DUBAI: Iran and the US are engaged in outright proxy warfare, the effects of which are playing out across the Middle East region. Although neither side appears to be looking for a direct confrontation, vulnerable Arab countries with split political loyalties are paying the biggest price.
That seems to be the consensus view of Middle East experts as low-intensity wars rage on in several parts of the region in addition to the full-on Gaza conflict.
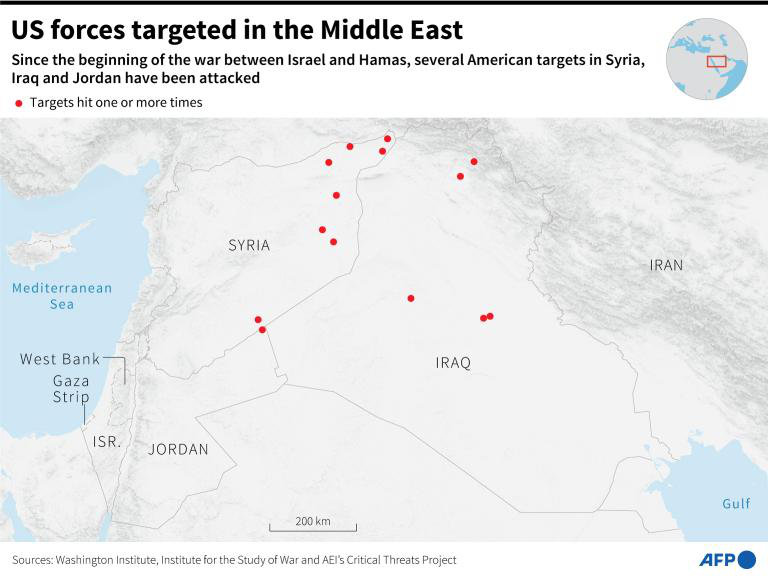
Since Oct. 7 last year, Iran-backed militias have mounted more than 170 attacks on US military bases and assets in Syria, Iraq and Jordan in response to US support for Israel in the Israel-Hamas war, prompting American retaliation.
Meanwhile, Iran’s Houthi allies in Yemen have launched repeated attacks on commercial and military shipping in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, likewise prompting retaliatory strikes by the US and UK on militia targets.
While analysts believe the US and Iran are unlikely to become embroiled in a direct conflict, attacks by Iranian proxies are expected to occur for as long as Israel’s military campaign in Gaza continues.
Some experts think Iran is acutely aware of the Biden administration’s fear of a regional escalation and has sought to exploit this fact as a means of influencing the course of the war in Gaza.
Ali Alfoneh, a senior fellow at the Arab Gulf States Institute in Washington, believes Iran is trying “to instrumentalize that fear by directly ordering, indirectly encouraging, or acquiescing to proxy attacks against Israel, the US, and international shipping.”

This photo released by the Houthi Media Center shows the Iran-backed Houthi forces boarding the cargo ship Galaxy Leader on Nov. 19, 2023, in the Red Sea off the coast of Yemen. (Handout via AP)
In this way, Iran “hopes a terrified Biden administration will increase pressure on Israel to end the war before total destruction of Hamas,” he told Arab News.
However, this proxy war is playing out on the sovereign territories of Syria, Iraq, Jordan, and Yemen — all nations that can ill afford to be swept up in a regional conflict. Some commentators say Arab lives in these countries are being treated as expendable.
“I think the attacks signal bloody bargaining between America and Israel on one side and Iran on the other,” Eyad Abu Shakra, a journalist at Asharq Al-Awsat, told Arab News.

