DUBAI: Demand for food is fast outstripping production capacity in many parts of the world, raising the specter of shortage and hunger as overfarming of mineral-rich soils leads to land degradation and exhaustion of finite freshwater sources.
In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), water is being referred to as the “new blue gold” as rivers and natural aquifers get rapidly depleted amid a warming climate and overexploitation of reserves, depriving farmers of the means to irrigate their crops and hydrate their livestock.
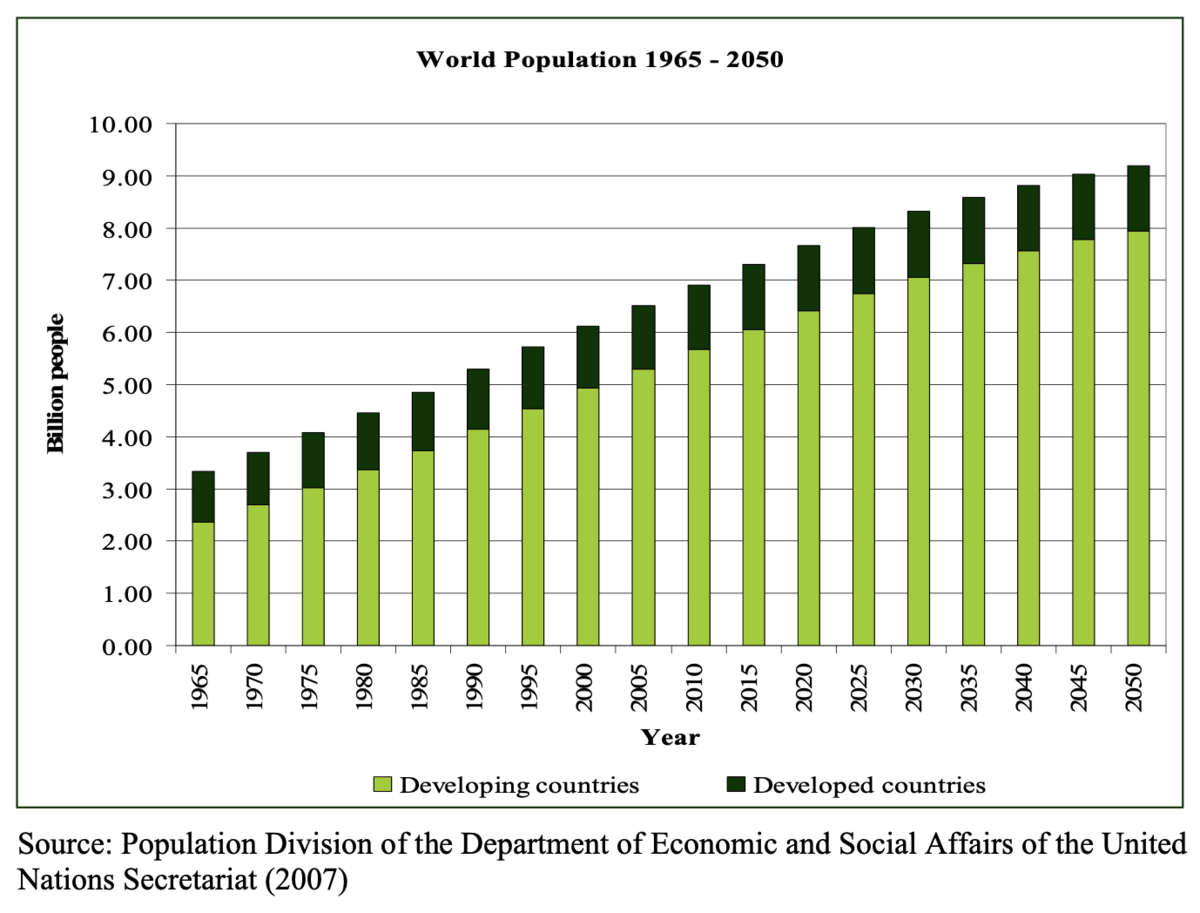
Projections by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) show that feeding a global population of 9.1 billion people by 2050 would require raising overall food production by around 70 percent, resulting in even greater water use.
Infographic from the FAO's "How to Feed the World in 2050" report.
Around 28 percent of the MENA region’s estimated population of 350 million is entirely dependent on agriculture for their livelihoods. In fact, farming accounts for 13 percent of the region’s gross domestic product and plays a crucial role in building food system resilience.
“The Arab region is food insecure and relies heavily on imports,” Peter Blezard, founder and director of UK-based Engage Crop Solutions, which specializes in crop enhancement and nutritional products in 26 countries worldwide, told Arab News.
