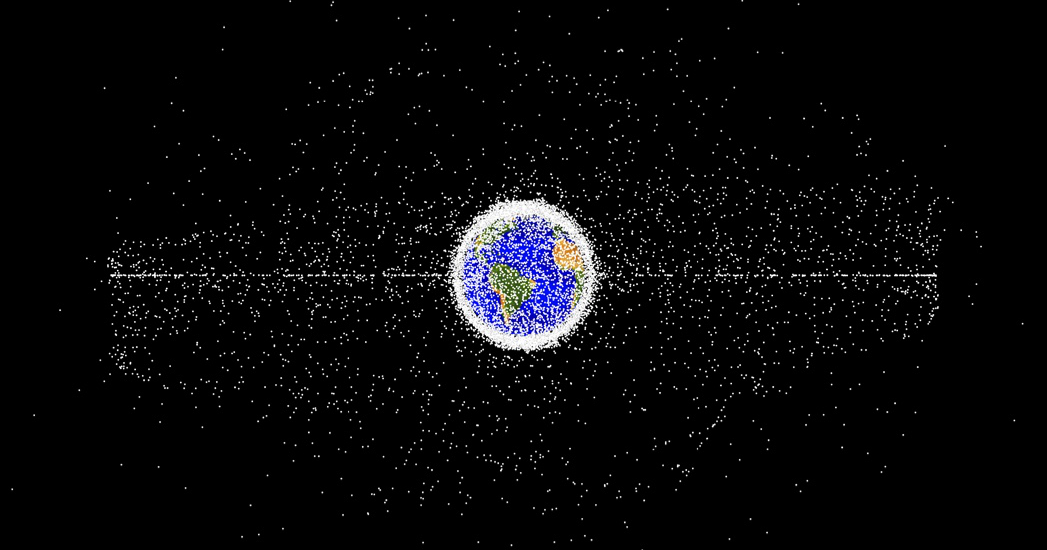
This illustration from the Interconnected Disaster Risks 2023 report of the UNU Institute for Environment and Human Security shows computer-generated images of objects in Earth orbit being tracked as of January 2019. Approximately 95% of the objects in the illustration, according to the report that included space debris among its six risk tipping points. (Credit: UNU-EHS)
As objects in space travel at speeds exceeding 25,000 km per hour, any collision may be “catastrophic,” and even the smallest objects can cause significant damage, according to the same UNU-EHS report.
Asked about the Artemis Accords, which Saudi Arabia signed in 2022, the NASA administrator described it as “a common sense set of principles of the peaceful uses of space.
“For example, in the Artemis Accords, we have that you would come to the aid and assistance of a nation that would have a problem in space,” he said.
“We would develop common elements so that you could help each other out, perhaps remotely in space. But, basically, the thrust of it is the peaceful use of space.”
Saudi Arabia is the 21st country globally and the fourth Middle Eastern nation to sign the Artemis Accords, which set out common principles, guidelines and best practices to ensure safe, peaceful and sustainable space exploration.
Nelson’s visit to the Kingdom is intended to explore future collaboration between the US space agency and key government officials, while also emphasizing the significance of civil space cooperation in the broader US-Saudi relationship
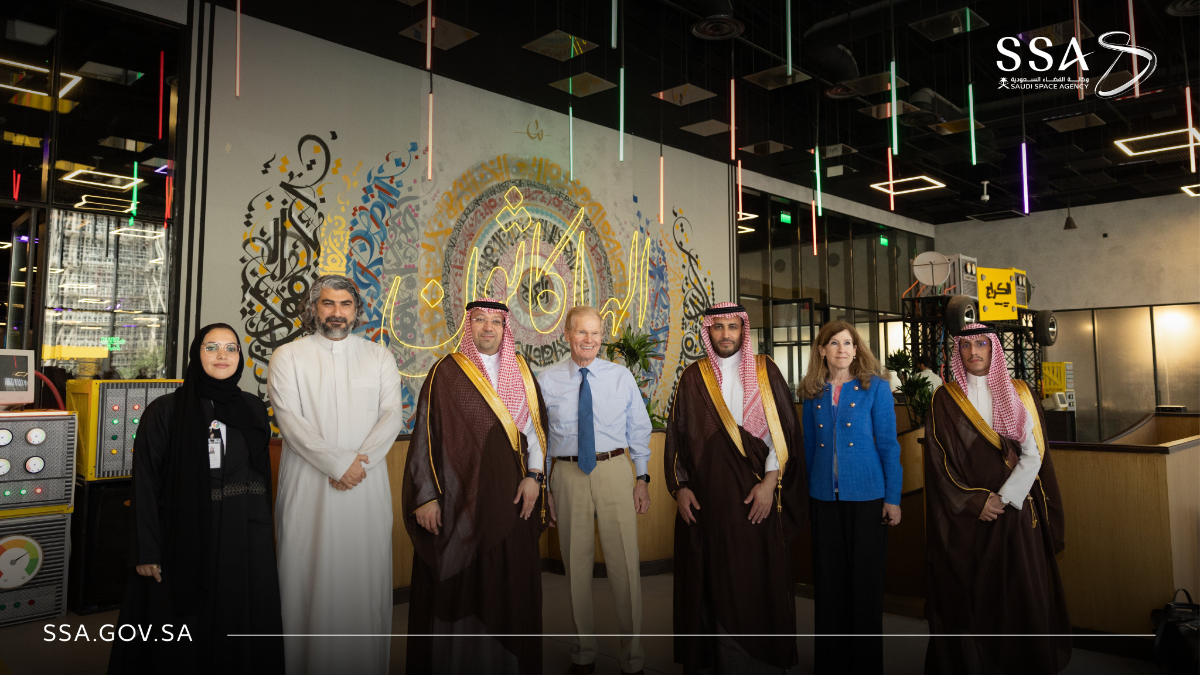

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson’ and key Saudi government officials explored future collaboration between the US space agency and the Kingdom's space agency. (
The Saudi Space Agency was launched by royal decree in December 2018 to accelerate economic diversification, enhance research and development, and raise private-sector participation in the global space industry.
Since its launch, the Kingdom’s state-funded space program has struck deals with several of the world’s established space agencies, astronautical companies and top universities to benefit from advanced technological cooperation.
Saudi Arabia’s space industry holds great potential for growth after recording $400 million in revenue in 2022, according to a report by the Saudi Communications, Space and Technology Commission published late last year.
The global space economy is projected to expand to $1.8 trillion by 2035, marking a threefold increase from $630 billion in 2023, according to research published by the World Economic Forum in April.
A growing number of businesses across sectors including agriculture, construction, insurance and climate-change mitigation, are expected to drive the new and expanding space economy.
This rapid surge is being driven by reduced costs and broader accessibility to space-enabled technologies, encompassing various commercial sectors such as communications, positioning, navigation, timing, Earth observation services, tourism and manufacturing.
While state-sponsored investments will remain the cornerstone of the industry, enhanced collaboration between various stakeholders across public and private sectors will be increasingly important to fully realize the sector’s potential in the future.

