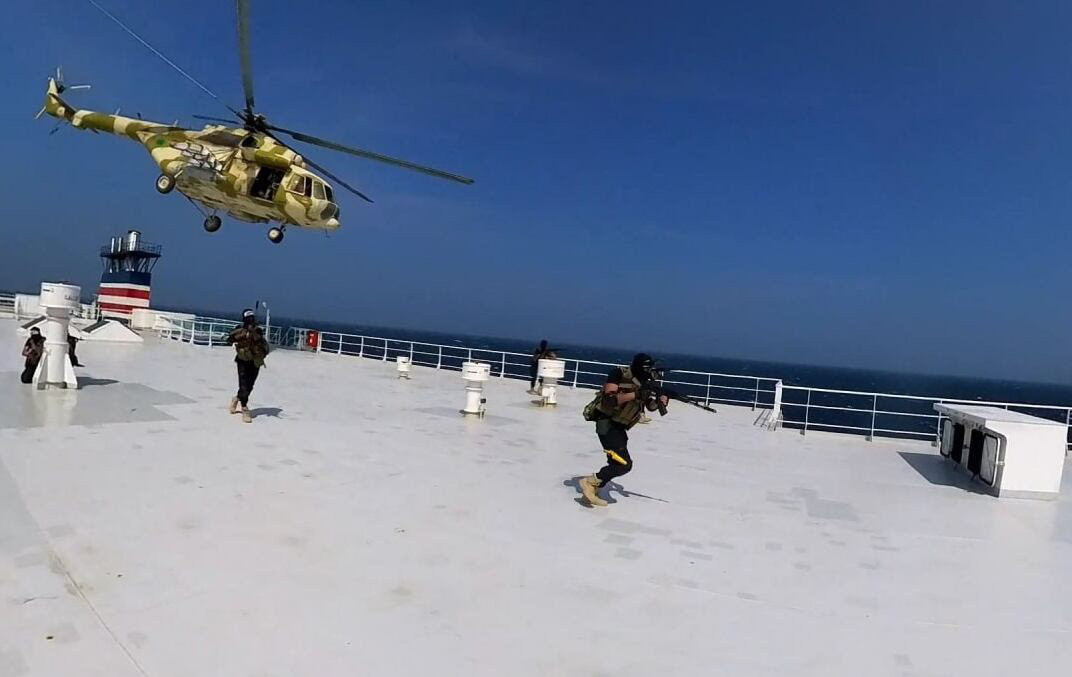
US soldiers patrol the town of al-Qahtaniyah in Syria's northeastern Hasakeh province near the Turkish border. (AFP/File)
“I don’t think there is any ‘war of survival’ or a ‘war of elimination’ between the two camps, the Israeli-American camp and the Iranian camp. They are bargaining, as if in a bazaar, but with blood. The Iranians are fighting the Americans with Arab lives and vice versa.”
This bargaining, as it were, has the potential to get out of hand, however.
On Jan. 28, US forces stationed at Tower 22, a remote installation in Jordan, close to the Syrian and Iraqi borders, came under drone attack, leaving three US soldiers dead and 34 wounded.
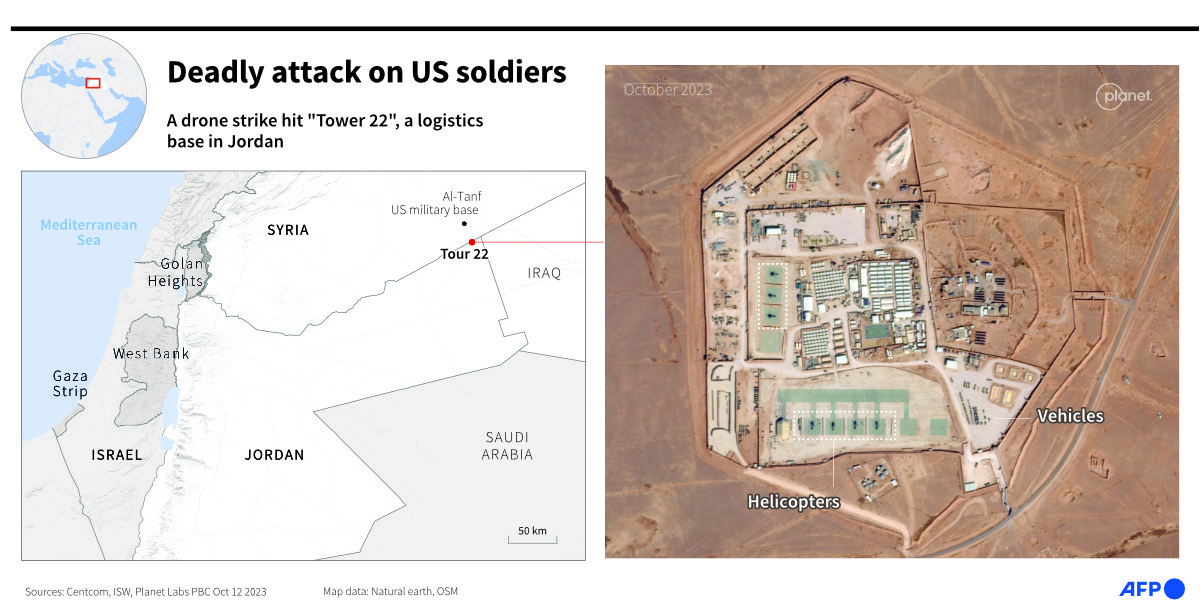
US President Joe Biden said the drone attack was launched from Iraq by an Iran-backed militia. He vowed to retaliate at a time and in a manner of America’s choosing.
