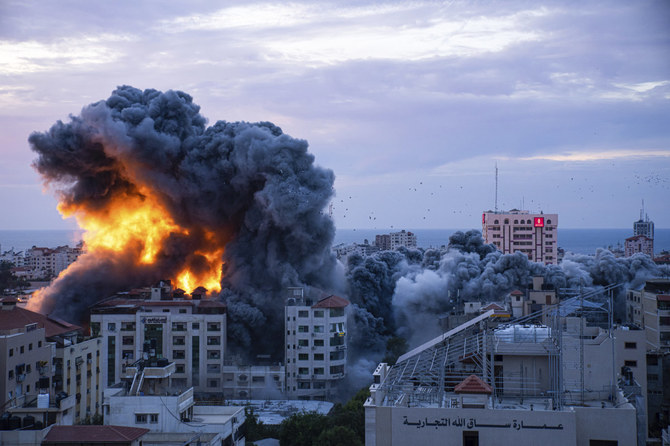
LONDON: Israel is sending mixed messages, announcing on the one hand that it is withdrawing some forces from Gaza, while also indicating the war will continue for many months, with a shift to more targeted operations and preparations for a full-scale conflict with Hezbollah.
Commentators are divided over the rationale behind the purported drawdown and the apparent signaling of a wider conflict, suggesting that the announcement could be the result of US pressure, economic necessity, or even an acceptance that the old strategy is simply not working.
In early January, a military spokesperson said the Israel Defense Forces would withdraw some units from the besieged Palestinian enclave as part of a shift toward “more targeted operations.”

Israeli military vehicles drive towards Gaza on January 13, 2024, amid the ongoing conflict between Israel and the Palestinian Islamist group Hamas. (REUTERS)
Daniel Hagari, an IDF spokesperson, later told The New York Times that “the war has shifted a stage, but the transition will be with no ceremony; it’s not about big announcements.”
Another IDF spokesperson later seemed to suggest that, at least for northern Gaza, the bombing campaign had reached its climax, claiming that Hamas in that part of the Gaza Strip had been “dismantled.”
Jordanian analyst Osama Al-Sharif told Arab News the scaling down had “yet to be verified,” but, should it occur, would likely equate to the withdrawal of roughly 7,000 troops.

Israeli security forces examine a road hit by a rocket fired from Lebanon, in Kiryat Shmona, northern Israel, on Jan. 11, 2024. (AP
According to one military statement, the withdrawal of five brigades was intended to give “training and rest” to those who had been engaged in the ground offensive since the war began on Oct. 7.
By citing the need for training, the statement made clear that any suggestions the war will be brought to an imminent end, at least without pressure, will not be forthcoming from the Israeli side.
Indeed, an official quoted by Reuters news agency said the next stage of the offensive would “take six months at least and involve intense mopping-up missions against the terrorists. No one is talking about doves of peace being flown from Shujayea.”

Members of the Palestinian Ezzedine al-Qassam Brigades take part in a demonstration by supporters of the Hamas movement in Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip, on October 27, 2022, a year before Hamas launched a massive attack against Israeli targets near the border. (AFP/File)
Al-Sharif said the withdrawals could mean “any number of things.” Since northern Gaza is now little more than “rubble,” there may simply be an insufficient number of targets to justify their continued presence, he said.
“It could also mean that some troops are being relocated to the north, where tensions are on the rise. It is clear that Hezbollah is not seeking an escalation and is aware of the terrible cost an all-out war with Israel could bring,” he added.
Shlomo Brom, a retired brigadier general previously in charge of Israel’s strategic military planning, suggested in a recent interview with Al Jazeera that the move could have been in response to US pressure.
Certainly, the withdrawal appears to have gone down well with the Biden administration.
Three US officials told Politico the move was seen as indicative of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu finally taking heed of Washington’s demands to reduce civilian casualties.
US success in convincing Netanyahu to shift from high-intensity operations to more targeted strikes would definitely help to explain the changes on the ground.
So far, however, this does not appear to have happened, sowing further confusion over the reasoning behind the troop withdrawal. Al-Sharif said it may be a sign the IDF has accepted that it has failed to achieve its stated war aims.
“We can say that the situation in Gaza remains a fluid one and Israel has not been able to achieve any of its declared targets,” he said. “But we can also say that it appears bent on carrying out mass destruction of the Gaza (refugee) camps as well as of Khan Younis. And while Hamas appears to be holding up quite well, this has been at a hefty cost to civilian life.”