“This is because growers face significant challenges due to the heat, desertification, aridity and drought that define the region” — issues, he says, that are ultimately the result of water scarcity.
It is, perhaps, no surprise that the UN has chosen water as the theme for this year’s World Food Day, which falls on Oct. 16, emphasizing its vital role in food production, nutrition and sustainable development.
Antonio Guterres, the UN secretary-general, has cited sustainable management of water for agriculture and food production as an essential factor in ending hunger, achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals ahead of 2030, and preserving water for future generations.
About 70 percent of global freshwater use is linked to agriculture — a figure that is much higher in some parts of the Arab world at 92 percent, with the aridity of the climate forcing farmers to continue with unsustainable practices.
“Around 40 percent of global food is produced in artificially irrigated areas and these irrigated farms can use 300 percent more water than the crop needs,” said Blezard.
IN NUMBERS
780 million People worldwide who are going hungry.
50 million Children at risk of death from severe wasting.
84 million People in the MENA region reliant on agriculture.
70% Current global freshwater use linked to agriculture.
9.1 billion Projected global population by 2050.
70% Required increase in food production to meet demand by 2050.
With farmers already consuming a huge proportion of the region’s available freshwater, Blezard says the Arab world’s ambitions of becoming self-sufficient in food production will only increase the demand for water.
“Growers and innovators are responding to the challenge, but this is a major issue as many fear the water table will dry up if we continue to extract water at the current rate for agriculture,” he said.
So, how can global food production be doubled to keep pace with population growth in a world of finite freshwater?

The good news is that there are crop technologies that helped reduce wastage of crop water. Engage Crop Solutions, for example, has proven that a 50 percent reduction on water use is possible without any loss in quality of growth of a crop. (Infographic from engagecropsolutions.com)
“The conversation must move away from the looming threat of our water running out and, instead, start to focus on the solutions and what we must do to preserve our precious water resources,” said Blezard.
“The challenge is greatest for agriculture and that is why growers must take the lead, finding new ways to reduce water use and taking advantage of new technologies and more efficient irrigation and cooling systems.”
Roma Vora, a farm manager at Aranya Farms in Abu Dhabi, told Arab News she is constantly exploring new technologies to help improve water quality and efficiency on her farm.
“In agriculture, the lack of water can significantly decrease yield and affect its quality, and it’s a challenge we have to manage meticulously in organic farming,” said Vora.
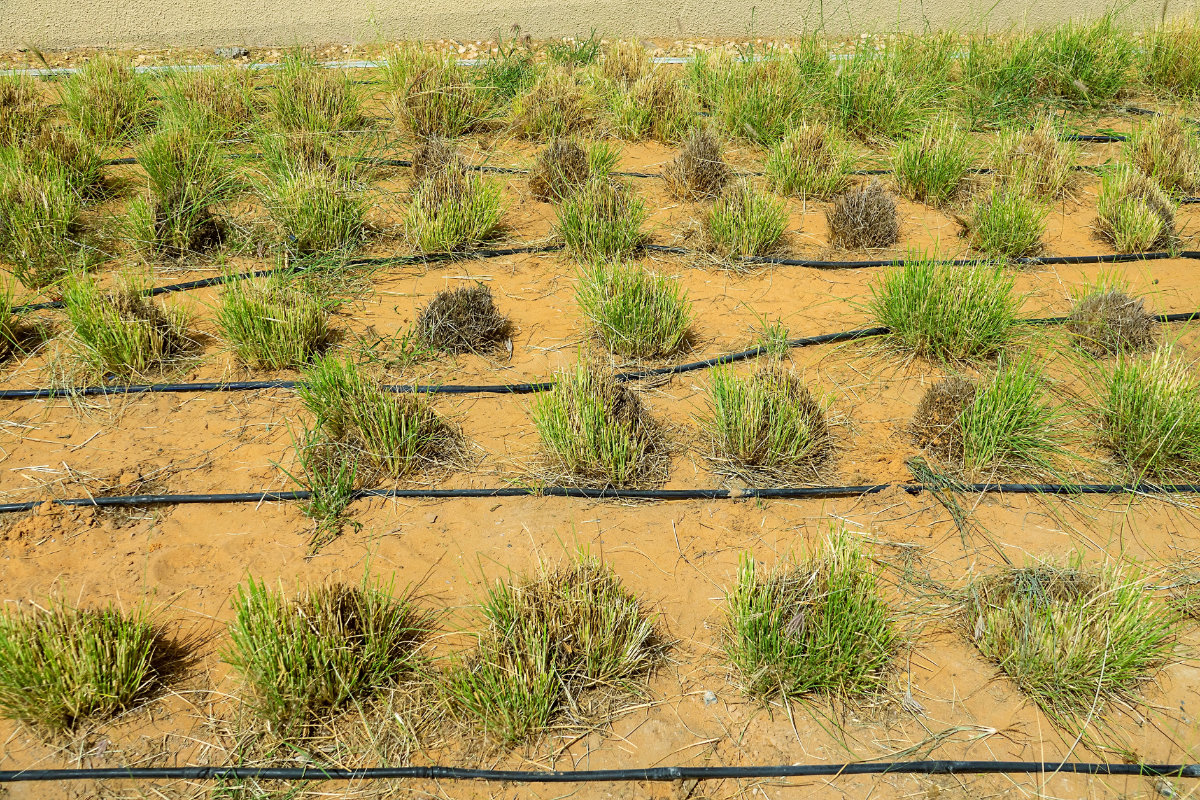

Drip irrigation remains the most commonly used system in the Arabian Peninsula. (Shutterstock)
The effects of shifts in temperatures and weather patterns have already caused Vora to rethink farming practices. “We usually begin our first harvest mid-October, but given the high-heat conditions, we are expecting our harvest only by early November,” she said.
