DUBAI: Is there any hope for the children of Gaza amid the ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict, restrictions on aid access, and a looming famine in the north of the enclave?
According to UN Children’s Fund spokesperson James Elder, who recently toured the length of Gaza, only an immediate ceasefire can turn the humanitarian situation around.
Appearing on the Arab News current affairs show “Frankly Speaking” via video link from Rafah, on the Gaza-Egypt border, Elder said that opening multiple entry points and delivering sufficient aid could help save the most vulnerable, including the one in three children under the age of two in the north of Gaza who are suffering from acute malnutrition.

Speaking to “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen from Rafah, James Elder lauded the irreplaceable role played in the humanitarian response by UNRWA and highlighted Israel’s unmet obligations under international law to allow sufficient aid to enter Gaza. (AN photo)
“The ability to scale out, to get aid across an area, is what UNICEF does,” Elder told “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen.
“We have the world’s largest humanitarian supply hub in Denmark. We airlift, we ship, we do everything. We have warehouses here in the region as well. So, multiple warehouses … consistently ready to bring in that aid.”
However, until Israel lifts its restrictions on how much aid is permitted to enter the embattled enclave, enabling UNICEF and other humanitarian agencies to deliver much-needed relief, many fear the extreme food insecurity already endured by Palestinians will escalate into a full-blown famine.
In the wide-ranging interview, Elder described the irreplaceable role played in the humanitarian response by the cash-strapped UN Relief and Works Agency, UNRWA, and highlighted Israel’s unmet obligations under international law to allow sufficient aid to enter Gaza.
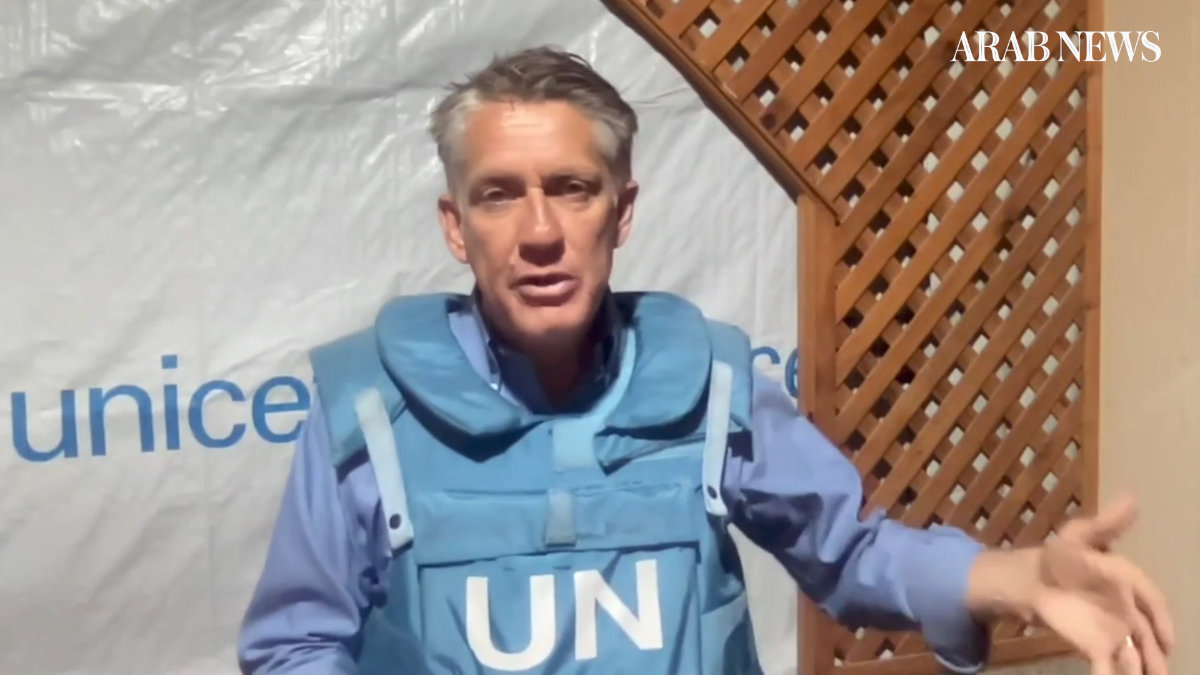

Speaking to “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen from Rafah, James Elder lauded the irreplaceable role played in the humanitarian response by UNRWA and highlighted Israel’s unmet obligations under international law to allow sufficient aid to enter Gaza. (AN photo)
Elder also spoke about the “annihilation” of Gazan cities and the threats posed to UN workers and aid recipients amid the fighting, which had made the Palestinian territory “potentially the most dangerous place on the planet.”