On Feb. 3, the US military launched an air assault on 85 targets at seven locations across Iraq and Syria including command and control headquarters and weapon storage sites used by Iran-backed militias and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
This was followed on Feb. 7 by a drone attack on eastern Baghdad that killed Abu Baqir Al-Saadi, commander of Kataib Hezbollah, the Iraqi militia that Washington had deemed responsible for the attack on US troops in Jordan.
Iran of course denies links to any militias in the Middle East. For instance, in a Jan. 29 letter to the UN Security Council, Amir Saeid Iravani, Iran’s ambassador to the UN, said: “There is no group affiliated with the Islamic Republic or Iran’s armed forces, whether in Iraq, Syria, or elsewhere that operates directly or indirectly under the control of the Islamic Republic of Iran or acts on its behalf.
“Therefore, the Islamic Republic of Iran is not responsible for the actions of any individual or group within the region.”

Iran denies links to any militias in the Middle East. But to fighters and supporters of Lebanon's Hezbollah, there is no hiding what is obvious. (AFP/File photo)
Some Republican lawmakers had exhorted the administration to authorize a direct strike against Iran, even if it risked sparking a wider escalation. Others accused Biden of responding too slowly and giving the enemy too much forewarning.
Wary about being dragged into another potentially open-ended Middle East war, especially during an election year, Biden has appeared keen to limit the scope of America’s retaliation.
“The Biden administration partially called the Islamic Republic’s bluff by harshly reacting to the killing of three American servicemen and women in Jordan, but publicly signaled that it would not target Iranian territory,” said Alfoneh.
“Retaliating for the loss of American life was a correct response, but the US would perhaps be better off keeping the Islamic Republic guessing about America’s retaliation, which may include Iranian territory in the future.”

US President Joe Biden has warned Iran to rein in its proxy militias or face American retaliation. (AFP/File)
Iran is likewise mindful of the potential blowback from its activities. But by operating through its network of proxies throughout the region, Tehran feels it can deny any involvement in attacks on Israel or US targets while reaping the benefits.
“After 1979, when Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini declared the export of the Islamic revolution, Iranians formed the IRGC,” said Abu Shakra.
“It was almost an open secret that they would fight their wars of negotiations with the Americans and Israelis in Arab cities rather than fight them in Iran’s cities.
“They eventually took over Beirut, Baghdad, Damascus and Sanaa, and now they are negotiating with the Americans and the Israelis through massacres, in which the Arabs are paying the price, not the Iranians.”