She said soil-based organic farming offers many environmental benefits, including conservation and biodiversity, which are essential for ecological balance.
While organic farming is “resource-intensive,” Vora believes it is still much more sustainable than importing every item of food.
“The focus should be maintained on ‘local’ farming, and that would pave the way for a healthier, more resilient future for the Arab world,” she said.
A study by Kuwait Financial Center’s research arm, Marmore, assessing the state of the Gulf Cooperation Council countries’ food security, says the area has sufficient financial buffers to ensure continuous food imports, but its reliance on imports makes it vulnerable to supply-chain disruptions.

Aside from finding ways to cut production costs of food, the cost of shipping is also a challenge that need to be addressed worldwide. (AFP file photo)
“The study stated that in January 2022, food shipping costs to the country reportedly increased tenfold, from $1,400 to $14,000 per ton, while food inflation in March 2023 was recorded at 7.46 percent year-over-year, rising from 7 percent year-over-year in the previous month,” said Blezard.
The global pandemic, conflicts in Ukraine and elsewhere, rising freight costs, and protectionist controls on commodities such as rice and sugar have exposed the vulnerability of global supply chains and food systems in recent years, causing the price of essential foodstuffs to rise and stockpiles to dwindle.
Now the growing scale and frequency of extreme weather events, such as drought and flash flooding, are adding to those pressures.
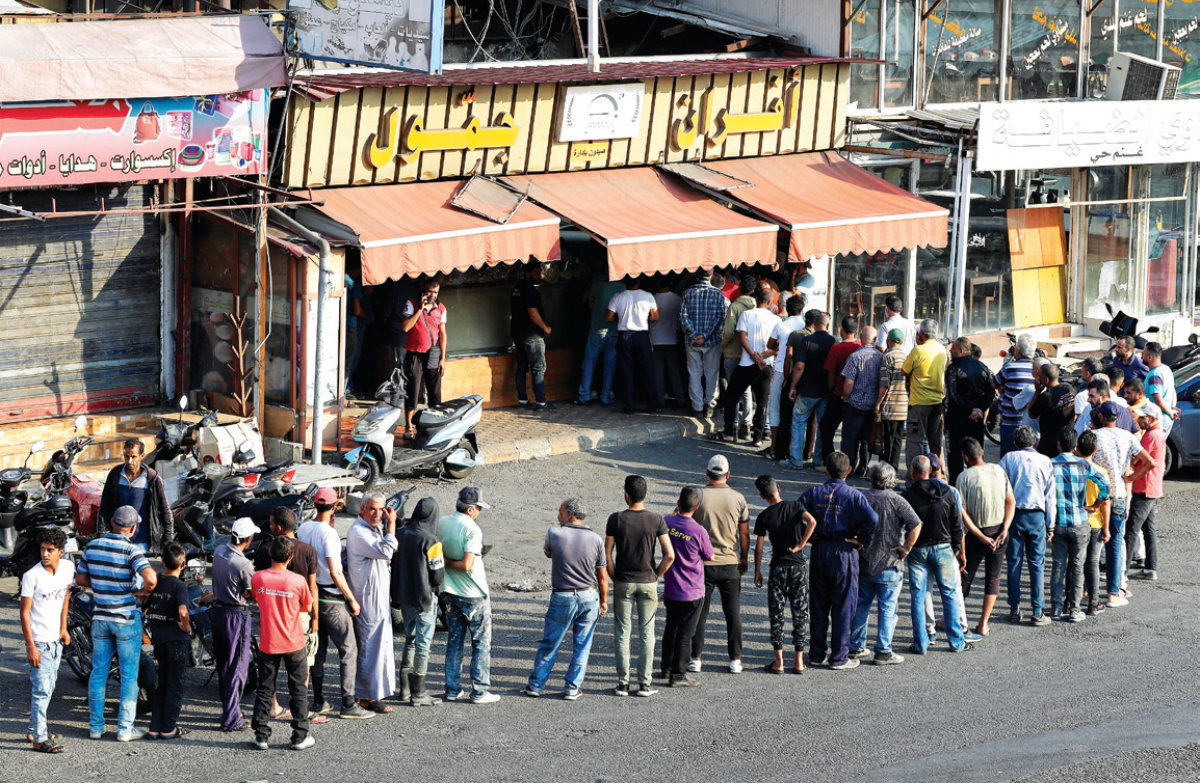

Lebanon has been hit by food shortages since it experienced a debt default in 2020. (AFP file photo)
“Rising energy prices and production costs for most of the world’s farmers, coupled with adverse weather conditions in a lot of countries, will reduce the global production of certain foods,” said Blezard.