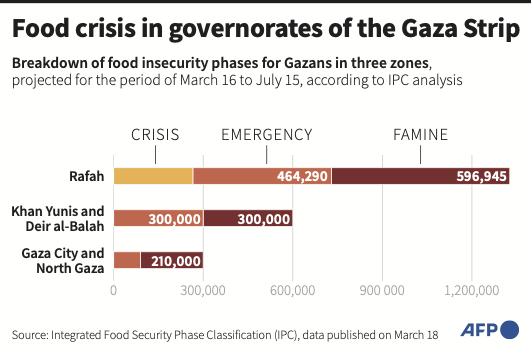
A UN-backed report released in March warned that unless the hostilities are halted and unrestricted aid is allowed to flow into the Gaza Strip, famine could occur by the end of May. The report said 70 percent of Gaza’s 2.3 million-strong population is experiencing catastrophic levels of hunger and food insecurity.
The International Court of Justice at The Hague warned on Thursday that “famine is setting in” as a result of Israel’s continued restrictions on the flow of aid.
In a unanimous ruling, the UN’s highest court ordered Israel to take “all the necessary and effective action” to ensure basic food supplies reach the Palestinian people without delay.
And while saving people in Gaza from starvation is achievable, it will take longer to address “things like disease, the devastation to the health system, to hospitals, to water systems, to sewerage,” said Elder.
Since Israel launched its Gaza operation in retaliation for the Hamas-led attack of October 7, the enclave has become a graveyard for at least 13,000 children, according to UN figures.
Acute malnutrition now affects 31 percent of children under the age of two in the northern governorates, while at least 23 children have already died of starvation and dehydration.
Creating these conditions could amount to a war crime, the UN human rights chief, Volker Turk, told the BBC on Thursday, adding that there was a “plausible” case that Israel was using starvation as a weapon of war in Gaza.
“International humanitarian law is very clear on proportionalities and on what warring factions can do,” said Elder. “We have seen so many breaches in this war, and for children it seems to make no difference right now. Children don’t understand whether international law is being abided by or not.
“Right now, all they are doing is facing the severity of something that no child ever, ever should have to endure.”
In the initial months of the conflict, the bulk of aid distribution and relief work was carried out by UNRWA, which has supported Palestinian refugees in Gaza, the West Bank, Jordan, Syria and Lebanon since 1949.
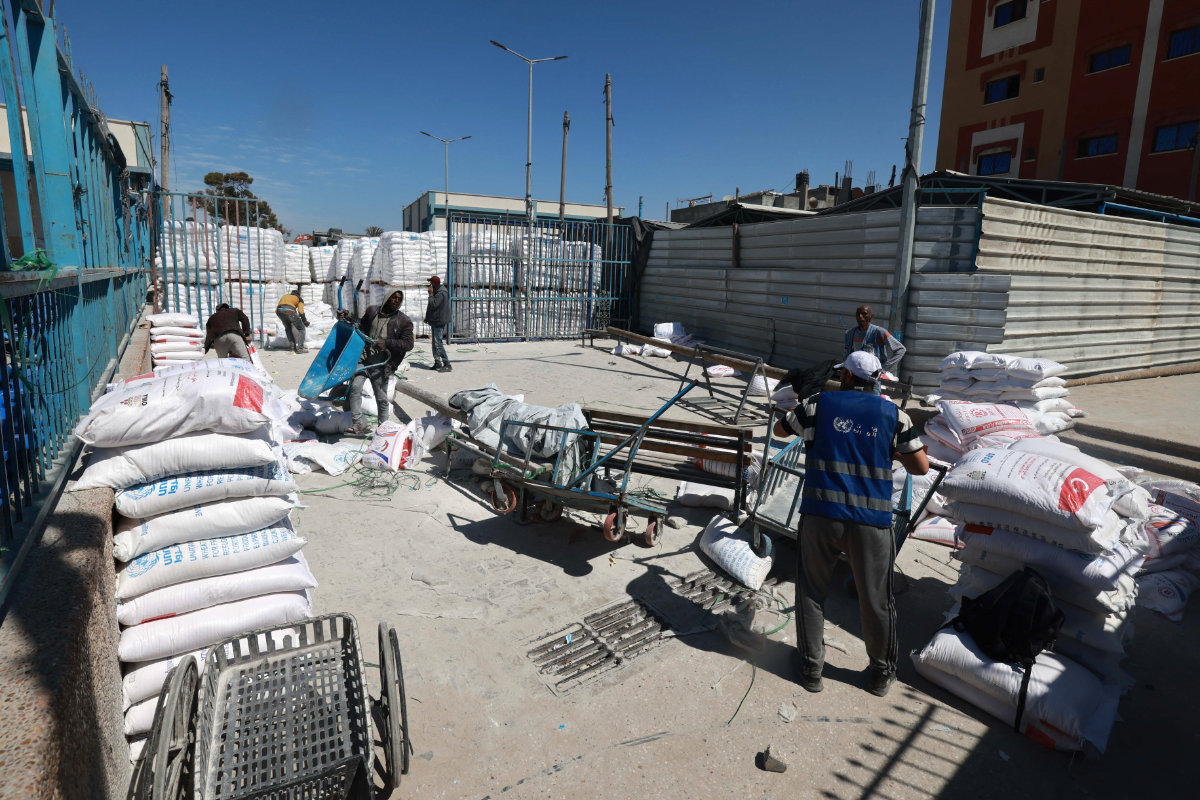