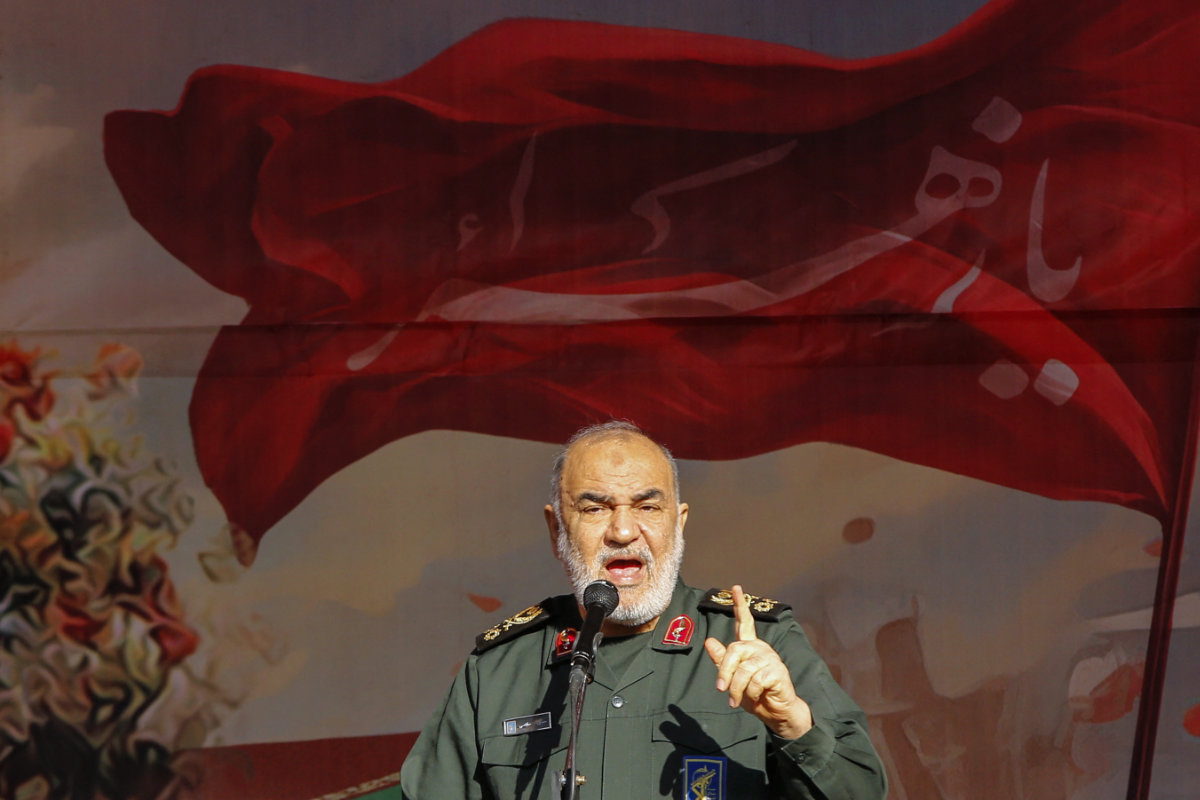

Hossein Salami, head of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. (AFP)
Nevertheless, according to analysts, Iran has sometimes overplayed its hand, leading to a more aggressive US response, as was the case when the administration of former President Donald Trump ordered the killing of Quds Force commander Qassem Soleimani in Jan. 2020, allegedly to stave off a planned attack on US forces in Iraq.
“They are reminded of the accepted bargaining limits,” said Abu Shakra. “The assassination of Qassem Soleimani, for example, was such a reminder and a big hit. Both America and Iran are still respecting ‘the rules of engagement.’”
The latest US retaliation does appear to have had an impact. On Feb. 12, the Pentagon announced there had been 186 US casualties in Iraq, Syria and Jordan since Oct. 18. A day later, on Feb. 13, it declared there had been no further attacks on US forces.