In response, GCC nations, including the UAE, Qatar and Kuwait, have implemented long-term security measures to guard against systemic shocks, adopting strategies such as boosting domestic production, diversifying imports, reducing waste, and embracing agri-tech.
Examples of such agri-tech models include vertical farming, and digital tools that enhance supply chains and increase food production. Given the aridity of the region, such innovations are essential for expanding local production sustainably.
“In response to unfavorable climate conditions for agriculture, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have also invested in farmlands overseas,” said Blezard.
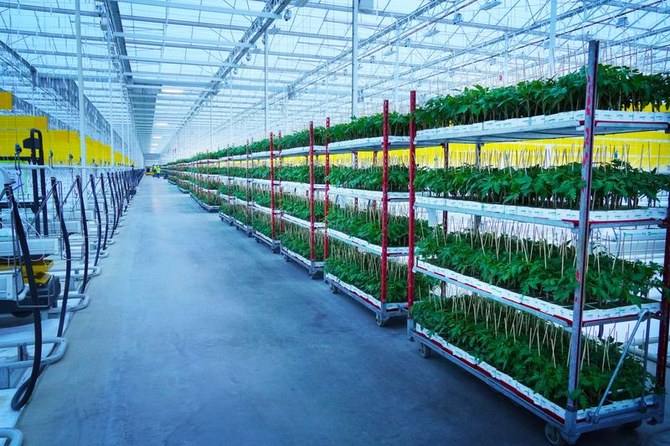

Saudi Arabia's first of a kind indoor vertical farm, a joint venture agreement between the Kingdom's Public Investment Fund and the US-based AeroFarms, expects an annual production capacity of up to 1.1 million kilos of agricultural crops. (Supplied)
As the GCC area imports 80-90 percent of its food, shoring up existing supply chains could make the system more resilient.
Soham Chokshi, CEO and co-founder of Shipsy, a smart logistics management platform, said supply chains can be made more efficient and agile by digitalizing import and cross-border logistics processes.
“Ensuring real-time visibility of container movement, using analytics and artificial intelligence to manage logistics failures and risks proactively, and automatically partnering with logistics service providers with expertise in managing food supply chains can make a winning difference,” Chokshi told Arab News.
Additionally, by leveraging a “software as a service” smart logistics management platform, governments and businesses can facilitate communication and data sharing among supply-chain partners, improving coordination and responsiveness to disruptions.
“Supply chain leaders can use data-driven inventory management to maintain optimal stock levels, reducing overstocking or under-stocking issues,” said Chokshi. “This ensures that food products are available when needed, reducing waste and improving efficiency.”
To address this issue, governments in the MENA region are establishing new ministries tasked with creating various agri-tech development teams.
“The aim for many countries is to be self-reliant on food by 2050, but to also develop a strategy that will promote world leading innovation in food security,” said Blezard.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
These ministries or authorities will oversee food security, food safety, and biosecurity in the region, with their primary responsibility being to establish an efficient food security governance model.
In turn, this model will look to facilitate global agricultural trade, diversify international food sources, and enhance sustainable technology-enabled domestic food supply throughout the value chain, Blezard said.
Additionally, according to him, the model will support the establishment of new businesses through investments in the region. However, to sustain this initiative, the creation of globally competitive tax rates and trade zones is crucial.
This would attract mainstream venture capital firms and banks, encouraging the development of new businesses equipped with advanced infrastructure for handling large-volume commodities.
“This model will facilitate global agri-business trade and diversify international food sources, enhancing sustainable technology-enabled domestic food supply across the value chain,” Blezard said.
