UN workers prepare humanitarian food aid at a UNRWA warehouse/distribution center in Rafah for distribution to Palestinian refugees amid continuing battles between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas. The warehouse was partially hit by an Israeli strike on March 13, 2024. (AFP)
However, in January, more than a dozen countries suspended funding for UNRWA after Israel claimed that 12 of the UN agency’s staff had participated in the October 7 attack, while 450 others were “military operatives in terror groups.”
Although an internal investigation and a separate independent investigation have been launched to examine the allegations, the bulk of UNRWA’s funding is still yet to be restored, bringing its operations in Gaza to the brink of collapse.
Elder said UNICEF and other aid agencies are in no position to assume UNRWA’s responsibilities if it goes under.
“UNRWA is the backbone of humanitarian aid in the Gaza Strip,” he said. “UNRWA has got thousands and thousands of very brave workers, of teachers, of doctors, of pharmacists, of nurses, of you name it.
“UNICEF has deep specialties in child protection and nutrition and so forth, but in terms of that full manpower across the Gaza Strip, the people of Gaza need UNRWA.”
He added: “Fifty percent of food aid getting to those civilians in the north was delivered by UNRWA. That has now been blocked. That’s fast-tracking catastrophe.”

Israeli demonstrators gather by the border fence with Egypt at the Nitzana border crossing in southern Israel on February 18, 2024, as they attempt to block humanitarian aid trucks from entering into Israel on their way to the Gaza Strip. (AFP)
Gaza has become an extremely dangerous place for aid agencies to operate.
“People have been killed receiving aid, aid workers — more aid workers, more of my United Nations colleagues killed in this war than in any time since the advent of the United Nations. This is the reality that people are dealing with,” said Elder.
“Now the UN does work in very dangerous places. That’s what we do. Afghanistan, Sudan, Ukraine, here in Gaza. But we need to be very clear. International humanitarian law is unequivocal. Israel has a legal obligation to facilitate aid, not just getting in, but then to ensure it is safely distributed to those most in need.”