Displaced Palestinians collect food at a refugee camp in Rafah, southern Gaza Strip, amid continuing battles between Israel and the militant group Hamas. (AFP/File)
Nevertheless, there have been other signals of shifting strategy, including a suspected Israeli drone strike in Beirut earlier this month that killed senior Hamas leader Saleh Al-Arouri.
This was followed by the killing of Wissam Al-Tawil, deputy head of Hezbollah’s Radwan Force, in a suspected Israeli drone strike on a vehicle in the southern Lebanese town of Khirbet Selm.
Then, on Jan. 9, Ali Hussein Burji, commander of Hezbollah’s aerial forces in southern Lebanon, was also killed in Khirbet Selm in another suspected Israeli airstrike.
FASTFACTS
Israel’s military confirmed on Jan. 8 that it was pulling thousands of troops out of the Gaza Strip.
Officials say the IDF is shifting from a large-scale ground and air campaign to a more targeted phase.
Israel says around 1,300 people, mostly civilians, died in Oct. 7 Hamas attack.
More than 23,350 people killed in Gaza in retaliatory military action by Israel.
These attacks did not come without consequences, however. In response, Hezbollah announced it had mounted a drone attack against an Israeli army base on Jan. 9, raising the possibility of a wider regional escalation.
Kobi Michael, a senior researcher at the INSS Tel Aviv University and Misgav Institute for National Security, is wary about the chances of an expanded war.
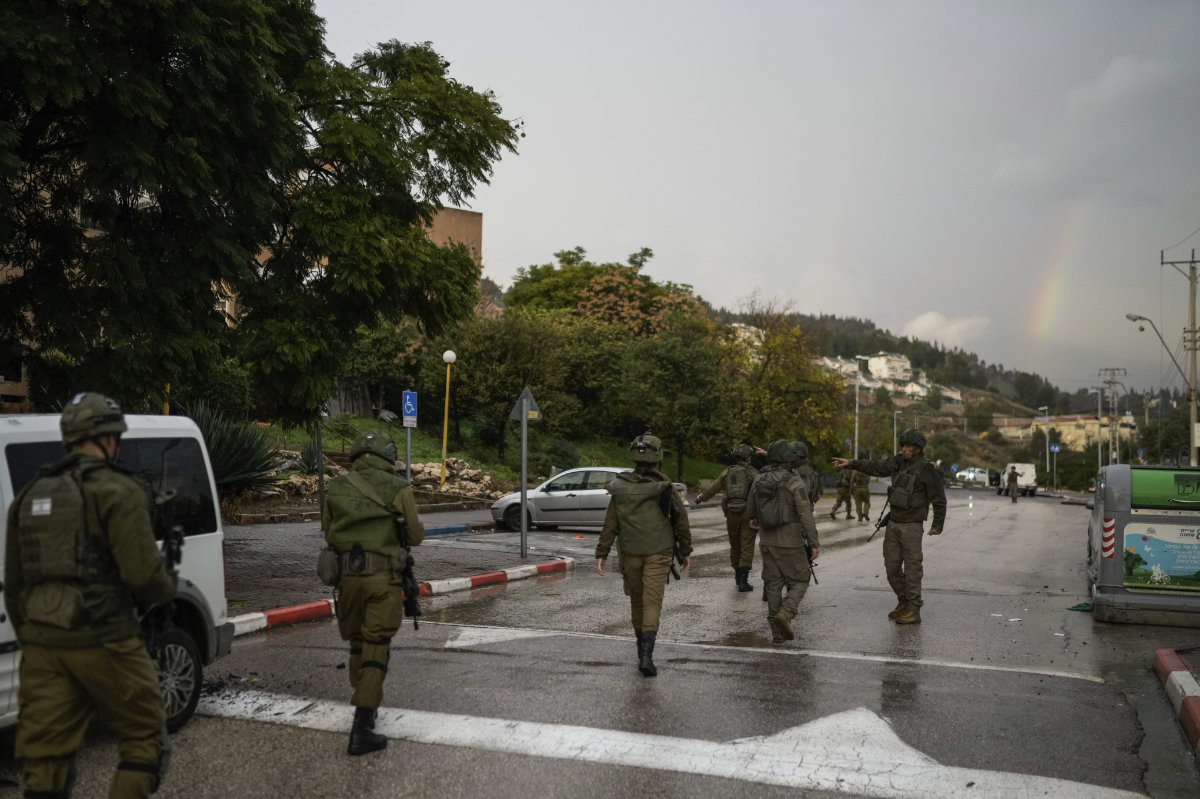

Israeli security forces examine a road hit by a rocket fired from Lebanon, in Kiryat Shmona, northern Israel, Thursday, Jan. 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Leo Correa)
“I do not think the withdrawal of troops from Gaza is connected to the prospect of the war expanding onto another front, and I do not think either Israel or Hezbollah want to be drawn into a war with one another, although there are clear red lines,” Michael told Arab News.