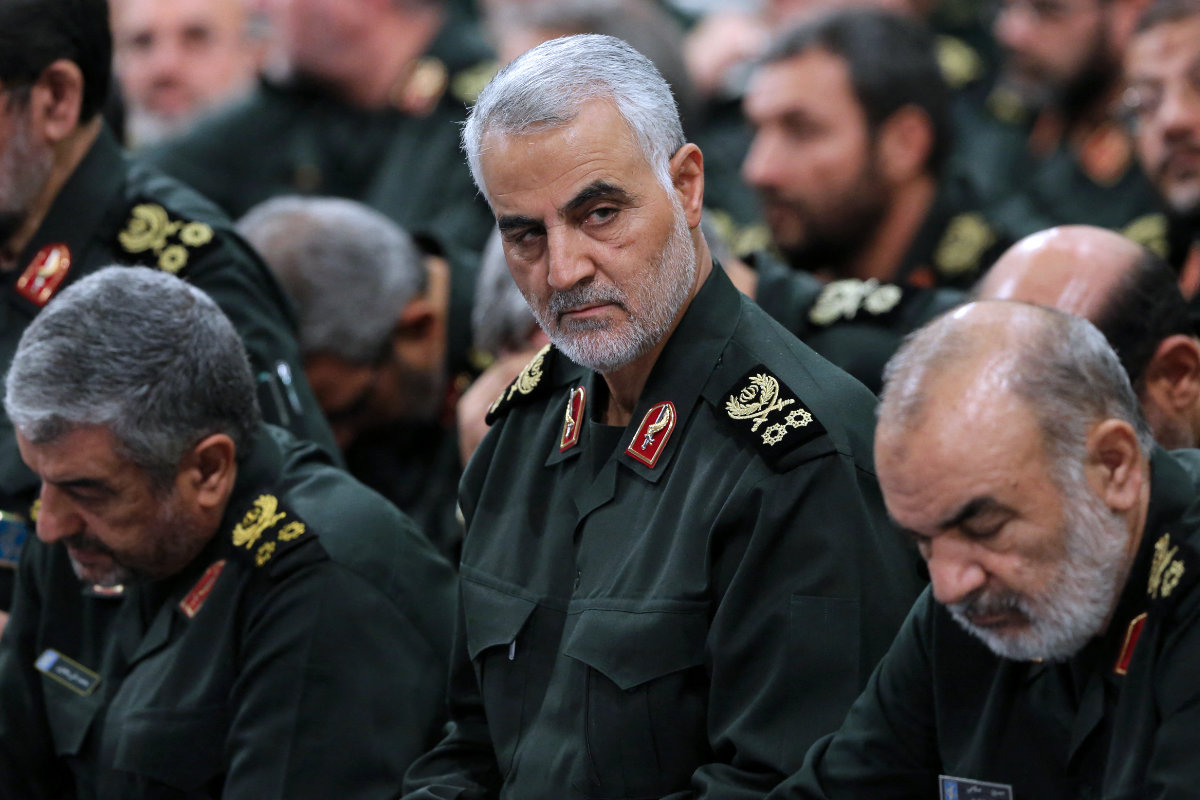

The killing of major general Qassem Soleimani, commander of Iran's Quds Force, by US forces in early 2020 has served notice to Iran's authorities that it does not pay to overplay their hands. (Tasnim News photo via AFP/File)
Washington is also likely in no hurry to attack Iran directly because the survival of the Islamic Republic has other uses. “It’s important to note that Iran is a sizable player whom the West can ‘use’ in any role,” said Abu Shakra.
“Whether Washington admits it or not, Iran is a very important bulwark against the rise of Sunni militant Islam. Iran is also a potential counterbalance against a nuclear Pakistan. Iran is an important bulwark against the expansion of the Chinese in the Gulf.
“No one has the strategic interest of destroying Iran. Neither America, nor Russia, nor India can ignore the role or influence of Iran.”
Critics of the Biden administration say its hesitance about a direct confrontation with Iran was demonstrated by its response to the Hamas-led attack on southern Israel on Oct. 7, including efforts through media leaks to play down an Iranian link and prevent a regional escalation.
INNUMBERS
• 269 People killed in Lebanon since violence erupted in October 2023.
• 40 Civilians are believed to be among the dead in Lebanon.
• 16 Israeli nationals were killed in the north, including 6 civilians.
When Israel began its retaliatory campaign in Gaza, the US said there was no proof that Iran was behind the Oct. 7 attack, said Abu Shakra. Then, within a week or two, the US said it did not want the conflict to spread.
“They wanted it to be limited,” he said. “The Americans did not want any involvement with the Iranian militias in Lebanon and Iraq. I think unless the Iranians overplay their cards and become too arrogant, the current fighting will remain limited to Iran’s Arab appendages.
“I think neither the US nor Israel nor the pro-Tehran Iraqi regime or Iran itself has any real interest in direct confrontation, which would be apocalyptic if it were to happen.”

Iran has little to gain from a direct conflict with the US and so it outsources its activities to proxies to tilt regional affairs in its favor.. (AFP/File)
Likewise, Alfoneh believes Iran has little to gain from a direct conflict with the US. Instead, it can outsource its activities to proxies to tilt regional affairs in its favor.