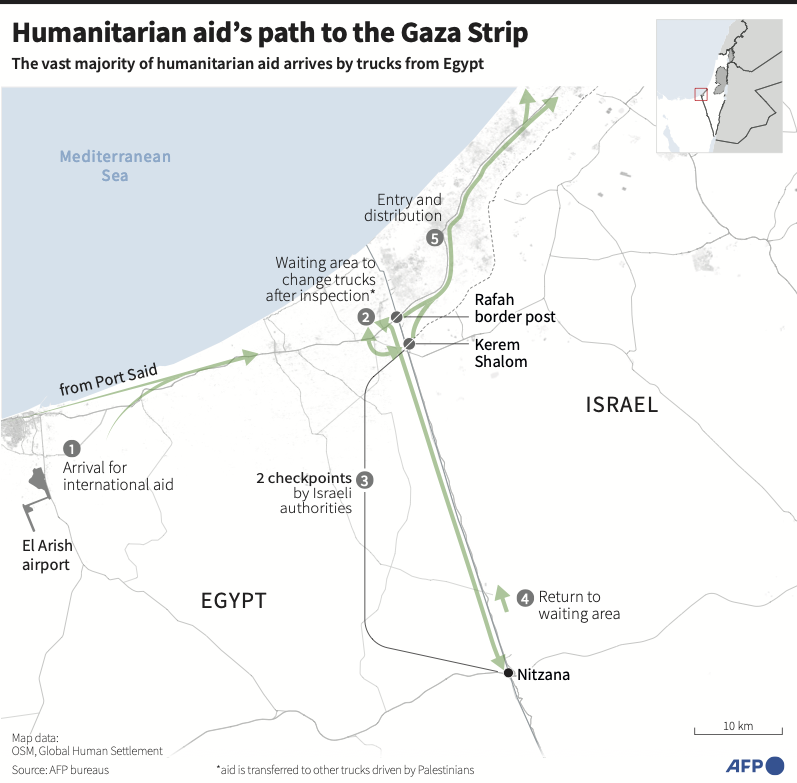
During his journey along the length of the Gaza Strip, Elder was appalled by the scale of the humanitarian catastrophe. While traveling through the Rafah border crossing from Egypt, he saw “hundreds of trucks blocked there with life-saving aid on the wrong side of the border.”
“We are not getting nearly enough aid in,” he added.
Later, during his visit to northern Gaza, he saw “people hanging on to life, children and families who urgently need food.” And yet, “there are crossings there that could be opened, old crossings where you would have aid within 10 or 15 minutes.”
With road access into Gaza limited by Israeli forces, aid agencies have been examining options for a maritime corridor. In mid-March, the Open Arms set sail from Cyprus towing 200 tonnes of flour, protein, and rice bound for Gaza.
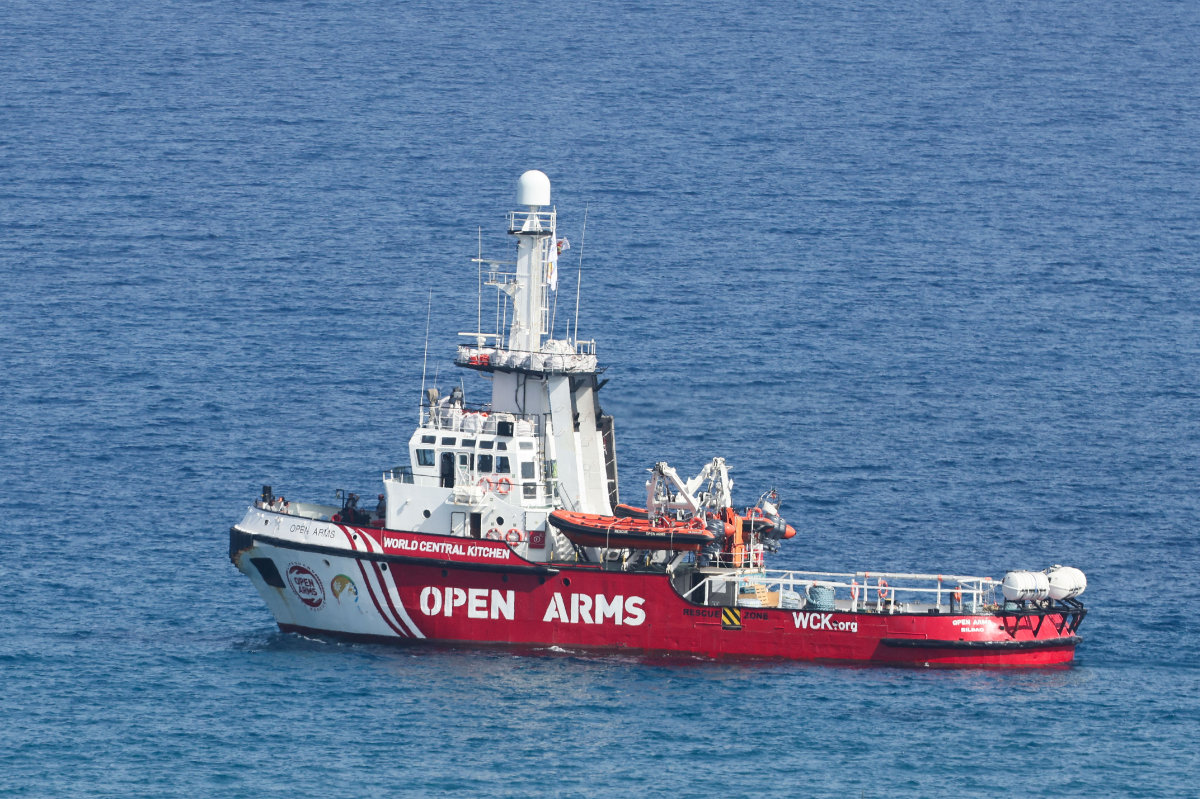

The Open Arms, a rescue vessel owned by a Spanish NGO, departs with humanitarian aid for Gaza from Larnaca, Cyprus, on March 30, 2024. (REUTERS)
“Any aid is useful aid, but the ship had the equivalent of around 12 trucks,” said Elder. “There’s 50 times 12 trucks on the other side of the border.”