“It is important to understand that Israel’s relationship with Hezbollah is one I term ‘kinetic diplomacy.’ Each day each side sets these red lines and both sides seem keen to stick to them.”
While the two sides have been locked in their deadliest confrontation in 17 years, Hezbollah’s deputy leader Naim Qassem said that the group had no intention of expanding the war from Lebanon.
But if Israel expands it, the response is inevitable to the “maximum extent required to deter Israel,” he said in a live-streamed speech.
Al-Sharif, the Jordanian analyst, said the only party that would want to expand the war “at any cost” was Netanyahu, “and his far-right partners,” with the incumbent prime minister having failed to reverse what has been a marked deterioration in his poll ratings, which were already falling before the war began.
Oubai Shahbandar, a journalist and former Middle East defense adviser to the Pentagon, would not be drawn on the chances of a wider war, but warned it would bring new challenges for the IDF.
“Hezbollah is better armed, with more advanced weaponry and advantageous terrain, as well as a direct line of supply to Iranian weaponry, compared to Hamas, so prospects of an all-out war pose unique military challenges (for Israel),” Shahbandar told Arab News.
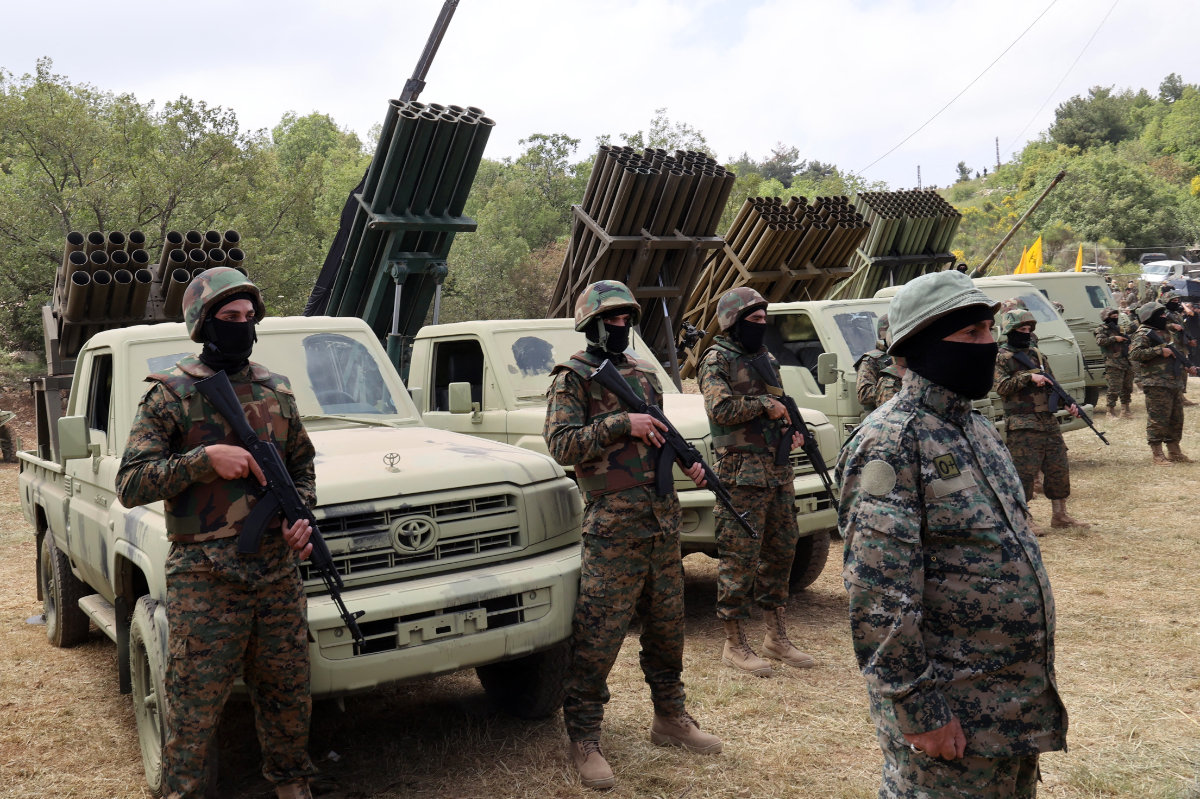

Hezbollah fighters stand near multiple rocket launchers during a press tour in the southern Lebanese village of Aaramta on May 21, 2023. (AFP/File)
While not denying the potential difficulties, Michael, the Israeli academic, seemed confident that the IDF was well placed to fight a war with Hezbollah should it come to this.