“The Islamic Republic achieved all of its objectives on Oct. 7,” said Alfoneh. “Hamas’ terrorist incursion into Israel shattered the myth of Israel’s invulnerability.
“Iran got even with Israel, which for years has bombed Iranian and allied positions in Syria, and even engaged in operations on Iranian soil, and the attack sabotaged diplomatic normalization between Saudi Arabia and Israel.”
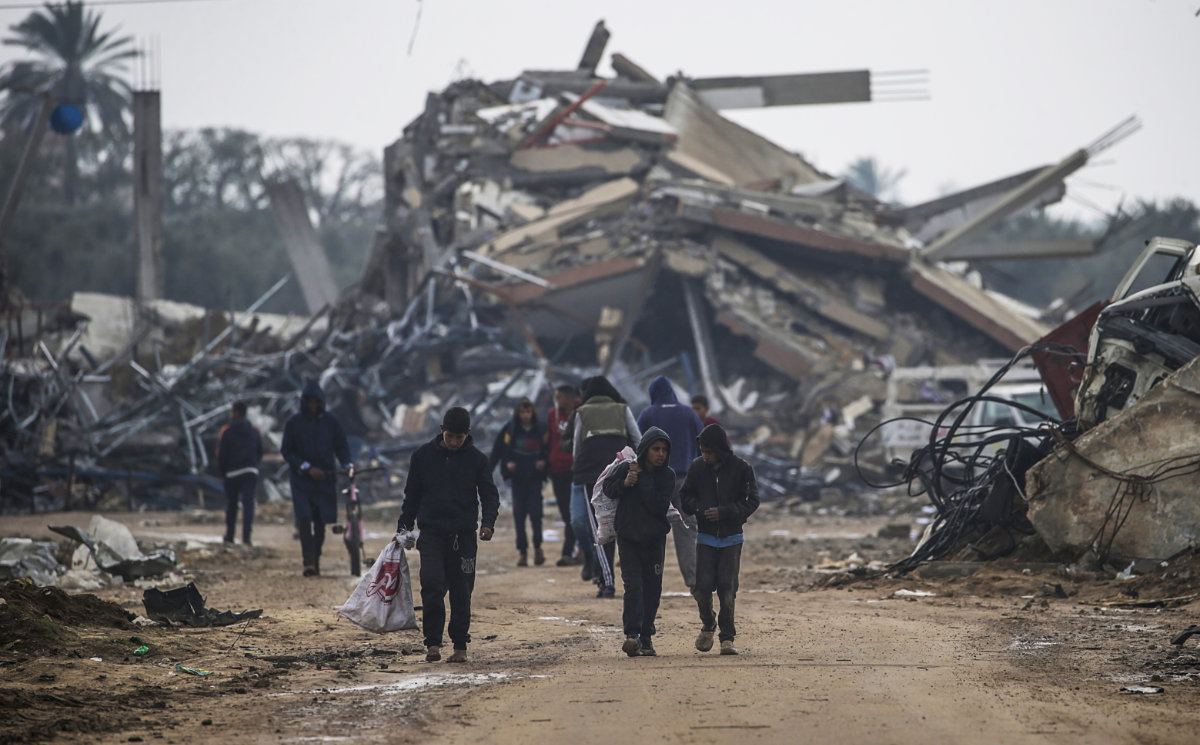

The fate of Hamas and Palestinian civilians is of no interest to Iran, which perceives them as expendable pawns, says Ali Alfoneh, a senior fellow at the Arab Gulf States Institute in Washington. (AFP photo)
The interests of the Palestinians, and indeed the populations of the wider Arab region caught in the crossfire, are thereby secondary to these geopolitical goals.
“The fate of Hamas and Palestinian civilians is of no interest to the Islamic Republic, which perceives them as expendable pawns in a grander chess game in the region,” said Alfoneh.
“Therefore, the Islamic Republic is not interested in spreading the war in Gaza, which may directly entangle Iran in a war with Israel and, possibly, with the US.”