Another aid access workaround pursued by the US, Jordan and Egypt is airdrops, parachuting aid into Gaza.
However, airdrops are usually used “when people are massively cut off from humanitarian assistance — a flood or a natural disaster,” said Elder. “Here, they’re not cut off. There’s a road network. Road is the efficient, effective way. Roads are what will turn around this humanitarian catastrophe with a ceasefire.”
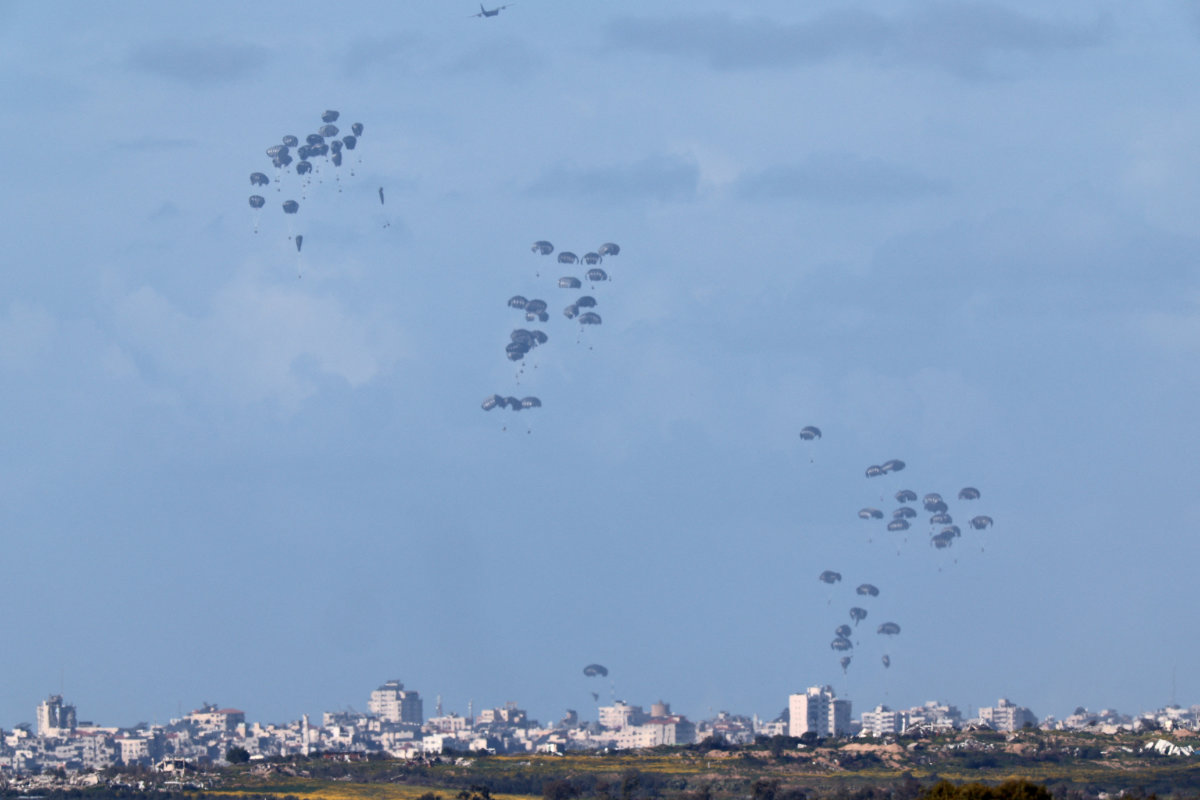

Jordan, along with the US, German and other European countries had been delivering food aid to Gaza by parachutes, but the scale of starvation in the Israeli-besieged enclave is barely enough, according to humanitarian agencies. (AFP)
Echoing criticism of Israel’s limits on the flow of aid, Elder said: “We need to be very clear. International humanitarian law is unequivocal. Israel has a legal obligation to facilitate aid, not just getting in, but then to ensure it is safely distributed to those most in need.”