“Yes, Hezbollah is not Hamas. But the IDF has the capabilities to fight a war with Hezbollah, and it is also prepared to fight that war if it has to. Of course, it would rather resolve the situation in Gaza first, but it is constantly monitoring those red lines,” he said.
“What you have to remember, though, is that Israel already fights on seven fronts — against Hamas, Hezbollah, in Syria, the West Bank, west Iraq, and Yemen. And then there is Iran itself, which is the seventh front, and it is on this front that the fighting on all the others is determined. Iran is the hand that shakes the cradle. Iran determines the intensity on all the other fronts.”
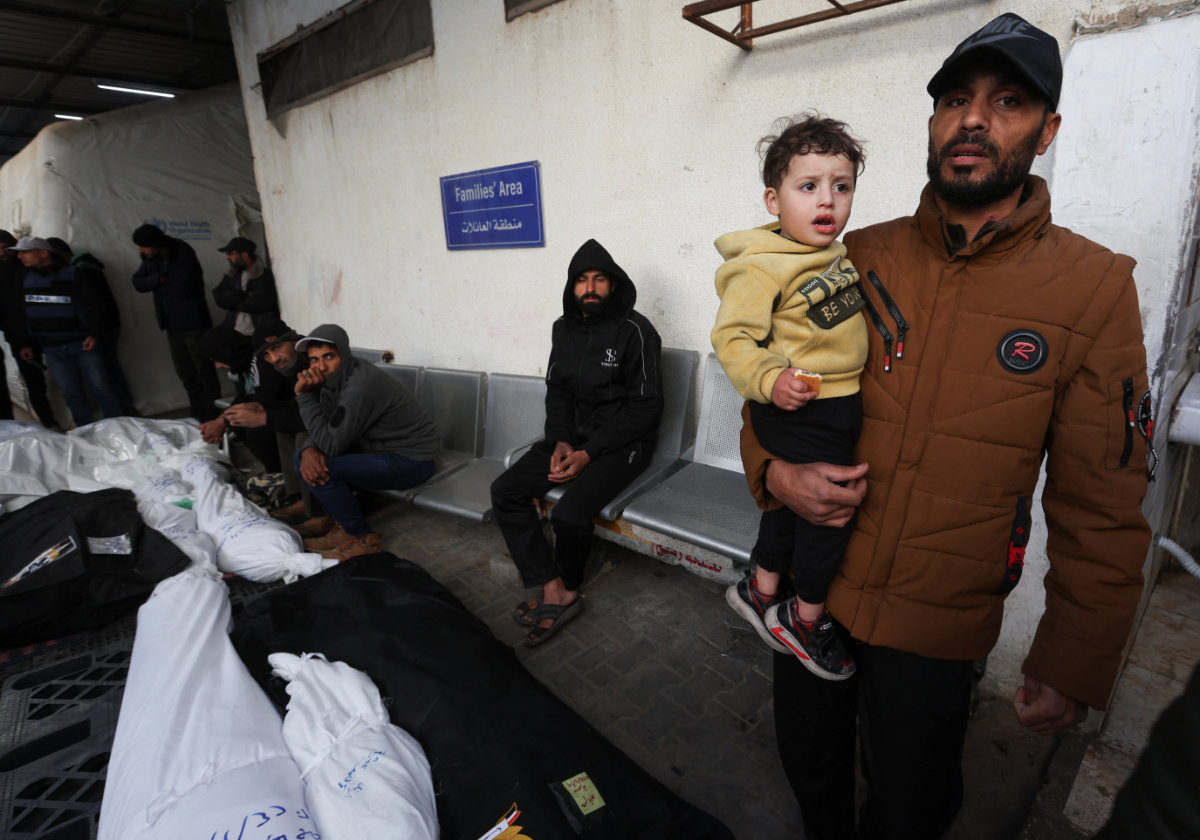

Despite the enormous toll in Palestinian lives and suffering, Israel has indicated that the war will continue for many months, with a shift to targeted operations and preparations
for a clash along the Israel border. (Reuters)
Where Michael and Shahbandar agree is that any sort of wider regional war would lead to “massive, unprecedented stress on social-economic life in Israel.”
