BENGALURU, India: Abinaya Tamilarasu said her four cows are part of the family. She has a degree in commerce from a local college, but prefers being home milking cows and tending to her family’s land.
“Our family cannot let farming go, it’s a way of life for us,” said the 28-year-old, who lives on her family farm in India’s southern Tamil Nadu state. Even when she could be making more money elsewhere, she said she’s “still happy we have our cows.”
India is the world’s largest milk producer, and is home to 80 million dairy farmers who made 231 million tons of milk last year. Many farmers, like Tamilarasu, only have a few cows, but the industry as a whole has 303 million bovine cattle like cows and buffalo, making it the largest contributor to planet-warming methane emissions in the country. The federal government has made some positive steps to reduce methane, but wants to focus emissions cuts elsewhere, like by moving to renewable energy, saying most methane emissions are a fact of life. But experts say the industry can and should make more reductions that can quickly limit warming.
India is the third largest emitter of methane in the world, according to figures published earlier this month by the International Energy Agency, and livestock are responsible for about 48 percent of all methane emissions in India, the vast majority from cattle. Methane is a potent planet-warming gas that can trap more than 80 times more heat in the atmosphere in the short term than carbon dioxide.
The Indian government has not joined any global pledges to cut methane emissions, which many see as low-hanging fruit for climate solutions, as methane emissions only last in the atmosphere for about a dozen years, compared to CO2 that can linger for a couple of hundred years.
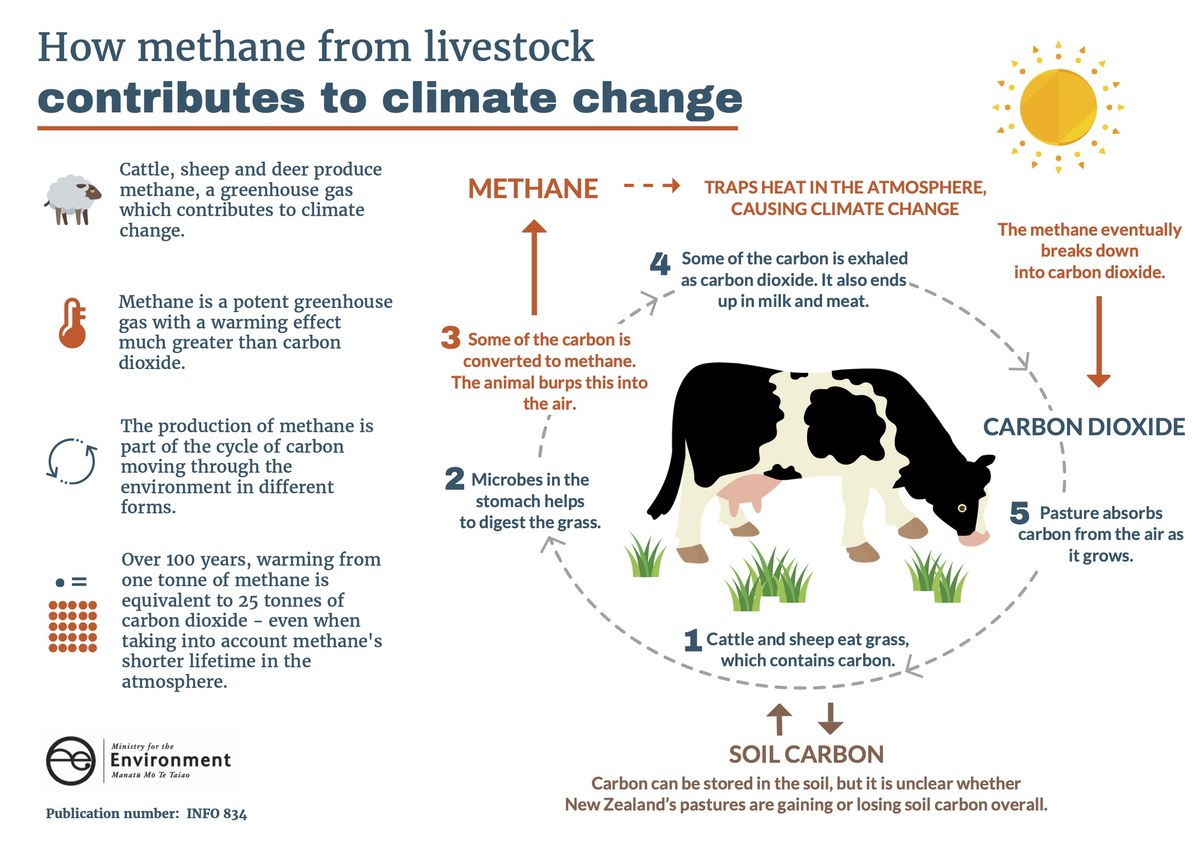
Infographic courtesy of New Zealand's Ministry for the Environment
But there’s some work on methane reduction in agriculture on the national level: The government’s National Dairy Development Board, which works with over 17 million farmers across the country, is looking into genetic improvement programs to provide more nutritious feed to livestock which would make cows more productive, meaning each farmer would need fewer cows to produce the same amount of milk. Studies by the NDDB show that emissions are reduced by as much as 15 percent when a balanced diet is provided to the animals.
The board is also looking into reducing crop burning, a high-emitting practice that some farmers use to clear their lands, by feeding those crops to cows.
“Climate-smart dairying is the need of the hour,” said Meenesh Shah, the board’s chairman.
Vineet Kumar, from the New Delhi-based Center for Science and Environment, agreed that good quality feed can help lower emissions. He also said encouraging more local breeds that emit less can help. “These solutions can be a win-win for everyone,” he said.
But Thanammal Ravichandran, a veterinarian based in the southern Indian city of Coimbatore, noted that there’s currently a shortage of feed in India, so farmers give their cattle whatever they can, which is mostly lower quality and higher emitting.
“Farmers are also not able to invest in better quality feed for their cattle,” she said. To get better, and more affordable feed, dairy farmers need more government support, she said.
Whatever measures are taken to reduce methane emissions, experts note that it should have minimal impact on farmers’ livelihoods, and should account for the ways people raise their livestock.
“Livestock have been closely integrated within the Indian farming system,” said Kumar, meaning any drastic changes to farming methods would have severe effects on farmers. He added that efforts to reduce emissions shouldn’t reduce the use of cow manure as fertilizer on India’s farms, as chemical fertilizers emit nitrous oxide, an even more potent greenhouse gas.
But looking at India’s methane emissions as a whole could provide some more obvious solutions to slashing the gas, said Bandish Patel, an energy analyst at the climate thinktank Ember. Focusing on the energy sector is an easy win for targeted reduction of methane emissions, he said.
“You look at agriculture, those emissions are very dispersed in nature, whereas, with oil, gas and coal mining, there are very pointed sources from which you can basically reduce methane going forward,” he said.
Shah from the NDDB added that India’s high agricultural emissions must be considered in the context of the country being home to the world’s largest cattle population, the largest producer of milk, and the largest rice exporter, as rice production also produces significant methane emissions.
“In this light, India’s agriculture sector emissions must be considered significantly low,” Shah said. Because of its large population, India’s per capita emissions are well below average.
For dairy farmers like Tamilarasu, better welfare for her cows and programs for farmers to have better practices are welcome, but she won’t be leaving her cows for the climate any time soon. She plans to continue dairy farming for the foreseeable future.
“The way we see it, our cows and us support each other. If we can make their lives better, they will make ours better too,” she said.

