On March 25, the UN Security Council passed a resolution demanding an immediate ceasefire in Gaza for the Islamic holy month of Ramadan, which ends in less than a fortnight.
Elder said the resolution must be “substantive and not symbolic” because a ceasefire “allows the United Nations to flood the Gaza Strip with humanitarian aid and we can turn this imminent famine around.”
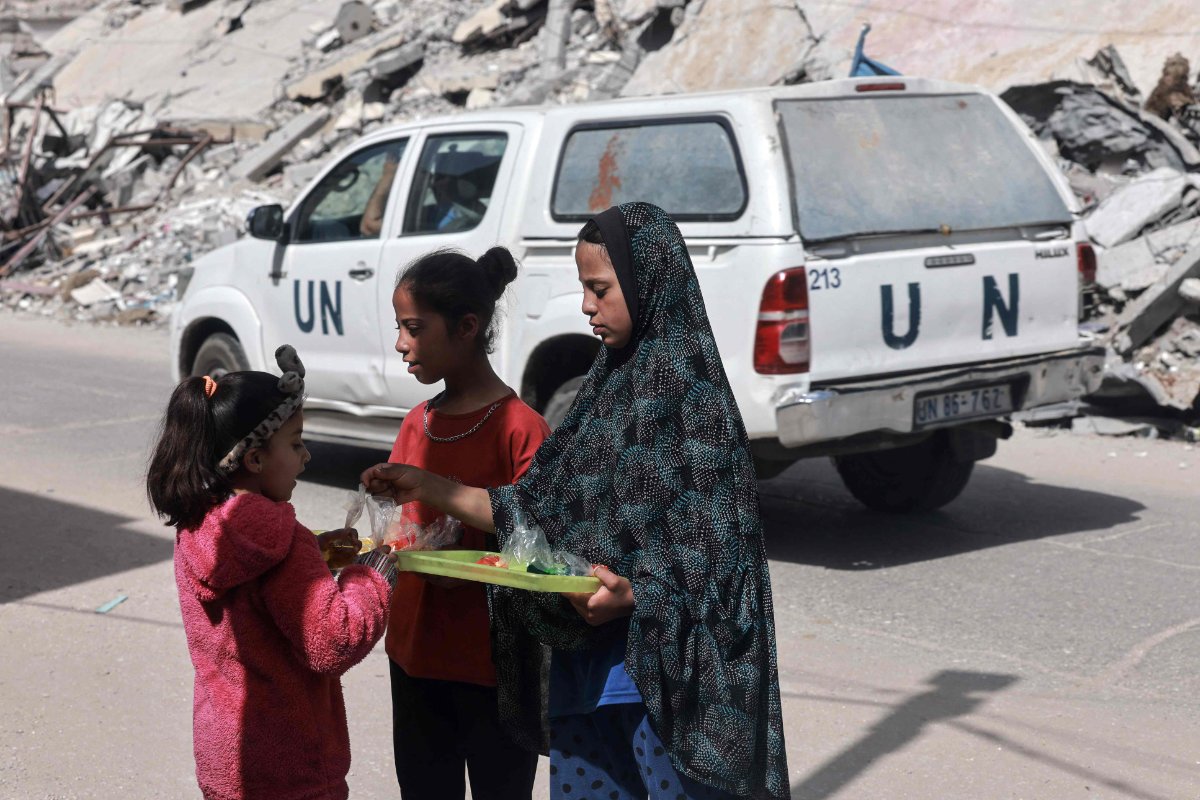

A United Nations vehicle drives by as Palestinian girls share a food ration in Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip on March 31, 2024. (AFP)
A ceasefire, said Elder, would also allow Israel to bring home its citizens who have been held hostage in Gaza since October 7. “There are children here somewhere underground or whatever horrendous torment they are enduring,” he said. “End the torment, get hostages home.”