They see this as a possible motivating factor behind the IDF’s decision to withdraw some of its troops from Gaza, with Shahbandar pointing to the economic strain brought about by maintaining 300,000 reservists.
“A considerable percentage of the workforce was mobilized for this war and there is a need to rotate them back into civilian life for the sake of the economy,” he said.
Indices monitoring Israel’s economy have shown less-than-favorable ratings, even as the government says the economy can handle the demands of a war. The Israel Economy Index predicts a 2.2 percent drop in 2023’s national economic growth rate.
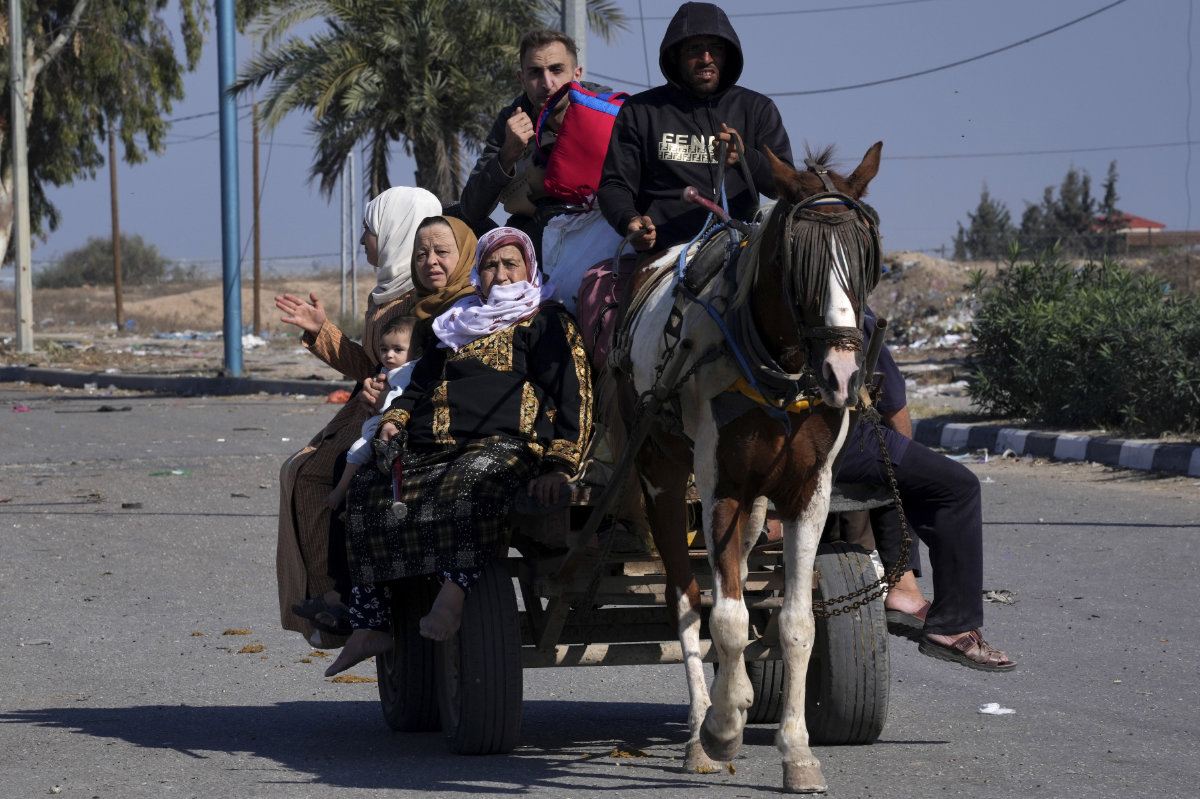

Despite the enormous toll in Palestinian lives and suffering, Israel has indicated that the war will continue for many months, with a shift to targeted operations and preparations
for a clash along the Israel border. (AP)
For Michael, the planned limited Israeli troop withdrawal reflects a shift in the conduct of the war. “One thing we can say accurately is that it is changing, not ending,” he said.
“Everything is so deeply dependent on developments on the ground. Consider, you have the leadership of Hamas in Khan Younis. If they are caught or killed, this will affect the manner in which the remaining fighters continue to action this war.
“Really, the aim is destroying Hamas’s center of operations. To achieve this, the IDF constantly goes through very intensive learning processes on the ground. I expect another change soon.”
Michael believes that such a shift could occur in as little as two to three weeks, and may revolve around further withdrawals of units operating inside Gaza and their relocation to emerging trouble spots.