He added: “A ceasefire means families — a mother and a child can go to bed with absolute certainty that they will wake up. They haven’t had that for many months.”
In November and December last year, Elder said he visited Al-Nasr Hospital in Khan Younis, where the “incredible” health workers were “doing 24-36-hour shifts in a war zone.”
“They were doing the work that they knew they love to do, and they were born to do as some had said, but they were terrified because their families were outside.”
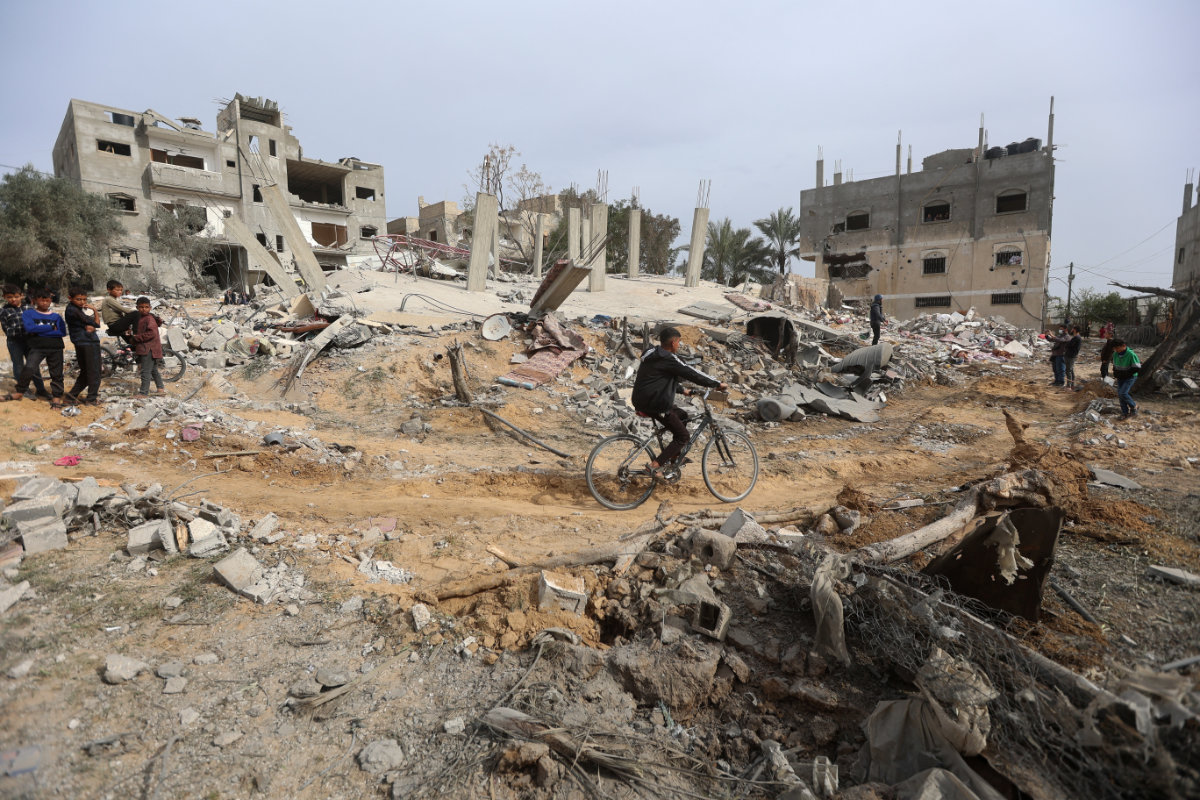

Palestinians inspect the site of an Israeli strike on a house in Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip on March 29, 2024. (REUTERS)
Returning to Khan Younis in recent days, Elder said: “I went through it now and it’s just annihilated, street after street, rubble everywhere. I have not seen that level of devastation, which in my mind segued to here, to Rafah, and why we cannot see that happen here.”
Now, it is as though Khan Younis and Gaza City no longer exist. “Just cracked rubble and steel as far as you can see and stunned looking people, because home after home has been destroyed,” he said.
Rafah, meanwhile, “is a city of tents. It’s a city of children. This is where families were meant to go to stay safe. And there’s a desperation here, but there is a solidarity. People do what they can for each other.”
He added: “I’ve been across the Gaza Strip. In the north is a level of suffering that I can’t say defies words, but it is getting to a point where, well, we’re seeing children die of malnutrition, of dehydration.”
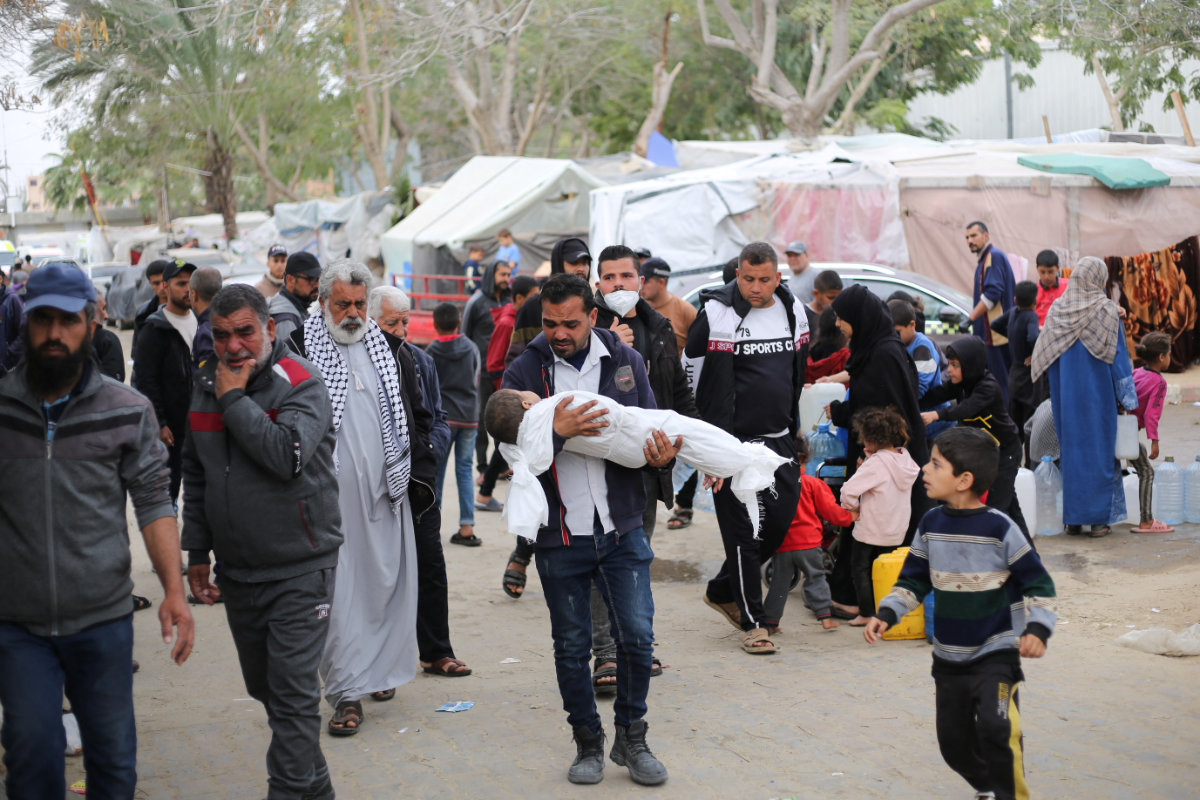

A mourner carries the body of a Palestinian child killed in an Israeli strike in Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip on March 29, 2024. (REUTERS)
“You see parents in tears over a child’s cot, a child who is paper thin. This is a mother who’s done everything she can to protect her child from these relentless … bombardments. And now she’s trying to protect her child from starvation.
“These mothers and fathers are learning that the real decisions about the safety of their children are being made by people elsewhere. So, there is a level of stress and anxiety across the Gaza Strip.”
Elder said the situation in Gaza “speaks to the mental trauma here of more than a million children.
“As a child psychologist said to me, we are in uncharted territory here when it comes to the mental health of girls and boys in Gaza.”


























